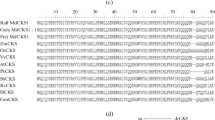
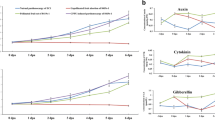
Abstract
Plant D-type cyclin genes (CYCDs) are important regulators of cell division. However, little is known on their participation during the early developmental stage of cucumber fruit. In this study, cucumber CYCD genes were identified and characterized. The expression levels of these genes during early fruit development were assessed from 0 to 8 days after anthesis (DAA). The results revealed the presence of 13 different CYCD genes, which were named according to identity percentages of the corresponding orthologs in Arabidopsis thaliana and poplar. The genomic organization of each subgroup CYCD was similar to their orthologs in A. thaliana and poplar. The expression levels of CsCYCD genes were analyzed in cucumber fruits under different treatments including natural parthenocarpic fruit, pollinated fruit, and N-(2-chloro-4-pyidyl)-N′-phenyurea (CPPU)-induced parthenocarpic fruit. The highest expression levels of most CsCYCDs genes were at four DAA in natural parthenocarpic and pollinated fruits. Interestingly, the expression patterns of 8 of 13 CsCYCD genes in natural parthenocarpic fruit were similar to those in pollinated fruit, but different from those in CPPU-induced parthenocarpic fruit. Collectively, the results of this study provide insights on the CYCDs involved in cucumber parthenocarpic fruit development.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando K, Carr K, Grumet R (2012) Transcriptome analyses of early cucumber fruit growth identifies distinct gene modules associated with phases of development. BMC Genomics 13(1):518–534
Ben-Cheikh W, Perez-Botella J, Tadeo FR, Talon M, Primo-Millo E (1997) Pollination increases gibberellin levels in developing ovaries of seeded varieties of citrus. Plant Physiol 114(2):557–564
Bohner J, Bangerth F (1988) Effects of fruit set sequence and defoliation on cell number, cell size and phytomone levels of tomato fruits (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) with a truss. Plant Growth Regul 7:141–155
Boniotti MB, Gutierrez C (2001) A cell-cycle-regulated kinase activity phosphorylates plant retinoblastoma protein and contains, in Arabidopsis, a CDKA/cyclin D complex. Plant J 28(3):341–350
Boonkorkaew P, Hikosaka S, Sugiyama N (2008) Effect of pollination on cell division, cell enlargement, and endogenous hormones in fruit development in a gynoecious cucumber. Sci Hortic 116(1):1–7
Boonstra J (2003) Progression through the G1-phase of the on-going cell cycle. J Cell Biochem 90(2):244–252
Buendía-Monreal M, Rentería-Canett I, Guerrero-Andrade O, Bravo-Alberto CE, Martínez-Castilla LP, García E, Vázquez-Ramos JM (2011) The family of maize D-type cyclins: genomic organization, phylogeny and expression patterns. Physiol Plant 143(3):297–308
Cockcroft CE, den Boer BGW, Healy JMS, Murray JAH (2000) Cyclin D control of growth rate in plants. Nature 405(6786):575–579
Collins C, Dewitte W, Murray JAH (2012) D-type cyclins control cell division and developmental rate during Arabidopsis seed development. J Exp Bot 63(10):3571–3586
De Veylder L, de Almeida Engler J, Burssens S, Manevski A, Lescure B, Van Montagu M, Engler G, Inzé D (1999) A new D-type cyclin of Arabidopsis thaliana expressed during lateral root primordia formation. Planta 208(4):453–462
Dewitte W, Riou-Khamlichi C, Scofield S, Healy JMS, Jacqmard A, Kilby NJ, Murray JAH (2003) Altered cell cycle distribution, hyperplasia, and inhibited differentiation in Arabidopsis caused by the D-type cyclin CYCD3. Plant Cell 15(1):79–92
Dewitte W, Scofield S, Alcasabas AA, Maughan SC, Menges M, Braun N, Collins C, Nieuwland J, Prinsen E, Sundaresan V (2007) Arabidopsis CYCD3 D-type cyclins link cell proliferation and endocycles and are rate-limiting for cytokinin responses. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA 104(36):14537–14542
Ewen ME, Sluss HK, Sherr CJ, Matsushime H, Kato J, Livingston DM (1993) Functional interactions of the retinoblastoma protein with mammalian D-type cyclins. Cell 73(3):487
Feng C, Chen M, Xu C, Bai L, Yin X, Li X, Allan AC, Ferguson IB, Chen K (2012) Transcriptomic analysis of Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) fruit development and ripening using RNA-Seq. BMC Genomics 13(1):19–34
Fu FQ, Mao WH, Shi K, Zhou YH, Asami T, Yu JQ (2008) A role of brassinosteroids in early fruit development in cucumber. J Exp Bot 59(9):2299–2308
Fu F, Mao W, Shi K, Zhou Y, Yu J (2010) Spatio-temporal changes in cell division, endoreduplication and expression of cell cycle-related genes in pollinated and plant growth substances-treated ovaries of cucumber. Plant Biol 12(1):98–107
Gillaspy G, Ben-David H, Gruissem W (1993) Fruits: a developmental perspective. Plant Cell 5(10):1439–1451
Guo A-Y, Zhu Q-H, Chen X, Luo J-C (2007) GSDS: a gene structure display server. Yi Chuan 29(8):1023–1026
Hu Y, Bao F, Li J (2008) Promotive effect of brassinosteroids on cell division involves a distinct CycD3-induction pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant J 24(5):693–701
Huang S, Li R, Zhang Z, Li L, Gu X, Fan W, Lucas WJ, Wang X, Xie B, Ni P (2009) The genome of the cucumber, Cucumis sativus L. Nat Genet 41(12):1275–1281
Huntley R, Healy S, Freeman D, Lavender P, de Jager S, Greenwood J, Makker J, Walker E, Jackman M, Xie Q (1998) The maize retinoblastoma protein homologue ZmRb-1 is regulated during leaf development and displays conserved interactions with G1/S regulators and plant cyclin D (CycD) proteins. Plant Mol Biol 37(1):155–169
Kim IS, Okubo H, Fujieda K (1992) Endogenous levels of IAA in relation to parthenocarpy in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Sci Hortic 52(1–2):1–8
Kono A, Umeda-Hara C, Adachi S, Nagata N, Konomi M, Nakagawa T, Uchimiya H, Umeda M (2007) The Arabidopsis D-type cyclin CYCD4 controls cell division in the stomatal lineage of the hypocotyl epidermis. Plant Cell 19(4):1265–1277
Koroleva OA, Tomlinson M, Parinyapong P, Sakvarelidze L, Leader D, Shaw P, Doonan JH (2004) CycD1, a putative G1 cyclin from Antirrhinum majus, accelerates the cell cycle in cultured tobacco BY-2 cells by enhancing both G1/S entry and progression through S and G2 phases. Plant Cell 16(9):2364–2379
Kvarnheden A, Yao JL, Zhan X, O'Brien I, Morris BA (2000) Isolation of three distinct CycD3 genes expressed during fruit development in tomato. J Exp Bot 51(352):1789–1797
Lewis DH, Burge GK, Hopping ME, Jameson PE (2006) Cytokinins and fruit development in the kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa). II. Effects of reduced pollination and CPPU application. Physiol Plant 98(1):187–195
Li Y, Yu JQ, Ye QJ, Zhu ZJ, Guo ZJ (2003) Expression of CycD3 is transiently increased by pollination and N-(2-chloro-4-pyridyl)-N′-phenylurea in ovaries of Lagenaria leucantha. J Exp Bot 54(385):1245–1251
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Meijer M, Murray JAH (2001) Cell cycle controls and the development of plant form. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4(1):44–49
Menges M, Pavesi G, Morandini P, Bögre L, Murray JAH (2007) Genomic organization and evolutionary conservation of plant D-type cyclins. Plant Physiol 145(4):1558–1576
Morgan DO (1997) Cyclin-dependent kinases: engines, clocks, and microprocessors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 13(1):261–291
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 5(7):621–628
Nakagami H, Kawamura K, Sugisaka K, Sekine M, Shinmyo A (2002) Phosphorylation of retinoblastoma-related protein by the cyclin D/cyclin-dependent kinase complex is activated at the G1/S-phase transition in tobacco. Plant Cell 14(8):1847–1857
Nugent J, Alfa CE, Young T, Hyams JS (1991) Conserved structural motifs in cyclins identified by sequence analysis. J Cell Sci 99(3):669–674
Riou-Khamlichi C, Huntley R, Jacqmard A, Murray JAH (1999) Cytokinin activation of Arabidopsis cell division through a D-type cyclin. Science 283(5407):1541–1544
Sjut V, Bangerth F (2006) Effect of pollination or treatment with growth regulators on levels of extractable hormones in tomato ovaries and young fruits. Physiol Plant 53(1):76–78
Soni R, Carmichael JP, Shah ZH, Murray J (1995) A family of cyclin D homologs from plants differentially controlled by growth regulators and containing the conserved retinoblastoma protein interaction motif. Plant Cell 7(1):85–103
Sorrell DA, Combettes B, Chaubet-Gigot N, Gigot C, Murray JAH (1999) Distinct cyclin D genes show mitotic accumulation or constant levels of transcripts in tobacco bright yellow-2 cells. Plant Physiol 119(1):343–352
Takeno K, Ise H, Minowa H, Dounowaki T (1992) Fruit growth induced by benzyladenine in Cucumis sativus L.: influence of benzyladenine on cell division, cell enlargement and indole-3-acetic acid content. J Jap Soc Hort Sci 60:915–920
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Uemukai K, Iwakawa H, Kosugi S, de Uemukai S, Kato K, Kondorosi E, Murray JAH, Ito M, Shinmyo A, Sekine M (2005) Transcriptional activation of tobacco E2F is repressed by co-transfection with the retinoblastoma-related protein: cyclin D expression overcomes this repressor activity. Plant Mol Biol 57(1):83–100
Vandepoele K, Raes J, De Veylder L, Rouzé P, Rombauts S, Inzé D (2002) Genome-wide analysis of core cell cycle genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 14(4):903–916
Wang G, Kong H, Sun Y, Zhang X, Zhang W, Altman N, Ma H (2004) Genome-wide analysis of the cyclin family in Arabidopsis and comparative phylogenetic analysis of plant cyclin-like proteins. Plant Physiol 135(2):1084–1099
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China grant (The 973 Program: 2012CB3904), the Youth Science and Technology Innovation Fund program of Nanjing Agricultural University (No. KJ2012013), the Fundamental Research of Nanjing Agricultural University (Y0201100253) program, and the Ph.D. Program Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (20120097120037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, L., Li, J., Zhang, T. et al. Identification and Expression Analysis of D-type Cyclin Genes in Early Developing Fruit of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 32, 209–218 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-013-0637-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-013-0637-5