Abstract
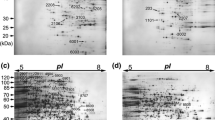
Rice spikelets display different grain-filling patterns depending on their position on a panicle. The superior spikelets (SS) elongated soon after flowering, whereas the inferior spikelets (IS) hardly elongate and are morphologically stagnant at early grain-filling stage. The developmental stagnancy of IS often leads to slow grain-filling and a low grain weight. To better understand the mechanism of the stagnancy, we took a two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE)-based proteomic and phosphoproteomic approach to profile the proteins with expression abundance as well as the phosphorylation of SS and IS at the early grain-filling stage. A total of 81 protein spots were found to be significantly different in expression abundance, and 27 protein spots significantly differed in phosphorylation. Bioinformatic analyses implicated that the proteins might be involved in the diverse cellular processes including sugar conversion, starch synthesis, energy pathway, signal transduction, cell growth/division, and protein synthesis and destination. Moreover, using the pull-down assay, we identified 29 14-3-3 binding proteins, and altogether, these 14-3-3 protein was found the important scaffold in the signaling networks of IS development. Our findings provided new proteomic and phosphoproteomic insights on the developmental stagnancy of rice IS that could be highly useful for the improvement of the grain-filling of rice and other cereal crops.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SS:
-
Superior spikelets
- IS:
-
Inferior spikelets
- 2-DE:
-
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
- SuSase:
-
Sucrose synthase
- AGPase:
-
Adenosine diphosphate-glucose pyrophosphorylase
- StSase:
-
Starch synthase
- SBE:
-
Starch branching enzyme
- IAA:
-
Indole acetic acid
- GAs:
-
Gibberellins
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- DSS:
-
Developmental stagnancy stage
- MALDI-TOF-MS:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry
- LC–ESI-MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography electro-spray ionization tandem mass spectrometry
- DAF:
-
Days after flowering
- DPs:
-
Differently expressed protein spots
- DPPs:
-
Differently expressed phosphoprotein spots
- PPDK:
-
Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase
- GLP:
-
Germin-like protein
- UDPase:
-
UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
- GBSS:
-
Granule-bound starch synthase
- TCA:
-
Tricarboxylic acid cycle
- PPP:
-
Pentose phosphate pathway
- CBB:
-
Coomassie Brilliant Blue
- TPI:
-
Triosephosphate isomerase
- FBA:
-
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase
- GPI:
-
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase
- PGM:
-
Phosphoglycerate mutase
- PFK:
-
Phosphofructokinase
- PGK:
-
Phosphoglycerate kinase
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- MDH:
-
Malate dehydrogenase
References
Agrawal GK, Thelen JJ (2006) Large scale identification and quantitative profiling of phosphoproteins expressed during seed filling in oilseed rape. Mol Cell Proteomics 5:2044–2059
Alexander RD, Morris PC (2006) A proteomic analysis of 14-3-3 binding proteins from developing barley grains. Proteomics 6:1886–1896
Ao HJ, Wang SH, Zou YB, Peng SB, Tang QY, Fang YX, Xiao AM, Chen YM, Xiong CM (2008) Study on yield stability and dry matter characteristics of super hybrid rice. Sci Agric Sin 41:1927–1936
Carrari F, Fernie AR (2006) Metabolic regulation underlying tomato fruit development. J Exp Bot 57:1883–1897
Chastain CJ, Chollet R (2003) Regulation of pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase by ADP-/Pi-dependent reversible phosphorylation in C3 and C4 plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 41:523–532
Chastain CJ, Failing CJ, Manandhar L, Zimmerman MA, Lakner MM, Nguyen TH (2011) Functional evolution of C4 pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase. J Exp Bot 62:3083–3091
Chitteti BR, Peng Z (2007) Proteome and phosphoproteome dynamic change during cell dedifferentiation in Arabidopsis. Proteomics 7:1473–1500
Cochrane M, Duffus C (1983) Endosperm cell number in cultivars of barley differing in grain weight. Ann Appl Biol 102:177–181
Cohen P (1985) The role of protein phosphorylation in the hormonal control of enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem 151:439–448
Comparot S, Lingiah G, Martin T (2003) Function and specificity of 14-3-3 proteins in the regulation of carbohydrate and nitrogen metabolism. J Exp Bot 54:595–604
El-Sharkawy I, Mila I, Bouzayen M, Jayasankar S (2010) Regulation of two germin-like protein genes during plum fruit development. J Exp Bot 61:1761–1770
Fageria N (2007) Yield physiology of rice. J Plant Nutr 30:843–879
Fait A, Angelovici R, Less H, Ohad I, Urbanczyk-Wochniak E, Fernie AR, Galili G (2006) Arabidopsis seed development and germination is associated with temporally distinct metabolic switches. Plant Physiol 142:839–854
Farré EM, Tiessen A, Roessner U, Geigenberger P, Trethewey RN, Willmitzer L (2001) Analysis of the compartmentation of glycolytic intermediates, nucleotides, sugars, organic acids, amino acids, and sugar alcohols in potato tubers using a nonaqueous fractionation method. Plant Physiol 127:685–700
Fernie AR, Carrari F, Sweetlove LJ (2004) Respiratory metabolism: glycolysis, the TCA cycle and mitochondrial electron transport. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:254–261
Gao J, Agrawal GK, Thelen JJ, Xu D (2009) P3DB: a plant protein phosphorylation database. Nucleic Acids Res 37:960–962
Guo YC, Lin WX, Liang YY, Yu GJ, Chen HF (2001) Physioecological studies on dry matter production and yield formation in new plant type (NPT) rice I. Dry matter produc tion and grain filling characteristics in NPT. J Fujian Agric Univ 30:16–21
Gururaj A, Barnes CJ, Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R (2004) Regulation of phosphoglucomutase 1 phosphorylation and activity by a signaling kinase. Oncogene 23:8118–8127
Hennen-Bierwagen TA, Lin Q, Grimaud F, Planchot V, Keeling PL, James MG, Myers AM (2009) Proteins from multiple metabolic pathways associate with starch biosynthetic enzymes in high molecular weight complexes: a model for regulation of carbon allocation in maize amyloplasts. Plant Physiol 149:1541–1559
Hewezi T, Petitprez M, Gentzbittel L (2006) Primary metabolic pathways and signal transduction in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.): comparison of transcriptional profiling in leaves and immature embryos using cDNA microarrays. Planta 223:948–964
Ishimaru T, Matsuda T, Ohsugi R, Yamagishi T (2003) Morphological development of rice caryopses located at the different positions in a panicle from early to middle stage of grain filling. Funct Plant Biol 30:1139–1149
Ishimaru T, Hirose T, Matsuda T, Goto A, Takahashi K, Sasaki H, Terao T, Ishii R, Ohsugi R, Yamagishi T (2005) Expression patterns of genes encoding carbohydrate-metabolizing enzymes and their relationship to grain filling in rice (Oryza sativa L.): comparison of caryopses located at different positions in a panicle. Plant Cell Physiol 46:620–624
Iwasaki Y, Mae T, Makino A, Ohira K, Ojima K (1992) Nitrogen accumulation in the inferior spikelet of rice ear during ripening. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 38:517–525
Jones R, Roessler J, Ouattar S (1985) Thermal environment during endosperm cell division in maize: effects on number of endosperm cells and starch granules. Crop Sci 25:830–834
Kang HG, Park S, Matsuoka M, An G (2005) White‐core endosperm floury endosperm‐4 in rice is generated by knockout mutations in the C4-type pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase gene (OsPPDKB). Plant J 42:901–911
Kato T, Shinmura D, Taniguchi A (2007) Activities of enzymes for sucrose-starch conversion in developing endosperm of rice and their association with grain filling in extra-heavy panicle types. Plant Prod Sci 10:442–450
Lin WX, Wu ZQ, Liang YY (1992) Impact of climatic conditiong on the grain-filling properties of hybrid rice. Chin J Agrometeorology 13:4–8
Lur HS, Setter TL (1993) Role of auxin in maize endosperm development (timing of nuclear DNA endoreduplication, zein expression, and cytokinin). Plant Physiol 103:273–280
Mackintosh C (2004) Dynamic interactions between 14-3-3 proteins and phosphoproteins regulate diverse cellular processes. Biochem J 381:329–342
Mayer U, Jürgens G (2002) Microtubule cytoskeleton: a track record. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:494–501
Mechin V, Thevenot C, Le Guilloux M, Prioul JL, Damerval C (2007) Developmental analysis of maize endosperm proteome suggests a pivotal role for pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase. Plant Physiol 143:1203–1219
Membré N, Berna A, Neutelings G, David A, David H, Staiger D, Vásquez JS, Raynal M, Delseny M, Bernier F (1997) cDNA sequence, genomic organization and differential expression of three Arabidopsis genes for germin/oxalate oxidase-like proteins. Plant Mol Biol 35:459–469
Meyer LJ, Gao J, Xu D, Thelen JJ (2012) Phosphoproteomic analysis of seed maturation in Arabidopsis, rapeseed, and soybean. Plant Physiol 159:517–528
Mohapatra P, Patel R, Sahu S (1993) Time of flowering affects grain quality and spikelet partitioning within the rice panicle. Funct Plant Biol 20:231–241
Peng S, Cassman KG, Virmani S, Sheehy J, Khush G (1999) Yield potential trends of tropical rice since the release of IR8 and the challenge of increasing rice yield potential. Crop Sci 39:1552–1559
Peng T, Lv Q, Zhang J, Li JZ, Du YX, Zhao QZ (2011) Differential expression of the microRNAs in superior and inferior spikelets in rice (Oryza sativa.L). J Exp Bot 62:4943–4954
Reiland S, Messerli G, Baerenfaller K, Gerrits B, Endler A, Grossmann J, Gruissem W, Baginsky S (2009) Large-scale Arabidopsis phosphoproteome profiling reveals novel chloroplast kinase substrates and phosphorylation networks. Plant Physiol 150:889–903
Sehnke PC, Chung HJ, Wu K, Ferl RJ (2001) Regulation of starch accumulation by granule-associated plant 14-3-3 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:765–770
Sehnke PC, DeLille JM, Ferl RJ (2002) Consummating signal transduction the role of 14-3-3 proteins in the completion of signal-induced transitions in protein activity. Plant Cell 14:339–354
Singh B, Jenner C (1982) Association between concentration of organic nutrients in the grain, endosperm cell number and grain dry weight within the ear of wheat. Funct Plant Biol 9:83–95
Song JM, Dai S, Li HS, Liu AF, Chen DG, Chu XS, Tetlow I, Emes M (2009) Expression of a wheat endosperm 14-3-3 protein and its interactions with starch biosynthetic enzymes in amyloplasts. Acta Agron Sin 35:1445–1450
Tadege M, Dupuis I, Kuhlemeier C (1999) Ethanolic fermentation: new functions for an old pathway. Trends Plant Sci 4:320–325
Tan F, Li G, Chitteti BR, Peng Z (2007) Proteome and phosphoproteome analysis of chromatin associated proteins in rice (Oryza sativa.L). Proteomics 7:4511–4527
Tang T, Xie H, Wang YX, Lu B, Liang JS (2009) The effect of sucrose and abscisic acid interaction on sucrose synthase and its relationship to grain filling of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Exp Bot 60:2641–2652
Tetlow IJ (2006) Understanding storage starch biosynthesis in plants: a means to quality improvement. Can J Bot 84:1167–1185
Tetlow IJ, Wait R, Lu Z, Akkasaeng R, Bowsher CG, Esposito S, Kosar-Hashemi B, Morell MK, Emes MJ (2004) Protein phosphorylation in amyloplasts regulates starch branching enzyme activity and protein-protein interactions. Plant Cell 16:694–708
Thitisaksakul M, Jiménez RC, Arias MC, Beckles DM (2012) Effects of environmental factors on cereal starch biosynthesis and composition. J Cereal Sci 56:67–80
Thomas D, Guthridge M, Woodcock J, Lopez A (2005) 14-3-3 protein signaling in development and growth factor responses. Curr Top Dev Biol 67:285–303
Vassileva VN, Fujii Y, Ridge RW (2005) Microtubule dynamics in plants. Plant Biotechnol 22:171–178
Wang X, Bian Y, Cheng K, Zou H, Sun SM, He JX (2012) A comprehensive differential proteomic study of nitrate deprivation in Arabidopsis reveals complex regulatory networks of plant nitrogen responses. J Proteome Res 11:2301–2315
Wojtaszek P, Stobiecki M, Bolwell GP (1997) Changes in the composition of exocellular proteins of suspension-cultured Lupinus albus cells in response to fungal elicitors or CuCl2. J Exp Bot 48:2015–2021
Xu SB, Li T, Deng ZY, Chong K, Xue Y, Wang T (2008) Dynamic proteomic analysis reveals a switch between central carbon metabolism and alcoholic fermentation in Oryza sativa filling grains1. Plant Physiol 48:908–925
Yang JC, Zhang JH (2006) Grain filling of cereals under soil drying. New Phytol 169:223–236
Yang JC, Zhang JH (2010) Grain-filling problem in 'super' rice. J Exp Bot 61:1–4
Yang JC, Wang ZQ, Lang YZ, Zhu QS (1998) ATPase activity in the developing grains and its regulation in intersubspecific hybrid rice. J Yangzhou Univ Nat Sci 1:13–17
Yang JC, Su B, Wang ZQ, Zhu QS (1999) Characteristics and physiology of grain filling in intersubspecific hybrid rice. Sci Agric Sin 1:61–70
Yang JP, Zhang S, Wang Z, Visperas Z, Zhu RM (2002a) Grain and dry matter yields and partitioning of assimilates in japonica/indica hybrid rice. Crop Sci 42:766–772
Yang JC, Zhang JH, Huang Z, Wang ZQ, Zhu QS, Liu L (2002b) Correlation of cytokinin levels in the endosperms and roots with cell number and cell division activity during endosperm development in rice. Ann Bot 90:369–377
Yang JC, Zhang JH, Wang ZQ, Zhu QS (2003) Hormones in the grains in relation to sink strength and postanthesis development of spikelets in rice. Plant Growth Regul 41:185–195
Yang JC, Zhang JH, Wang ZQ, Liu K, Wang P (2006) Post-anthesis development of inferior and superior spikelets in rice in relation to abscisic acid and ethylene. J Exp Bot 57:149–160
Yoshida S, Forno D, Cock J, Gomez K (1976) Determination of sugar and starch in plant tissue. Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice. The International Rice Research Institute, Philippines, pp 46–49
Zeeman SC, Kossmann J, Smith AM (2010) Starch: its metabolism, evolution, and biotechnological modification in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:209–234
Zhang H, Tan GL, Yang LN, Yang JC, Zhang JH, Zhao BH (2009) Hormones in the grains and roots in relation to post-anthesis development of inferior and superior spikelets in japonica/indica hybrid rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:195–204
Zhang ZX, Chen J, Li Z, Chen HF, Fang CX et al (2012) Differential proteomic expressions between superior and inferior spikelets of rice in response to varied nitrogen treatments. Aust J Crop Sci 6:316–325
Zhang ZX, Zhao H, Tang J, Li Z, Li Z, Chen DM, Lin WX (2014) A proteomic study on molecular mechanism of poor grain-filling of rice (Oryza sativa L.) inferior spikelets. PLoS One 9:e89140
Zhou JL, Chen LB, Zhou GQ (1992) A study on the dynamic state and physiology of grain filling of subspecific hybrid rice. Hybrid Rice 5:36–40
Zhu GH, Ye NH, Yang JC, Peng XX, Zhang JH (2011) Regulation of expression of starch synthesis genes by ethylene and ABA in relation to the development of rice inferior and superior spikelets. J Exp Bot 11:3907–3916
Acknowledgments
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31271670, 31401306) and the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Fujian, China (No. 2012J01075, 2013J01092).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhixing Zhang and Jun Tang are co-first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Tang, J., Du, T. et al. Mechanism of Developmental Stagnancy of Rice Inferior Spikelets at Early Grain-Filling Stage as Revealed by Proteomic Analysis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 33, 1844–1863 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-015-0880-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-015-0880-z