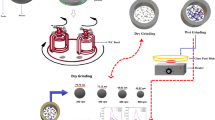
Monoclinic Li 2 TiO 3 phase is prepared from Li 2 CO 3 and TiO 2 mixtures by using a high-energy ball milling method, combined with subsequent calcinations at low temperature. Pure phase Li 2 TiO 3 nanopowders with the average particle size of 36.8 nm are obtained from the precursor milled for 20 h and calcined at 500°C for 5 h, i.e., 300°C lower than required by a conventional solid state reaction process or chemical routes. It is suggested that high-energy ball-milling method is a simple and practical route to synthesize Li 2 TiO 3 nanopowders.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Johnson, G. Hollenberg, N. Roux, et al., “Current experimental activities for solid breeder development,” Fusion Eng. Des., 8, 145–153 (1989).
N. Roux, J. Avon, A. Floreancing, et al., “Low-temperature tritium releasing ceramics as potential materials for the ITER breeding blanket,” J. Nucl. Mater., 233, 1431–1435 (1996).
N. Roux, G. Hollenberg, C. Johnson, et al., “Summary of experimental results for ceramic breeder materials,” Fusion Eng. Des., 27, 154–166 (1995).
L. Yuan and J. Bian, “Microwave dielectric properties of the lithium containing compounds with rock salt structure,” Ferroelectrics, 387, No. 1, 123–129 (2009).
Q. Zeng, W. Li, J. Shi, J. Guo, et al., “A new microwave dielectric ceramic for LTCC applications,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 89, No. 5, 1733 –1735 (2006).
C. Huang, Y. Tseng, and J. Chen, “High-Q dielectrics using ZnO-modified Li2TiO3 ceramics for microwave applications,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 32, No. 12, 3287–3295 (2012).
J. Bian and Y. Dong, “New high Q microwave dielectric ceramics with rock salt structures: (1−x)Li2TiO3+xMgO system (0≤x≤0.5),” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 30, No. 2, 325–330 (2010).
Y. Li, C. Xu, X. Wang, et al., “Synthesis of Li2TiO3 ceramic breeder powders by in-situ hydrolysis and its characterization,” Mater. Letters, 89, 25–27 (2012).
X. Wu, Z. Wen, B. Lin, et al., “Sol–gel synthesis and sintering of nanosize Li2TiO3 powder,” Mater. Letters., 62, No. 6, 837–839 (2008).
C. Yu, K. Yanagisawa, S. Kamiya, et al., “Monoclinic Li2TiO3 nanoparticles via hydrothermal reaction: Processing and structure,” Ceram. Int., 40, No. 1, 1901–1908 (2014).
L. Kong, T. Zhang, J. Ma, et al., “Progress in synthesis of ferroelectric ceramic materials via high-energy mechanochemical technique,” Prog. Mater. Sci., 53, No. 2, 207–322 (2008).
Z. Fu, P. Liu, X. Chen, et al., “Low-temperature synthesis of Mg4Nb2O9 nanopowders by high-energy ball-milling method,” J. Alloys Comp., 493, No. 1, 441–444 (2010).
M. Wang, K. Woo, and C. Lee, “Preparing La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 conductive perovskite via optimal processes: High-energy ball milling and calcinations,” Energ. Convers. Manag., 52, No. 3, 1589–1592 (2011).
H. Klung and L. Alexander, X-ray Diffraction Procedures, Wiles, New York (1974), p. 687.
Y. Ding and J. Bian, “Structural evolution, sintering behavior and microwave dielectric properties of (1–x)Li2TiO3+xLiF ceramics,” Mater. Res. Bull., 48, No. 8, 2776–2781 (2013).
Acknowledgement
This work was partly supported by the Master/Doctor Foundation of Anhui University of Science and Technology, and the Young Teachers’ Scientific Research Foundation of Anhui University of Science and Technology (Grant No. QN201328).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 54, Nos. 7–8 (504), pp. 37–43, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, JL., Fu, ZF., Gao, J. et al. A Simple Method to Synthesize Nanosized Li2TiO3 Powders Through High-Energy Ball-Milling. Powder Metall Met Ceram 54, 410–415 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-015-9730-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-015-9730-7