Abstract
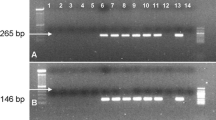
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) and its isoform, eIF(iso)4E, play important roles in protein translation and recently reported to be involved in plant–virus interactions. A cDNA encoding the tomato eIF(iso)4E was cloned based on a tentative consensus (TC170275) in TIGR (http://www.tigr.org/), and was designated as SleIF(iso)4E, with an open reading frame of 603 nucleotides encoding a protein of 200 amino acids. The calculated molecular weight of the SleIF(iso)4E protein was 22.85 kD, and the theoretical isoelectric point was 5.76. The amino acid sequence of SleIF(iso)4E showed 66–91% identity with eIF(iso)4Es in pepper, tobacco, pea and maize, and 44–51% identity with eIF4Es from other plants. The phylogenetic relationship and tertiary structure comparisons indicate that SleIF(iso)4E share high homology and strict conserved regions with other members of the eIF4E family, a characteristic of all members of this family. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR showed varying expression levels of SleIF(iso)4E in different tissues. By comparing eIF(iso)4E coding sequences between resistant and susceptible tomato genotypes, correlation between sequence variations and virus resistance was identified. These findings provide good grounds for future research on the role of SleIF(iso)4E in translation initiation and plant–virus interactions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albar L, Bangratz-Reyser M, Hébrard E, Ndjiondjop MN, Jones M, Ghesquière A (2006) Mutations in the eIF(iso) 4G translation initiation factor confer high resistance of rice to Rice yellow mottle virus. Plant J 47:417–26. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02792.x
Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T (2006) The SWISS-MODEL Workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195–201. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti770
Ayme V, Petit-Pierre J, Souche S, Palloix A, Moury B (2007) Molecular dissection of the potato virus Y VPg virulence factor reveals complex adaptations to the pvr2 resistance allelic series in pepper. J Gen Virol 88:1594–601. doi:10.1099/vir.0.82702-0
Beauchemin C, Boutet N, Laliberte JF (2007) Visualization of the interaction between the precursors of VPg, the viral protein linked to the genome of turnip mosaic virus, and the translation eukaryotic initiation factor iso4E in Planta. J Gen Virol 81:775–82
Boisnard A, Albar L, Thiéméle D, Rondeau M, Ghesquière A (2007) Evaluation of genes from eIF4E and eIF4G multigenic families as potential candidates for partial resistance QTLs to Rice yellow mottle virus in rice. Theor Appl Genet 116:53–62. doi:10.1007/s00122-007-0646-6
Browning KS (2004) Plant translation initiation factors: it is not easy to be green. Biochem Soc Trans 32:589–91. doi:10.1042/BST0320589
Bruun-Rasmussen M, Moller IS, Tulinius G, Hansen JK, Lund OS, Johansen IE (2007) The same allele of translation initiation factor 4E mediates resistance against two Potyvirus spp. in Pisum sativum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:1075–82. doi:10.1094/MPMI-20-9-1075
Gao Z, Johansen E, Eyers S, Thomas CL, Ellis THN, Maule AJ (2004) The potyvirus recessive resistance gene, sbm1, identifies a novel role for translation initiation factor eIF4E in cell-to-cell trafficking. Plant J 40:376–385. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02215.x
German-Retana S, Walter J, Doublet B, Roudet-Tavert G, Nicaise V, Lecampion C, Houvenaghel MC, Robaglia C, Michon T, Le Gall O (2008) Mutational analysis of plant cap-binding protein eIF4E reveals key amino acids involved in biochemical functions and potyvirus infection. J Virol 82:7601–7612. doi:10.1128/JVI.00209-08
Graff JR, Konicek BW, Carter JH, Marcusson EG (2008) Targeting the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 68:631–634. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5635
Kang BC, Yeam I, Frantz JD, Murphy JF, Jahn MM (2005) The pvr1 locus in Capsicum encodes a translation initiation factor eIF4E that interacts with Tobacco etch virus VPg. Plant J 42:392–405. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02381.x
Khan MA, Miyoshi H, Ray S, Natsuaki T, Suehiro N, Goss DJ (2006) Interaction of genome-linked protein (VPg) of turnip mosaic virus with wheat germ translation initiation factors eIFiso4E and eIFiso4F. J Biol Chem 281:28002–28010. doi:10.1074/jbc.M605479200
Lellis AD, Kasschau KD, Whitham SA, Carrington JC (2002) Loss-of-susceptibility mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana reveal an essential role for eIF(iso) 4E during potyvirus infection. Curr Biol 12:1046–1051. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00898-9
Marcotrigiano J, Gingrans AC, Sonenberg N, Burley SK (1997) Cocrystal structure of the messenger RNA 5′ cap-binding protein (eIF4E) bound to 7-methyl-GDP. Cell 89:951–961. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80280-9
Michon T, Estevez Y, Walter J, German-Retana S, Le Gall O (2006) The potyviral virus genome-linked protein VPg forms a ternary complex with the eukaryotic initiation factors eIF4E and eIF4G and reduces eIF4E affinity for a mRNA cap analogue. FEBS J 273:1312–22. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05156.x
Nicaise V, German-Retana S, Sanjuán R, Dubrana MP, Mazier M, Maisonneuve B, Candresse T, Caranta C, LeGall O (2003) The eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E controls lettuce susceptibility to the potyvirus lettuce mosaic virus. Plant Physiol 132:1272–1282. doi:10.1104/pp.102.017855
Nicaise V, Gallois JL, Chafiai F, Allen LM, Schurdi-Levraud V, Browning KS, Candresse T, Caranta C, Le Gall O, German-Retana S (2007) Coordinated and selective recruitment of eIF4E and eIF4G factors for potyvirus infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 581:1041–1046. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.02.007
Nieto C, Morales M, Orjeda G, Clepet C, Monfort A, Sturbois B, Puigdomenech P, Pitrat M, Caboche M, Dogimont C, Garcia-Mas J, Aranda MA, Bendahmane A (2006) An eIF4E allele confers resistance to an uncapped and non-polyadenylated RNA virus in melon. Plant J 48:452–462. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02885.x
Ray S, Yumak H, Domashevskiy A, Khan MA, Gallie DR, Goss DJ (2006) Tobacco etch virus mRNA preferentially binds wheat germ eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 4G rather than eIFiso4G. J Biol Chem 281:35826–34. doi:10.1074/jbc.M605762200
Robaglia C, Caranta C (2006) Translation initiation factors: a weak link in plant RNA virus infection. Trends Plant Sci 11:40–45. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2005.11.004
Ruffel S, Dussault MH, Palloix A, Moury B, Bendahmane A, Robaglia C, Caranta C (2002) A natural recessive resistance gene against potato virus Y in pepper corresponds to the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E). Plant J 32:1067–75. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01499.x
Ruffel S, Gallois JL, Lesage ML, Caranta C (2005) The recessive potyvirus resistance gene pot-1 is the tomato orthologue of the pepper pvr2-eIF4E gene. Mol Genet Genomics 274:346–353. doi:10.1007/s00438-005-0003-x
Ruffel S, Gallois JL, Moury B, Robaglia C, Palloix A, Caranta C (2006) Simultaneous mutations in translation initiation factors eIF4E and eIF(iso) 4E are required to prevent pepper veinal mottle virus infection of pepper. J Gen Virol 87:2089–2098. doi:10.1099/vir.0.81817-0
Sato M, Nakahara K, Yoshii M, Ishikawab M, Uyeda I (2005) Selective involvement of members of the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E family in the infection of Arabidopsis thaliana by potyviruses. FEBS Lett 579:1167–1171. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.12.086
Sippl and Wiederstein (2008) A note on difficult structure alignment problems. Bioinformatics 24:426–427. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm622
Stein N, Perovic D, Kumlehn J, Pellio B, Stracke S, Streng S, Ordon F, Graner A (2005) The eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E confers multiallelic recessive Bymovirus resistance in Hordeum vulgare (L. Plant J 42:912–922. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02424.x
Yeam I, Cavatorta JR, Ripoll DR, Kang BC, Jahn MM (2007) Functional dissection of naturally occurring amino acid substitutions in eIF4E that confers recessive Potyvirus resistance in plants. Plant Cell 19:2913–28. doi:10.1105/tpc.107.050997
Yoshii M, Nishikiori M, Tomita K, Yoshioka N, Kozuka R, Naito S, Ishikawa M (2004) The Arabidopsis Cucumovirus Multiplication 1 and 2 loci encode translation initiation factors 4E and 4G. J Virol 78:6102–11. doi:10.1128/JVI.78.12.6102-6111.2004
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Major State Basic Research Development Program (2009CB119000), National Nature Science Foundation of China (No.30671417, No.30800756), and Xinjiang Corps Doctor Fund of China (No.2008JC04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sequence data of SleIF(iso)4E from this article have been deposited at GenBank under accession number EU119958.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YY., Qi, MF., Sun, J. et al. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a Gene Encoding Eukaryotic Initiation Factor iso4E in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Plant Mol Biol Rep 27, 400–406 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0090-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0090-7