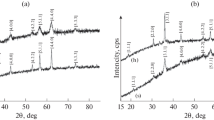
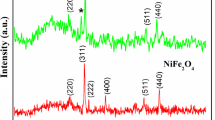
Nanoparticles of NiAlxFe 2–x O 4 (x = 0; 0.1; 0.2; 0.3; 0.4, and 0.5) are synthesized by sol–gel method with auto-combustion. X-ray diffraction patterns confirm the single phase spinel structure of the samples produced. The scanning electron microscope images indicate that the particle size of the samples lies in a nanometer range. Synthesized in this manner, the powder has high crystallinity and good morphological homogeneity. It is observed that the grain size decreases from 46 to 18 nm as the nonmagnetic Al content increases. The lattice constant and radiodensity of ferrites depending on the content of the component x are determined. The structural and adsorption characteristics of the synthesized samples are determined by analyzing nitrogen sorption isotherms at 77 K. It is demonstrated that the samples produced are mesoporous because their pores are 2–5 nm in size. The thermal processes are investigated by thermal analysis and infrared spectroscopy. It is established that the nitrate-citrate gel burns automatically and then directly transforms into nanosized ferrite particles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. V. Kopayev and V. S. Bushkova, “Application of the electron theory of sintering to the ferrite systems,” Acta Phys. Polon. A., 117, No. 1, 25–28 (2010).
C. Upadhyay, H. C. Verma, and S. Anand, “Cation distribution in nanosized Ni–Zn ferrites,” J. Appl. Phys., 95, No. 10, 5746–5751 (2004).
K. O. Low and F. R. Sale, “Electromagnetic properties of gel-derived NiCuZn ferrites,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 246, 30–35 (2002).
S. M. Yunus, H. S. Shim, C. H. Lee, et al., “Neutron diffraction studies of the diluted spinel ferrite ZnxMg0.75x Cu0.25Fe2O4,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 232, 121–132 (2001).
M. Gateshki, V. Petkov, S. K. Pradhan, and T. Vogt, “Structure of nanocrystalline MgFe2O4 from X-ray diffraction, Rietveld and atomic pair distribution function analysis,” J. Appl. Cryst., 38, 772–779 (2005).
X. Qi, J. Zhou, Z. Yue, et al., “Effect of Mn substitution on the magnetic properties of MgCuZn ferrites,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 251, 316–322 (2002).
N. S. Bhattacharyya and G. P. Srivastava, “Synthesis and characterization of Mg–Ni ferrite prepared by solgel auto–combustion method,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 262, 212–217 (2003).
S. Nasir, G. Asghar, M. A. Malik, and M. Anis-ur-Rehman, “Structural, dielectric and electrical properties of zinc doped nickel nanoferrites prepared by simplified the sol–gel method,” J. Sol–gel Sci. Technol., 59, 111–116 (2011).
C. Venkataraju, G. Sathishkumar, and K. Sivakumar, “Effect of cation distribution on the structural and magnetic properties of nickel substituted nanosized Mn–Zn ferrites prepared by co-precipitation method,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 322, No. 2, 230–233 (2010).
A. V. Kopayev, B. K. Ostafiichuk, I. P. Yaremiy, and I. Y. Vylka, “Structure and magnetic properties of Ni–Al ferrite nanopowders, synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion method,” X-Ray, Synchr. Neutr. Study, 10, 79–83 (2007).
A. V. Kopayev, B. K. Ostafiychuk, I. Y. Vylka, and D. L. Zadnipryannyy, “Peculiarities of nickelaluminum ferrites with nanopowder structure,” Mat.-wiss. u. Werkstofftech., 40, No. 1, 255–257 (2009).
M. Mozaffari and J. Amighian, “Preparation of Al-substituted Ni ferrite powders via mechanochemical processing,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 260, 244–249 (2003).
V. S. Bushkova and A. V. Kopayev, “Research electrical properties of composites systems (1–x) NiAl0.5Fe1.5O4–x BaTiO3,” J. Enterp. Techn., 52, Nos. 4–5, 43–47 (2011).
S. E. Shirsath, B. G. Toksha, R. H. Kadam, et al., “Doping effect of Mn2+ on the magnetic behavior in Ni– Zn ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion,” J. Phys. Chem. Sol., 71, No. 12, 1669–1675 (2010).
M. Atif and M. Nadeem, “Sol–gel synthesis of nanocrystalline Zn1–x NixFe2O4 ceramics and its structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties,” J. Sol–gel Sci. Technol., 72, 602–614 (2014).
S. Zahi, “Synthesis, Permeability and microstructure of the optimal nickel–zinc ferrites by sol–gel route,” J. Electromagn. Anal. Appl., 2, 56–62 (2010).
V. S. Bushkova, B. K. Ostafiichuk, and A. V. Kopayev, “Features of synthesis of complex oxide systems by means of SGA-method,” Phys. Chem. Sol. St., 15, No. 1, 182–185 (2014).
S. S. Suryawanshi, V. V. Deshpande, U. B. Deshmukh, et al., “XRD analysis and bulk magnetic properties of Al3+ substituted Cu–Cd ferrites,” Mat. Chem. Phys., 59, No. 3, 199–203 (1999).
A. T. Raghavender, R. G. Kulkarni, and K. M. Jadhav, “Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Al doped nickel ferrite synthesized by the sol–gel method,” Chinese J. Physics, 46, No. 3, 366–375 (2008).
J. Križan, J. Možina, I. Bajsic, and M. Mazaj, Synthesis and Fluorescent Properties of Chromium–Doped Aluminate Nanopowders,” Acta. Chim. Slov., 59, No. 1, 163–168 (2012).
Q. Geng, X. Zhao, X. Gao, et al., Low–temperature combustion synthesis of CuCr2O4 spinel powder for spectrally selective paints,” J. Sol–gel Sci. Technol., 61, 281–288 (2012).
E. E. Sileo, R. Rotelo, and S. E. Jacobo, “Nickel–zinc ferrites prepared by the citrate precursor method,” Physica B, 320, 257–260 (2002).
Z. Yue, W. Guo, J. Zhou, et al., “Synthesis of nanocrystalline NiCuZn ferrite powders by sol–gel autocombustion method,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 208, 55–60 (2000).
W. N. Martens, J. T. Kloprogge, R. L. Frost, and L. Rintoul, “Single crystal Raman study of erythrite Co3(AsO4)2∙8H2O,” J. Raman Spectr., 35, No. 3, 208–216 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 54, Nos. 9–10 (505), pp. 3–11, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bushkova, V.S., Ostafiychuk, B.K. Low-Temperature Synthesis and Characterization of Spinel Ferrite Powders. Powder Metall Met Ceram 54, 509–516 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-016-9743-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-016-9743-x