Abstract
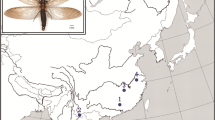
We isolated and characterized microsatellite loci in Viola websteri (Violaceae), an endangered species from Korea and endemic to Northeast Asia. A total of 27 microsatellite loci were developed and tested in Korean and Chinese populations. The number of alleles per locus varied from two to eight. The observed and expected heterozygosities within two populations were 0.000 to 1.000 and 0.080 to 0.816, respectively. Korean and Chinese populations were clearly distinguished by the private alleles from 16 loci. A total of 21 loci out of the 27 developed loci were successfully cross-amplified in 39 other Viola species. We believe that these microsatellite loci will be useful for future studies on genetic diversity and population structure of V. websteri, as well as other Viola species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allendorf FW, Luikart G, Aitken SN (2013) Conservation and the genetics of populations. Willey-Blackwell, Oxford
Barbara T, Palma-Silva C, Paggi GM, Bered F, Fay MF, Lexer C (2007) Cross-species transfer of nuclear microsatellite markers: potential and limitations. Mol Ecol 16:3759–3767
Bhawna M, Abdin Z, Arya L, Verma M (2015) Transferability of cucumber microsatellite markers used for phylogenetic analysis and population structure study in bottle gourd (Lagenaria siceraria (Mol.) Standl.). Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:2206–2223
Celik M, Wegnez J, Griveau C, Lambourdière J, Utge J, Noël F, Abdelkrim J, Machon N (2015) Development of microsatellite primers in the protected species Viola elatior (Violaceae) using next-generation sequencing. Appl Plant Sci 3(5):1500011
Chen YS, Yang QN, Ohba H, Nikitin VV (2007) Violaceae. In: Wu ZY, Raven PH, Hong DY (eds) Flora of China, vol 13
Cota LG, Moreira PA, Menezes EV, Gomes AS, Ericsson AR, Oliveira DA, Melo AF (2012) Transferability and characterization of simple sequence repeat markers from Anacardium occidentale to A. humile (Anacardiaceae). Genet Mol Res 11:4609–4616
Csencsics D, Brodbeck S, Holderegger R (2010) Cost-effective, species-specific microsatellite development for the endangered dwarf bulrush (Typha minima) using next-generation sequencing technology. J Hered 101:789–793
Cui XM, Dong YX, Hou XL, Cheng Y, Jing JY, Jin MF (2008) Development and characterization of microsatellite markers in Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis and transferability among related species. Agric Sci China 7:19–31
Culley TM (2005) Characterization of newly developed microsatellite loci in the stemmed yellow violet, Viola pubescens (Violaceae). Mol Ecol Notes 5:882–884
Dewoody J, Nason JD, Hipkins VD (2006) Mitigating scoring errors in microsatellite data from wild populations. Mol Ecol Notes 6:951–957
Echt CS, Vendramin GG, Nelson CD, Marquardt P (1999) Microsatellite DNA as shared genetic markers among conifer species. Can J For Res 29:365–371
Ellstrand NC, Elam DR (1993) Population genetic consequences of small population size; Implication for plant conservation. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 24:217–242
Fan L, Zhang MY, Liu QZ, Li LT, Song Y, Wang LF, Zhang SL, Wu J (2013) Transferability of newly developed pear SSR markers to other Rosaceae species. Plant Mol Biol Report 31(6):1271–1282
Finger A, Charlotte K (2010) Molecular methods: blessing or curse? In: Habel JC, Assmann T (eds) Relic species: phylogeography and conservation biology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 309–320
Gaudeul M, Taberlet P, Till-Bottraud I (2000) Genetic diversity in an endangered alpine plant, Eryngium alpinum L. (Apiaceae), inferred from amplified fragment length polymorphism markers. Mol Ecol 9:1627–1637
Godt MJW, Caplow F, Hamrick JL (2005) Allozyme diversity in the federally threatened golden paintbrush, Castilleja levisecta (Scrophulariaceae). Conserv Genet 6:87–99
Hall T (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hama E (2002) The wild violets of Japan in color. Sungmoondang, Tokyo
Hansen OK, Vendramin GG, Sebastiani F, Edwards J (2005) Development of microsatellite markers in Abies nordmanniana (Stev.) Spach and cross-species amplification in the Abies genus. Mol Ecol Notes 5:784–787
Hashimoto T (1967) The violets of Japan. Sungmoondang, Tokyo, p 153
Huang Y, Zhang CQ, Li DZ (2009) Low genetic diversity and high genetic differentiation in the critically endangered Omphalogramma souliei (Primulaceae): implications for its conservation. J Syst Evol 47:103–109
Jang SK, Cheon KS, Kim KA, Jang JH, Yoo KO (2010) Ecological characteristics of Viola websteri Hemsley habitats. Korean J Plant Res 23:261–273 (in Korean)
Komarov VL (1905) Flora Manshuriae. vol III. Petropoli, Russia, pp 69–70
Lee WT, Yoo KO (2007) Violaceae. In: Park CW (ed) The genera of vascular plants of Korea. Academy Publishing Company, Seoul, pp 393–402
Liu SR, Li WY, Long D, Hu CG, Zhang JZ (2013) Development and characterization of genomic and expressed SSRs in Citrus by genome-wide analysis. PLoS One 8(10):e75149
Mantello CC, Suzuki FI, Souza LM, Goncalves PS, Souza AP (2012) Microsatellite marker development for the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis): characterization and cross-amplification in wild Hevea species. BMC Res Notes 5:329
Mathithumilan B, Kadam NN, Biradar J, Reddy SH, Ankaiah M, Narayanan MJ, Makarla U, Khurana P, Sreeman SM (2013) Development and characterization of microsatellite markers for Morus spp. and assessment of their transferability to other closely related species. BMC Plant Biol 13:194
Meirmans PG, Hedrick PW (2011) Assessing population structure: F st and related measures. Mol Ecol Resour 11:5–18
Ministry of Environment (2012) Red Data Book 5 Vascular Plant, National Institute of Biological Resources, Incheon (in Korean)
Palibin J (1899) Acta Horti Petropolitani. Petropoli, Russia. 17:36
Palsbøll PJ, Bérubé M, Allendort FW (2007) Identification of management units using population genetic data. Trends Ecol Evol 22:11–16
Park YJ (2004) Genetic variation of four Viola species in Korea. Korea University, Seoul, Master Dissertation (in Korean)
Parker PG, Snow AA, Schug MD, Booton GC, Fuerst PA (1998) What molecules can tell us about populations: choosing and using a molecular marker. Ecology 79:361–382
Pekall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—an update. Bioinformatics 28:2537–2539
Primack RB (2004) A primer of conservation biology, 3rd edn. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts
Rai MK, Phulwaria M, Shekhawat NS (2013) Transferability of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers developed in guava (Psidium guajava L.) to four Myrtaceae species. Mol Bio Rep 40:5067–5071
Rasmussen KK, Kollmann J (2008) Low genetic diversity in small peripheral population of a rare European tree (Sorbus torminalis) dominated by clonal reproduction. Conserv Genet 9:1533–1539
Roa AC, Chavarriaga-Aguirre P, Duque MC, Maya MM, Bonierbale MW, Iglesias C, Tohme J (2000) Cross-species amplification of cassava (Manihot esculenta) (Euphorbiaceae) microsatellites: allelic polymorphism and degree of relationship. Am J Bot 87:1647–1655
Schwartz MK, Luikart G, Waples S (2007) Genetic monitoring as a promising tool for conservation and management. Trends Ecol Evol 22:25–33
Song JM, Lee GY, Kim NY, Yi JS (2010) Vegetation structure and site environment of natural habitat of an endangered plant, Viola websteri. J Korean For Soc 99:267–276 (in Korean)
Tero N, Aspi J, Siikamäki P, Jäkäläniemi A, Tuomi J (2003) Genetic structure and gene flow in a metapopulation of an endangered plant species, Silene tatarica. Mol Ecol 12:2073–2085
Untergrasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth B, Remm M, Rozen S (2012) Primer3 – new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 40:e115
Van Ooosterhout C, Hutchinson WF, Wills DPM, Shipley P (2004) MICRO-CHECKER: software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol Ecol Notes 4:535–538
Xiao LQ, Ge XJ, Gong X, Hao G, Zheng SX (2004) ISSR variation in the endemic and endangered plant Cycas guizhouensis (Cycadaceae). Ann Bot 94:133–138
Yoo KO, Jang SK (2010) Infrageneric relationships of Korean Viola based on eight chloroplast markers. J Syst Evol 48:474–481
Yoo KO, Kim JH (2006) Analysis of taxonomic relationships of Korean Viola based on trnL-trnF region sequences of chloroplast DNA. Flower Res J 14(3):232–240 (in Korean)
Yoo KO, Jang SK, Lee WT (2005) Phylogeny of Korean Viola based on ITS sequences. Korean J Plant Taxon 35:7–23 (in Korean)
Yoo KO, Jang SK, Lee WT (2007) Phylogenetic relationships of Korean Viola (Violaceae) based on matK and atpB-rbcL sequence data of chloroplast DNA. Korean J Plant Taxon 37:1–15 (in Korean)
Young A, Boyle T, Brown T (1996) The population genetic consequences of habitat fragmentation for plants. Trends Ecol Evol 11:413–418
Yu JN, Won C, Jun J, Lim YW, Kwak M (2011) Fast and cost-effective mining of microsatellite markers using NGS technology: an example of a Korean water hydropotes inermis argyropus. PLoS One 6:e26933
Zalapa JE, Cuevas H, Zhu H, Steffan S, Senalik D, Zeldin E, McCown B, Harbut R, Simon P (2012) Using next-generation sequencing approaches to isolate simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci in the plant sciences. Am J Bot 99:193–208
Zhang ZY, Han JW, Jin Q, Wang Y, Pang XM, Li YY (2013) Development and characterization of new microsatellites for walnut (Juglans regia). Genet Mol Res 12(4):4723–4734
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR), funded by the Ministry of Environment (MOE) of the Republic of Korea (NIBR201503102) under a memorandum of understanding on cooperation for biological research between NIBR and Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, People’s Republic of China. The authors thank Changgun Lim, Hyosig Won, and Jina Lim for their help collecting the samples and the two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
The fragment sizes of the distinguishable loci in both populations. (XLSX 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, JS., Zhang, X. & Kwak, M. Isolation and Characterization of Microsatellite Markers for Viola websteri (Violaceae) and Cross-Species Amplification within the Genus Viola . Plant Mol Biol Rep 35, 145–153 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-016-1011-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-016-1011-1