Abstract
Purpose
Anthropogenic activities have increased the nitrogen (N) inputs in terrestrial ecosystems, thereby altering both the carbon (C) and phosphorus (P) availability along with resource stoichiometry. Stoichiometric deviations between microbial biomass and resources availablity cause stoichiometric imbalances and nutrient limitations for microbial activity. However, whether N deposition will further aggravate the existing P limitation is unknown. Furthermore, how soil microbes respond to these conditions, along with the biogeochemical cycles they mediate, still remains unclear.
Methods
To answer these questions, a 7-year N addition experiment (+0, +50, +150 kg N ha−1 yr−1; CK, LN, HN) has been conducted in a subtropical evergreen-broadleaved forest in the Rainy Area of West China, where received the highest background N deposition in the world and the highest precipitation in inland China. Soil-available nutrients, microbial biomass, C-, N-, and P-acquiring enzyme activities, microbial community composition and diversity were measured.
Results
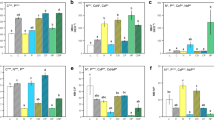
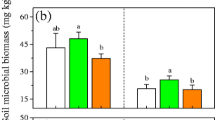
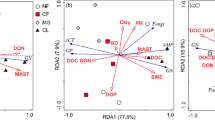
With increasing N addition, the soil DOC:AP and AN:AP ratios increased significantly, whereas microbial biomass C:P and N:P ratios decreased significantly, resulting in increased C:P and N:P imbalances between the soil microbes and resources, thereby aggravating the existing P limitation of microorganisms in this subtropical N-saturated forest. Microbial communities maintained stoichiometric homeostasis by increasing ACP enzyme activity (by 8.99% to 19.28% under N treatment) and threshold elements ratio (TER) at P-limited levels. The aggravated imbalance of C:P and N:P caused by N addition decreased the bacterial and fungal community alpha-diversity. Interestingly, changes in the beta-diversity of the bacterial rather than the fungal community responded more strongly to stoichiometric imbalance. Bacterial communities transitioned from coprophilous (Proteobacteria-dominated) to oligotrophic (Actinobacteriota-dominated) under N addition treatment.
Conclusions
This study not only highlights the importance of stoichiometric imbalances in regulating the soil microbial community structure and enzymatic activity, but also may help in understanding how global N deposition-induced resource stoichiometry changes affect the terrestrial C and nutrient flows.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber JD, Nadelhoffer KJ, Steudler P, Melillo JM (1989) Nitrogen saturation in northern forest ecosystems. BioScience 39:378–286
Aber J, Mcdowell W, Nadelhoffer K, Magill A, Berntson G, Kamakea M, Mcnulty S, Currie W, Rustad L, Fernandez I (1998) Nitrogen saturation in temperate forest ecosystems. Bioscience 48:921–934
Adamczyk B, Kilpeläinen P, Kitunen V, Smolander A (2014) Potential activities of enzymes involved in N, C, P and S cycling in boreal forest soil under different tree species. Pedobiologia 57:97–102
Ali HE, Reineking B, Münkemüller T (2017) Effects of plant functional traits on soil stability: intraspecific variability matters. Plant Soil 411:359–375
Bardgett RD, Van Der Putten WH (2014) Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature 515:505–511
Brookes PC, Powlson DS, Jenkinson DS (1982) Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 14:319–329
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842
Chen H, Li DJ, Xiao KC, Wang KL (2018a) Soil microbial processes and resource limitation in karst and non-karst forests. Funct Ecol 32:1400–1409
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Jia G (2018b) Fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one fastq preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34:884–890
Clemmensen KE, Bahr A, Ovaskainen O, Dahlberg A, Ekblad A, Wallander H, Lindahl B (2013) Roots and associated fungi drive long-term carbon sequestration in boreal forest. Science 339:1615–1618
Cui YX, Fang LC, Guo XB, Wang X, Zhang YJ, Li PF, Zhang XC (2018) Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation in rhizosphere soil in the arid area of the northern loess plateau, China. Soil Biol Biochem 116:11–21
Cui YX, Zhang YL, Duan CJ, Wang X, Zhang XC, Ju WL, Chen HS, Yue SC, Wang YQ, Li SQ, Fang LC (2020) Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation decreases the nitrogen cycling potential of soils in semi-arid agricultural ecosystems. Soil Tillage Res 197:104463
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Reich PB, Khachane AN, Campbell CD, Thomas N, Freitag TE, Abu Al-Soud W, Sørensen S, Bardgett RD, Singh BK (2017) It is elemental: soil nutrient stoichiometry drives bacterial diversity. Environ Microbiol 19:1176–1188
Deng L, Peng CH, Huang CB, Wang KB, Liu QY, Liu YL, Hai XY, Shangguan ZP (2019) Drivers of soil microbial metabolic limitation changes along a vegetation restoration gradient on the loess plateau, China. Geoderma 353:188–200
Eastman BA, Adams MB, Brzostek ER, Burnham MB, Carrara JE, Kelly C, Peterjohn WT (2021) Altered plant carbon partitioning enhanced forest ecosystem carbon storage after 25 years of nitrogen additions. New Phytol 230:1435–1448
Eastman BA, Adams MB, Peterjohn WT (2022) The path less taken: long-term N additions slow leaf litter decomposition and favor the physical transfer pathway of soil organic matter formation. Soil Biol Biochem 166:108567
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE:highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Elser JJ, Bracken MES, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater,marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 10:1135–1142
Fan YX, Lin F, Yang LM, Zhong XJ, Wang MH, Zhou JC, Chen YM, Yang YS (2018) Decreased soil organic P fraction associated with ectomycorrhizal fungal activity to meet increased P demand under N application in a subtropical forest ecosystem. Biol Fertil Soils 54:149–161
Fan YX, Yang LM, Zhong XJ, Yang ZJ, Lin YY, Guo JF, Chen GS, Yang YS (2020) N addition increased microbial residual carbon by altering soil P availability and microbial composition in a subtropical castanopsis forest. Geoderma 375:114470
Fanin N, Fromin N, Buatois B, Hättenschwiler S (2013) An experimental test of the hypothesis of non-homeostatic consumer stoichiometry in a plant litter–microbe system. Ecol Lett 16:764–772
Heuck C, Smolka G, Whalen ED, Frey S, Gundersen P, Moldan F, Fernandez IJ, Spohn M (2018) Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on phosphorus cycling in organic soil horizons of temperate forests. Biogeochemistry 141:167–181
Högberg MN, Yarwood SA, Myrold DD (2014) Fungal but not bacterial soil communities recover after termination of decadal nitrogen additions to boreal forest. Soil Biol Biochem 72:35–43
Huang YP, Wang QQ, Zhang WJ, Zhu P, Xiao Q, Wang CJ, Wu L, Tian YF, Xu MG, Gunina A (2021) Stoichiometric imbalance of soil carbon and nutrients drives microbial community structure under long-term fertilization. Appl Soil Ecol 168:104119
IUSS Working Group, W.R.B, World Reference Base for Soil Resources (2014) International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. World Soil Resources Reports. No. 106, FAO, Rome
Kaiser C, Franklin O, Dieckmann U, Richter A (2014) Microbial community dynamics alleviate stoichiometric constraints during litter decay. Ecol Lett 17:680–690
Kaspari M, Bujan J, Weiser MD, Ning DL, Michaletz ST, He ZL, Enquist BJ, Waide RB, Zhou JH, Turner BL, Wright SJ (2017) Biogeochemistry drives diversity in the prokaryotes fungi and invertebrates of a Panama forest. Ecology 98:2019–2028
Kyaschenko J, Clemmensen KE, Hagenbo A, Karltun E, Lindahl BD (2017) Shift in fungal communities and associated enzyme activities along an age gradient of managed Pinus sylvestris stands. ISME J 11:863–874
Lai XT, Cao LX, Tan HM, Fang S, Huang YL, Zhou SN (2007) Fungal communities from methane hydrate-bearing deep-sea marine sediments in South China Sea. ISME J 1:756–762
Li Y, Niu SL, Yu GR (2016) Aggravated phosphorus limitation on biomass production under increasing nitrogen loading: a meta-analysis. Glob Chang Biol 22:934–943
Li ZY, Qiu XR, Sun Y, Liu SN, Hu HL, Xie JL, Chen G, Xiao YL, Tang Y, Tu LH (2021) C:N:P stoichiometry responses to 10 years of nitrogen addition differ across soil components and plant organs in a subtropical Pleioblastus amarus forest. Sci Total Environ 796:148925
Liu WX, Liu LL, Yang X, Deng MF, Wang Z, Wang PD, Yang S, Li P, Peng ZY, Yang L, Jiang L (2021) Long-term nitrogen input alters plant and soil bacterial but not fungal beta diversity in a semiarid grassland. Glob Chang Biol 27:3939–3950
Lu XK, Vitousek PM, Mao QG, Gilliam FS, Luo YQ, Zhou GY, Zou XM, Bai E, Scanlon TM, Hou EQ, Mo JM (2018) Plant acclimation to long-term high nitrogen deposition in an N-rich tropical forest. PNAS 115:5187–5192
Lu XF, Hou EQ, Guo JY, Gilliam FS, Li JL, Tang SB, Kuang YW (2021) Nitrogen addition stimulates soil aggregation and enhances carbon storage in terrestrial ecosystems of China: a meta-analysis. Glob Chang Biol 27:2780–2792
Lugli LF, Andersen KM, Aragão LEOC, Cordeiro AL, Cunha HFV, Fuchslueger L, Meir P, Mercado LM, Oblitas E, Quesada CA, Rosa JS, Schaap KJ, Valverde-Barrantes O, Hartley IP (2020) Multiple phosphorus acquisition strategies adopted by fine roots in low-fertility soils in Central Amazonia. Plant Soil 450:49–63
Ma HY, Chen GT, Wang Y, Chen HX, Li QH, Tu LH (2021) Effects of nitrogen addition on soil solution chemistry in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. Acta Ecol Sin 23:9354–9363
Magoc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH:fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Manzoni S, Taylor P, Richter A, Porporato A, Ågren GI (2012) Environmental and stoichiometric controls on microbial carbon-use efficiency in soils. New Phytol 196:79–91
Mao QG, Lu XK, Zhou KJ, Chen H, Zhu XM, Mori T, Mo JM (2017) Effects of long-term nitrogen and phosphorus additions on soil acidification in an N-rich tropical forest. Geoderma 285:57–63
Matson PA, McDOWELL WH, Townsend AR, Vitousek PM (1999) The globalization of N deposition: ecosystem consequences in tropical environments. Biogeochemistry 46:67–83
Moorhead DL, Rinkes ZL, Sinsabaugh RL, Weintraub MN (2013) Dynamic relationships between microbial biomass respiration inorganic nutrients and enzyme activities:informing enzyme-based decomposition models. Front Microbiol 4:223
Moorhead DL, Sinsabaugh RL, Hill BH, Weintraub MN (2016) Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C N and P dynamics. Soil Biol Biochem 93:1–7
Mooshammer M, Wanek W, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, Richter A (2014) Stoichiometric imbalances between terrestrial decomposer communities and their resources:mechanisms and implications of microbial adaptations to their resources. Front Microbiol 5:1–10
Morrison EW, Frey SD, Sadowsky JJ, van Diepen LTA, Thomas WK, Pringle A (2016) Chronic nitrogen additions fundamentally restructure the soil fungal community in a temperate forest. Fungal Ecol 23:48–57
Nie YX, Wang M, Zhang W, Ni Z, Hashidoko Y, Shen W (2018) Ammonium nitrogen content is a dominant predictor of bacterial community composition in an acidic forest soil with exogenous nitrogen enrichment. Sci Total Environ 624:407–415
Peng Y, Peng Z, Zeng X, Houx JH (2019a) Effects of nitrogen-phosphorus imbalance on plant biomass production: a global perspective. Plant Soil 436:245–252
Peng Y, Song SY, Li ZY, Li S, Chen GT, Hu HL, Xie JL, Chen G, Xiao YL, Liu L, Tang Y, Tu LH (2019b) Influences of nitrogen addition and aboveground litter-input manipulations on soil respiration and biochemical properties in a subtropical forest. Soil Biol Biochem 142:107694
Peng Y, Li YJ, Song SY, Chen YQ, Chen GT, Tu LH (2022) Nitrogen addition slows litter decomposition accompanied by accelerated manganese release: a five-year experiment in a subtropical evergreen broadleaf forest. Soil Biol Biochem 165:108511
Phoenix GK, Emmett BA, Britton AJ, Caporn SJM, Dise NB, Helliwell R, Jones L, Leake JR, Leith ID, Sheppard LJ, Sowerby A, Pilkington MG, Rowe EC, Ashmore MR, Power SA (2012) Impacts of atmospheric nitrogen deposition: responses of multiple plant and soil parameters across contrasting ecosystems in longterm field experiments. Glob Chang Biol 18:1197–1215
Qu Z, Liu B, Ma Y (2020) The response of the soil bacterial community and function to forest succession caused by forest disease. Funct Ecol 34:2548–2559
Saiya-Cork KR, Sinsabaugh RL, Zak DR (2002) The effects of long-term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1309–1315
Schleuss PM, Widdig M, Heintz-Buschart A, Guhr A, Martin S, Kirkman K, Spohn M (2019) Stoichiometric controls of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling after long-term nitrogen and phosphorus addition in a Mesic grassland in South Africa. Soil Biol Biochem 135:294–303
Schleuss PM, Widdig M, Biederman LA, Borer ET, Crawley MJ, Kirkman KP, Seabloom EW, Wragg PD, Spohn M (2021) Microbial substrate stoichiometry governs nutrient effects on nitrogen cycling in grassland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 155:108168
Sinsabaugh RL, Lauber CL, Weintraub MN, Ahmed B, Allison SD, Crenshaw C, Contosta AR, Cusack D, Frey S, Gallo ME, Gartner TB, Hobbie SE, Holland K, Keeler BL, Powers JS, Stursova M, Takacs-Vesbach C, Waldrop MP, Wallenstein MD et al (2008) Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol Lett 11:1252–1264
Sinsabaugh RL, Hill BH, Shah JJF (2009) Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial or ganic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 462:795–798
Sinsabaugh RL, Manzoni S, Moorhead DL, Richter A (2013) Carbon use efficiency of microbial communities:stoichiometry methodology and modelling. Ecol Lett 16:930–939
Sinsabaugh RL, Turner BL, Talbot JM, Waring BG, Powers JS, Kuske CR, Moorhead DL, Shah JJF (2016) Stoichiometry of microbial carbon use efficiency in soils. Ecol Monogr 86:172–189
Soares M, Rousk J (2019) Microbial growth and carbon use efficiency in soil:links to fungal-bacterial dominance SOC-quality and stoichiometry. Soil Biol Biochem 131:195–205
Spohn M, Chodak M (2015) Microbial respiration per unit biomass increases with carbon-to-nutrient ratios in forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 81:128–133
Stark S, Männistö MK, Eskelinen A (2014) Nutrient availability and pH jointly constrain microbial extracellular enzyme activities in nutrient-poor tundra soils. Plant Soil 383:373–385
Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological stoichiometry: the biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. J Plankton Res 25:1183–1183
Tian J, Dungait JAJ, Lu XK, Yang YF, Hartley IP, Zhang W, Mo JM, Yu GR, Zhou JZ, Kuzyakov Y (2019) Long-term nitrogen addition modifies microbial composition and functions for slow carbon cycling and increased sequestration in tropical forest soil. Glob Chang Biol 25:3267–3281
Treseder KK (2008) Nitrogen additions and microbial biomass: a meta-analysis of ecosystem studies. Ecol Lett 11:1111–1120
Tu LH, Hu TX, Zhang J, Li XW, Hu HL, Liu L, Xiao YL (2013) Nitrogen addition stimulates different components of soil respiration in a subtropical bamboo ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 58:255–264
Turlapati SA, Minocha R, Bhiravarasa PS, Tisa LS, Thomas WK, Minocha SC (2013) Chronic N-amended soils exhibit an altered bacterial community structure in Harvard Forest. MA, USA 83: 478–493
Turner BL, Engelbrecht BMJ (2011) Soil organic phosphorus in lowland tropical rain forests. Biogeochemistry 103:297–315
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuringsoil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Vancov T, Keen B (2009) Amplification of soil fungal community DNA using the ITS86F and ITS4 primers FEMS. Microbiol Lett 296:91–96
Vitousek PM, Porder S, Houlton BZ, Chadwick OA (2010) Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen-phosphorus interactions. Ecol Appl 20:5–15
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wang JQ, Shi XZ, Zheng CY, Suter H, Huang Z (2020) Different responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to nitrogen deposition in a subtropical forest. Sci Total Environ 755:142449
Wang J, Liao LR, Ye ZC, Liu HF, Zhang C, Zhang L, Liu GB, Wang GL (2022) Different bacterial co-occurrence patterns and community assembly between rhizosphere and bulk soils under N addition in the plant–soil system. Plant Soil 471:697–713
Waring BG, Weintraub SRL, Sinsabaugh RL (2014) Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial nutrient acquisition in tropical soils. Biogeochemistry 117:101–113
Wear EK, Wilbanks EG, Nelson CE, Carlson CA (2018) Primer selection impacts specific population abundances but not community dynamics in a monthly time-series 16S rRNA gene amplicon analysis of coastal marine bacterioplankton. Environ Microbiol 20:2709–2726
Weber CF, Vilgalys R, Kuske CR (2013) Changes in fungal community composition in response to elevated atmospheric co2 and nitrogen fertilization varies with soil horizon. Front Microbiol 4:78
Wei SZ, Tie LH, Liao J, Liu X, Huang CD (2020) Nitrogen and phosphorus co-addition stimulates soil respiration in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. Plant Soil 450:171–182
Xiao H, Yang HL, Zhao ML, Monaco TA, Rong YP, Huang D, Song Q, Zhao K, Wang DP (2020) Soil extracellular enzyme activities and the abundance of nitrogen-cycling functional genes responded more to N addition than P addition in an inner Mongolian meadow steppe. Sci Total Environ 759:143541
Xu XF, Thornton PE, Post WM (2013) A global analysis of soil microbial biomass carbon nitrogen and phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystems. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 22:737–749
Yu GR, Jia YL, He NP, Zhu JX, Chen Z, Wang QF, Piao SL, Liu XJ, He HL, Guo XB, Wen Z, Li P, Ding GA, Goulding K (2019) Stabilization of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China over the past decade. Nat Geoence 12:424–429
Yuan XB, Niu DC, Gherardi LA, Liu Y, Wang Y, Elser JJ, Fu H (2019) Linkages of stoichiometric imbalances to soil microbial respiration with increasing nitrogen addition: evidence from a long-term grassland experiment. Soil Biol Biochem 138:107580
Yue K, Fornara DA, Yang WQ, Peng Y, Li ZJ, Wu FZ, Peng CG (2017) Effects of three global change drivers on terrestrial C:N:P stoichiometry: a global synthesis. Glob Chang Biol 23:2450–2463
Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, Keiblinger KM, Mooshammer M, Peñuelas J, Richter A, Sardans J, Wanek W (2015) The application of ecological stoichiometry to plant–microbial–soil organic matter transformations. Ecol Monogr 85:133–155
Zhang TA, Chen HYH, Ruan HH (2018) Global negative effects of nitrogen deposition on soil microbes. ISME J 12:1817–1825
Zhao YZ, Liang CF, Shao S, Chen JH, Qin H, Xu QF (2021) Linkages of litter and soil C:N:P stoichiometry with soil microbial resource limitation and community structure in a subtropical broadleaf forest invaded by Moso bamboo. Plant Soil 465:473–490
Zheng MH, Chen H, Li DJ, Luo YQ, Mo JM (2020) Substrate stoichiometry determines nitrogen fixation throughout succession in southern Chinese forests. Ecol Lett 23:336–347
Zhong ZK, Li WJ, Lu XQ, Gu YQ, Wu SJ, Shen ZY, Han XH, Yang GH, Ren CJ (2020) Adaptive pathways of soil microorganisms to stoichiometric imbalances regulate microbial respiration following afforestation in the loess plateau China. Soil Biol Biochem 151:108048
Zhou ZH, Wang CK, Jin Y (2017) Stoichiometric responses of soil microflora to nutrient additions for two temperate forest soils. Biol Fertil Soils 53:397–406
Zhu ZK, Ge TD, Luo Y, Liu SL, Xu XL, Tong CL, Shibistova O, Guggenberger G, Wu JS (2018) Microbial stoichiometric flexibility regulates rice straw mineralization and its priming effect in paddy soil. Soil Biol Biochem 121:67–76
Zhu XM, Liu M, Kou YP, Liu DY, Liu Q, Zhang ZL, Jiang Z, Yin HJ (2020) Differential effects of N addition on the stoichiometry of microbes and extracellular enzymes in the rhizosphere and bulk soils of an alpine shrubland. Plant Soil 449:285–301
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32071591). The authors would like to express their gratitude to EditSprings (http://www.editsprings.com/) for the expert linguistic services provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jeff R. Powell.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 48546 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, L., Li, Y., Zhong, Q. et al. Adaptation mechanisms of the soil microbial community under stoichiometric imbalances and nutrient-limiting conditions in a subtropical nitrogen-saturated forest. Plant Soil 489, 239–258 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06014-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06014-6