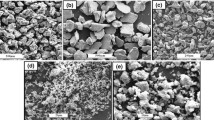
The effect of milling time and addition of elements on the microstructure, magnetic and mechanical properties of the Fe–xCo (x = 0, 5, 10, and 20 wt.%) matrix nanocomposite reinforced with 40 wt.% Al2O3 during mechanical alloying is examined. Fe–Al2O3 and Fe–Co–Al2O3 alloys are milled for 5, 15, 20, and 30 h and 20 h, respectively. The balance between the welding and fracturing and a steady-state situation is found out in the Fe–Co–40 wt.% Al2O3 nanocomposite after 20 h, due to the Co introduction into the Fe matrix, but not in the Fe–Al2O3 nanocomposite. After 30 h of milling, the average crystallite size was 5 nm in the Fe matrix. The lattice strain increased to ~0.64% in the Fe matrix after ≤30 h of milling and in the binary Fe–20 wt.% Co matrix after 20 h of milling; the average crystallite size was 3 nm. The lattice strain increased to ~0.56% for the Fe–20 wt.% Co matrix after ≤20 h of milling. The coercive field (Hc) increased from 6.407 to 82.027 Oe, while the saturation magnetization (Ms) decreased from 20.732 to 15.181 emu/g in the Fe matrix during milling. The Hc and Ms are maximum for the binary matrix (20 and 10% Co, respectively).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Fan, B. Liu, J. Zhang, et al., “Kinetic evaluation of combustion synthesis 3TiO2+7Al–3TiAl+2Al2O3 using non-isothermal DSC method,” Mater. Chem. Phys., 91, No. 1, 140–145 (2005).
G. P. Kelkar and A. H. Carim, “Phase equilibria in the Ti–AI–O system at 945°C and analysis of Ti/Al2O3 reactions,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 78, No. 3, 572–576 (1995).
Y.-I. Lee, J.-T. Lee, and Y.-H. Choa, “Effects of Fe–Ni alloy nanoparticles on the mechanical properties and microstructures of Al2O3/Fe–Ni nanocomposites prepared by rapid sintering,” Ceram. Int., 38, No. 5, 4305–4312 (2012).
J. Marrow, G. A. D. Briggs, and S. G. Roberts, “In-situ scanning acoustic microscopy of crack bridging in alumina,” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 14, No. 2, 111–116 (1994).
W. G. Fahrenholtz, D. T. Ellerby, and R. E. Loehman, “Al2O3–Ni composites with high strength and fracture toughness,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 83, No. 5, 1279–1280 (2000).
K. Konopka and A. Ozieblo, “Microstructure and the fracture toughness of the Al2O3–Fe composites,” Mater. Character., 46, Nos. 2–3, 125–129 (2001)
Paesano A., Jr., C. K. Matsuda, J. B. M. da Cunha, et al., “Synthesis and characterization of Fe–Al2O3 composites,” J. Magnet. Magn. Mater., 264, Nos. 2–3, 264–274 (2003).
E. Menendez, G. Salazar-Alvarez, A. P. Zhilyaev, et al., “Cold consolidation of metal–ceramic nanocomposite powders with large ceramic fractions,” Adv. Funct. Mater., 18, No. 20, 3293–3298 (2008).
M. F. Zawraha, R. A. Essawy, H. A. Zayed, et al., “Mechanical alloying, sintering and characterization of Al2O3–20 wt.% Cu nanocomposite,” Ceram. Int.,” 40, No. 1, 31–38 (2014).
Q. Feng, T. Li, H. Teng, et al., “Investigation on the corrosion and oxidation resistance of Ni–Al2O3 nanocomposite coatings prepared by sediment co-deposition,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 202, No. 17, 4137–4144 (2008).
T. Isobe, K. Daimon, T. Sato, et al., “Spark plasma sintering technique for reaction sintering of Al2O3/Ni nanocomposite and its mechanical properties,” Ceram. Int., 34, No. 1, 213–217 (2008).
E. S. Bagherzadeh, M. Dopita, T. Mütze, et al., “Morphological and structural studies on Al reinforced by Al2O3 via mechanical alloying,” Adv. Powder Technol., 26, No. 2, 487–493 (2015).
J. Liu, C. Suryanarayana, D. Ghosh, et al., “Synthesis of Mg–Al2O3 nanocomposites by mechanical alloying,” J. Alloys Compd., 563, 165–170 (2013).
L. F. C´otica, A. Paesano Jr., S. C. Zanatta, et al., “High-energy ball-milled (α-Fe2O3)(α-Al2O3) system: A study on the milling time effects,” J. Alloys Compd., 413, 265–272 (2006).
N. Forouzanmehr, F. Karimzadeh, and M. H. Enayati, “Synthesis and characterization of TiAl/α-Al2O3 nanocomposite by mechanical alloying,” J. Alloys Compd., 478, 257–259 (2009).
S. Z. Anvari, F. Karimzadeh, and M. H. Enayati, “Synthesis and characterization of NiAl–Al2O3 nanocomposite powder by mechanical alloying,” J. Alloys Compd., 477, 178–181 (2009).
J. Safari, G. H. Akbari, A. Shahbazkhan, et al., “Microstructural and mechanical properties of Al–Mg/Al2O3 nanocomposite prepared by mechanical alloying,” J. Alloys Compd., 509, 9419–9424 (2011).
A. Wagih, “Mechanical properties of Al–Mg/Al2O3 nanocomposite powder produced by mechanical alloying,” Adv. Powder Technol., 26, No. 1, 253–258 (2015).
C. Suryanarayana and N. Al-Aqeeli, “Mechanically alloyed nanocomposites,” Prog. Mater. Sci., 58, No. 4, 383–502 (2013).
L. Lu and Y. F. Zhang, “Influence of process control agent on inter diffusion between Al and Mg during mechanical alloying,” J. Alloys Compd., 290, Nos. 1–2, 279–283 (1999).
J. Gubicza, M. Kassem, G. Ribarik, et al., “The microstructure of mechanically alloyed Al–Mg determined by X-ray diffraction peak profile analysis,” Mater. Sci. Eng.: A, 372, Nos. 1–2, 115–122 (2004).
E. Howard, Swanson and Eleanor Tatge. Standard X-ray Diffraction Powder Patterns, National Bureau of Standards, Circular 539, 1, Issued June 15 (1953).
R. S. Liu, W. C. Shi, Y. C. Cheng, and C. Y. Huang “Crystal structures and peculiar magnetic properties of alpha- and gamma-(Al2O3) powders,” Mod. Phys. Lett. B, 11, Nos. 26–27, 1169–1174 (1997).
B. Prabhu, C. Suryanarayana, L. An, and R. Vaidyanathan, “Synthesis and characterization of high volume fraction Al–Al2O3 nanocomposite powders by high-energy milling,” Mater. Sci. Eng.: A, 425, Nos. 1–2, 192–200 (2006).
T. P. Yadav, R. M. Yadav, and D. P. Singh, “Mechanical milling: a top down approach for the synthesis of nanomaterials and nanocomposites,” Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2, No. 3, 22–48 (2012).
T. Ambrose, A. Gavrin, and C. L. Chien, “Formation and magnetic properties of nanocomposite Fe–Al2O3, using high-energy ball milling,” J. Magnet. Magn. Mater., 116, No. 3, L311–L314 (1992).
V. Rajkovic, D. Bozic, and M. T. Jovanovic, “Properties of copper matrix reinforced with nano- and microsized A12O3 particles,” J. All. Compd., Vol. 459, Nos. 1–2, 177–184 (2008).
B. Lonnberg, “Characterization of milled Si3N4 powder using X-ray peak broadening and surface area analysis,” J. Mater. Sci., 29, 3224–3230 (1994).
H. P. Klug and L. E. Alexander, X-Ray Diffraction Procedures: for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials, 2nd Edition. John Wiley and Sons. New York, London (1974), p. 992.
L. Zhao, J. Zwick, and E. Lugscheider, “The influence of milling parameters on the properties of the milled powders and the resultant coatings,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 168, Nos. 2–3, 179–185 (2003).
C. Suryanarayana and M. G. Norton, X-Ray Diffraction: A Practical Approach (Artech House Telecommunications), Springer, New York (1998), p. 273.
C. Suryanarayana, “Mechanical alloying and milling,” Prog. Mater. Sci., 46, Nos. 1–2, 1–84 (2001).
L. M. Lacroix, N. F. Huls, D. Ho, et al., “Stable single-crystalline body centered cubic Fe nanoparticles,” Nano Letters, 11, No. 4, 1641–1645 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 56, Nos. 3–4 (514), pp. 37–48, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Younes, A., Bacha, N.E., Zergoug, M. et al. Structural and Magnetic Properties of Fe–Co/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Powder Produced by Mechanical Alloying. Powder Metall Met Ceram 56, 148–157 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-017-9881-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-017-9881-9