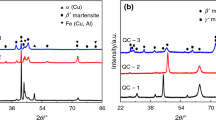
The paper examines the vacuum-sealed melt quenching and the properties of Cu–12% Al–3.5% Mn shape memory alloy fibers. The average effective diameter of the fibers is 113 μm. The temperatures of martensite transformations are determined by resistometric technique. Significant grain refinement, from 0.75 mm (in the starting alloy) to 40 μm (in the fibers), is achieved by rapid melt quenching.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Sittner and R. Stalmans, “Developing hybrid polymer composites with embedded shape-memory alloy wires,” JOM, 52, No. 10, 15–20 (2000).
G. A. Molodtsov, V. E. Bitkin, V. F. Simonov, and F. F. Urmasov, Shape-Stable and Intellectual Designs of Composite Materials [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (2000), p. 352.
V. A. Vasil’ev, B. S. Mitin, I. N. Pashkov, et al., High-Speed Melt Solidification [in Russian], Intermet Engineering, Moscow (1998), p. 400.
N. V. Tereshin, “Producing fibers from titanium nickelide by melt extraction,” Izv. Vusov. Tsvet. Metall., No. 1, 38–41 (2000).
A. G. Kostornov, V. N. Klimenko, M. M. Serov, et al., “Production of TiNi fibers by melt extraction,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 47, No. 7–8, 384–388 (2008).
K. Otsuka, K. Shimizu, Y. Suzuki, et al., Shape Memory Alloys [Russian translation], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1990).
G. G. Zak, G. Z. Zatul’skii, and K.-H. Jach, “Melt quenching of aluminum bronze with shape memory effect,” Prots. Lit., No. 2, 80–83 (1998).
J. Dutkiewicz, J. Morgiel, T. Czeppe, and E. Cesari, “Martensitic transformation in CuAlMn and CuAlNi melt spun ribbons,” J. Physique IV, 7, Issue C5, 167–172 (1997).
Yuhong Zheng, Chongjian Li, Farong Wan, and Yi Long, “Cu–Al–Mn alloy with shape memory effect at low temperature,” J. All. Compd., 441, 317–322 (2007).
U. S. Mallik and V. Sampath, “Effect of composition and ageing on damping characteristics of Cu–Al–Mn shape memory alloys,” Mater. Sci. Eng., 478A, 48–55 (2008).
L. E. Kozlova and A. N. Titenko, “Stress-induced martensitic transformation in polycrystalline aged Cu–Al–Mn alloys,” Mater. Sci. Eng., 438–440A, 738–742 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 51, No. 3–4 (484), pp. 75–81, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostornov, A.G., Klimenko, V.N., Serov, M.M. et al. Properties of Cu–Al–Mn shape memory alloy fibers produced by melt quenching. Powder Metall Met Ceram 51, 186–190 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-012-9415-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-012-9415-4