Abstract
Aims
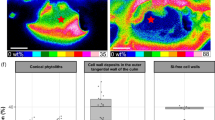
Phosphorus (P) deficiency-induced mobilization of rare earth elements (REEs) in the rhizosphere contributes to REE accumulation in the hyperaccumulator Phytolacca americana, but a lack of in situ methods for visualization of the root-soil interface limits our understanding of the underlying processes.
Methods
Diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) devices were used for probing root exudates, REEs and P in the P. americana rhizosphere. Desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and laser-ablation inductively coupled mass spectrometry were used for in situ imaging of root exudates, REEs and P sorbed on the DGT.
Results
The novel approach demonstrated here is capable of synchronously and quantitatively characterizing the distribution of root exudates and labile elements in the rhizosphere. The secretion fluxes of citrate and oxalate in the rhizosphere under P deficiency were three times higher than under P sufficient condition; and the lanthanum (La) fluxes in the rhizosphere under P deficiency were ten times greater than at P sufficiency condition. The enrichment of P and La under P deficiency and depletion under P sufficient conditions in the rhizosphere suggests that P deficiency-induced organic acid secretion is crucial for the mobilization of soil REEs and subsequent REE accumulation in P. americana.
Conclusion
The combination of DGT devices with mass spectrometry imaging is technically feasible for in situ synchronous imaging of root exudates, REEs and labile elements at the root-soil interface. Our study shed light on processes of mobilization of mineral elements in the rhizosphere induced as a side-effect of the P acquisition mechanism.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Álvarez-López V, Puschenreiter M, Santner J, Lehto N, Prieto-Fernández Á, Wenzel WW, Monterroso C, Kidd PS (2021) Evidence for nickel mobilisation in rhizosphere soils of Ni hyperaccumulator Odontarrhena serpyllifolia. Plant Soil 464:89–107
Badri DV, Vivanco JM (2009) Regulation and function of root exudates. Plant Cell Environ 32(6):666–681
Bhandari DR, Wang Q, Friedt W, Spengler B, Gottwald S, Römpp A (2015) High resolution mass spectrometry imaging of plant tissues: towards a plant metabolite atlas. Analyst 140(22):7696–7709
Cesco S, Lucini L, Miras-Moreno B, Borruso L, Mimmo T, Pii Y, Puglisi E, Spini G, Taskin E, Tiziani R, Zangrillo MS, Trevisan M (2021) The hidden effects of agrochemicals on plant metabolism and root-associated microorganisms. Plant Sci 311:111012
Chen YT, Wang Y, Yeh KC (2017) Role of root exudates in metal acquisition and tolerance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 39:66–72
Davison W, Zhang H (1994) In situ speciation measurements of trace components in natural waters using thin-film gels. Nature 367(6463):546–548
DeGroote KV, McCartha GL, Pollard AJ (2018) Interactions of the manganese hyperaccumulator Phytolacca americana L. with soil pH and phosphate. Ecol Res 33(4):749–755
Gomez-Zepeda D, Frausto M, Nájera-González H-R, Herrera-Estrella L, Ordaz-Ortiz J-J (2021) Mass spectrometry-based quantification and spatial localization of small organic acid exudates in plant roots under phosphorus deficiency and aluminum toxicity. Plant J 106(6):1791–1806
Gregory PJ, George TS, Paterson E (2022) New methods for new questions about rhizosphere/plant root interactions. Plant Soil 476:699–712
Guan D-X, He S-X, Li G, Teng HH, Ma LQ (2021) Application of diffusive gradients in thin-films technique for speciation, bioavailability, modeling and mapping of nutrients and contaminants in soils. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 52(7):3035–3079
Günther D, Hattendorf B (2005) Solid sample analysis using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 24(3):255–265
Han F, Shan X-Q, Zhang J, Xie Y-N, Pei Z-G, Zhang S-Z, Zhu Y-G, Wen B (2005) Organic acids promote the uptake of lanthanum by barley roots. New Phytol 165(2):481–492
Kreuzeder A, Santner J, Scharsching V, Oburger E, Hoefer C, Hann S, Wenzel WW (2018) In situ observation of localized, sub-mm scale changes of phosphorus biogeochemistry in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 424(1):573–589
Kuzyakov Y, Razavi BS (2019) Rhizosphere size and shape: temporal dynamics and spatial stationarity. Soil Biol Biochem 135:343–360
Lambers H, Hayes PE, Laliberté E, Oliveira RS, Turner BL (2015) Leaf manganese accumulation and phosphorus-acquisition efficiency. Trends Plant Sci 20(2):83–90
Lambers H, Wright IJ, Guilherme Pereira C, Bellingham PJ, Bentley LP, Boonman A, Cernusak LA, Foulds W, Gleason SM, Gray EF, Hayes PE, Kooyman RM, Malhi Y, Richardson SJ, Shane MW, Staudinger C, Stock WD, Swarts ND, Turner BL, Turner J, Veneklaas EJ, Wasaki J, Westoby M, Xu Y (2021) Leaf manganese concentrations as a tool to assess belowground plant functioning in phosphorus-impoverished environments. Plant Soil 461:43–61
Lehto NJ, Davison W, Zhang H (2012) The use of ultra-thin diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) devices for the analysis of trace metal dynamics in soils and sediments: a measurement and modelling approach. Environ Chem 9(4):415–423
Liu W-S, Chen Y-Y, Huot H, Liu C, Guo M-N, Qiu R-L, Morel JL, Tang Y-T (2020) Phytoextraction of rare earth elements from ion-adsorption mine tailings by Phytolacca americana: Effects of organic material and biochar amendment. J Clean Prod 275:122959
Liu C, Ding T-X, Liu W-S, Tang Y-T, Qiu R-L (2023) Phosphorus mediated rhizosphere mobilization and apoplast precipitation regulate rare earth element accumulation in Phytolacca americana. Plant Soil 483:697–709
Liu C, Liu W-S, van der Ent A, Morel JL, Zheng H-X, Wang G-B, Tang Y-T, Qiu R-L (2021) Simultaneous hyperaccumulation of rare earth elements, manganese and aluminum in Phytolacca americana in response to soil properties. Chemosphere 282:131096
Liu C, Sun D, Zheng H-X, Wang G-B, Liu W-S, Cao Y, Tang Y-T, Qiu R-L (2022) The limited exclusion and efficient translocation mediated by organic acids contribute to rare earth element hyperaccumulation in Phytolacca americana. Sci Total Environ 805:150335
Monei N, Hitch M, Heim J, Pourret O, Heilmeier H, Wiche O (2022) Effect of substrate properties and phosphorus supply on facilitating the uptake of rare earth elements (REE) in mixed culture cropping systems of Hordeum vulgare, Lupinus albus and Lupinus angustifolius. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:57172–57189
Oburger E, Jones DL (2018) Sampling root exudates – mission impossible? Rhizosphere 6:116–133
Oburger E, Schmidt H (2016) New methods to unravel rhizosphere processes. Trends Plant Sci 21(3):243–255
Pollard AJ (2022) Inadvertent uptake of trace elements and its role in the physiology and evolution of hyperaccumulators. Plant Soil 483:711–719
Pollard AJ, Reeves RD, Baker AJM (2014) Facultative hyperaccumulation of heavy metals and metalloids. Plant Sci 217–218:8–17
Ren M, Ding S, Dai Z, Wang J, Li C, Zhong Z, Cao J, Yang L, Tsang DCW, Xu S, Yang C, Wang Y (2021) A new DGT technique comprising a hybrid sensor for the simultaneous high resolution 2-D imaging of sulfides, metallic cations, oxyanions and dissolved oxygen. J Hazard Mater 403:123597
Santner J, Zhang H, Leitner D, Schnepf A, Prohaska T, Puschenreiter M, Wenzel WW (2012) High-resolution chemical imaging of labile phosphorus in the rhizosphere of Brassica napus L. cultivars. Environ Exp Bot 77:219–226
Singh S, Parihar P, Singh R, Singh VP, Prasad SM (2016) Heavy metal tolerance in plants: role of transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and ionomics. Front. Front Plant Sci 6:1143
Tao Q, Hou D, Yang X, Li T (2016) Oxalate secretion from the root apex of Sedum alfredii contributes to hyperaccumulation of Cd. Plant Soil 398(1–2):139–152
Tao Q, Zhao J, Li J, Liu Y, Luo J, Yuan S, Li B, Li Q, Xu Q, Yu X, Huang H, Li T, Wang C (2020) Unique root exudate tartaric acid enhanced cadmium mobilization and uptake in Cd-hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. J Hazard Mater 383:121177
Tiziani R, Mimmo T, Valentinuzzi F, Pii Y, Celletti S, Cesco S (2020) Root handling affects carboxylates exudation and phosphate uptake of white lupin roots. Front Plant Sci 11:584568
Tiziani R, Miras-Moreno B, Malacrinò A, Vescio R, Lucini L, Mimmo T, Cesco S, Sorgonà A (2022) Drought, heat, and their combination impact the root exudation patterns and rhizosphere microbiome in maize roots. Environ Exp Bot 203:105071
Tiziani R, Puschenreiter M, Smolders E, Mimmo T, Herrera JC, Cesco S, Santner J (2021) Millimeter-resolution mapping of citrate exuded from soil grown roots using a novel, low-invasive sampling technique. J Exp Bot 72(10):3513–3525
van der Ent A, Baker AJM, Reeves RD, Pollard AJ, Schat H (2013) Hyperaccumulators of metal and metalloid trace elements: facts and fiction. Plant Soil 362(1):319–334
van der Ent A, Nkrumah PN, Purwadi I, Erskine PD (2022) Rare earth element (hyper)accumulation in some Proteaceae from Queensland, Australia. Plant Soil 485:247–257
Veličković D, Anderton CR (2017) Mass spectrometry imaging: towards mapping the elemental and molecular composition of the rhizosphere. Rhizosphere 3:254–258
Veličković D, Lin VS, Rivas A, Anderton CR, Moran JJ (2020) An approach for broad molecular imaging of the root-soil interface via indirect matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Soil Biol Biochem 146:107804
White RA, Rivas-Ubach A, Borkum MI, Köberl M, Bilbao A, Colby SM, Hoyt DW, Bingol K, Kim Y-M, Wendler JP, Hixson KK, Jansson C (2017) The state of rhizospheric science in the era of multi-omics: a practical guide to omics technologies. Rhizosphere 3:212–221
Wiche O, Kummer N-A, Heilmeier H (2016) Interspecific root interactions between white lupin and barley enhance the uptake of rare earth elements (REEs) and nutrients in shoots of barley. Plant Soil 402(1):235–245
Williams PN, Santner J, Larsen M, Lehto NJ, Oburger E, Wenzel W, Glud RN, Davison W, Zhang H (2014) Localized flux maxima of arsenic, lead, and iron around root apices in flooded lowland rice. Environ Sci Technol 48(15):8498–8506
Yang X, Qin J, Li J, Lai Z, Li H (2021) Upland rice intercropping with Solanum nigrum inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi reduces grain cd while promoting phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 406:124325
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Hai-Yun Zhou (Instrumental Analysis & Research Center, Sun Yat-Sen University) for her help in DESI-MS analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41771343, 41920104003, 41877475, 42007110) and the 111 Project (B18060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chong Liu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing - Original Draft, Visualization. Ting-Xuan Ding: Methodology, Investigation, Visualization. Antony van der Ent, Chang Liu: Writing - Review & Editing. Wen-Shen Liu: Writing-Review & Editing, Funding acquisition. Jean Louis Morel, Catherine Sirguey: Review. Ye-Tao Tang, Rong-Liang Qiu: Supervision, Writing - Review & Editing, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Juan Barcelo.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 2.27 MB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Ding, TX., van der Ent, A. et al. A novel method for in situ imaging of root exudates and labile elements reveals phosphorus deficiency-induced mobilization of rare earth elements in the rhizosphere of Phytolacca americana. Plant Soil 495, 13–26 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06146-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06146-9