Abstract
Aims
The aims of the current study were to understand the variation in the abundance, diversity and structure of the diazotrophic communities in the rhizosphere soil of these three dominant plant species around Siding Pb–Zn mine.
Methods
Three dominant plant species (Pteris vittata, Miscanthus floridulus and Phragmites australis) were randomly selected, and rhizosphere soils were sampled from the rhizosphere of the plants.
Results
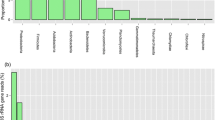
The nifH gene abundance in the rhizosphere soil of Pteris vittata was the highest among the three plant species. Variations in rhizosphere soil diazotrophic communities were mainly due to the changes in soil nutrient contents through plant‒soil system interactions. Diversity and structure of soil diazotrophic communities, including Alphaproteobacteria, Deltaproteobacteria and Cyanobacteria, were strongly influenced by soil heavy metals, ammonium nitrogen, soil moisture and available phosphorus contents. In addition, soil enzymes, especially urease, protease and alkaline phosphatase activities, also contributed to the structure of the diazotrophic communities. Alphaproteobacteria and Cyanobacteria play vital roles in the soil biological nitrogen fixation process. Heavy metal enrichment in mines provides electron donors for diazotrophs to support their activities in harsh environments. Diazotrophs can provide N to support plant growth in mines to help restore heavy metal-containing soil by dominant plants.
Conclusions
Our results showed the variations in diazotrophic community compositions in rhizosphere soil of three dominant plants and their impact on heavy metal accumulation. This study will help to determine the role and importance of soil properties and plant species in the soil biological nitrogen fixation process in highly contaminated mine areas.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Becerra-Castro C, Monterroso C, Prieto-Fernández A, Rodríguez-Lamas L, Loureiro-Viñas M, Acea MJ, Kidd PS (2012) Pseudometallophytes colonising Pb/Zn mine tailings: a description of the plant-microorganism-rhizosphere soil system and isolation of metal-tolerant bacteria. J Hazard Mater 217–218:350–359
Bent E, Németh D, Wagner-Riddle C, Dunfield K (2016) Residue management leading to higher field-scale N2O flux is associated with different soil bacterial nitrifier and denitrifier gene community structures. Appl Soil Ecol 108:288–299
Březinová TD, Vymazal J (2022) Distribution of heavy metals in Phragmites australis growing in constructed treatment wetlands and comparison with natural unpolluted sites. Ecol Eng 175
Canfield DE, Glazer AN, Falkowski PG (2010) The Evolution and Future of Earth’s Nitrogen Cycle. Science 330:192–196
Chandra R, Kumar V (2017) Phytoextraction of heavy metals by potential native plants and their microscopic observation of root growing on stabilised distillery sludge as a prospective tool for in situ phytoremediation of industrial waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:2605–2619
Che RX, Deng YC, Wang F, Wang WJ, Xu ZH, Hao YB, Xue K, Zhang B, Tang L, Zhou HK, Cui XY (2018) Autotrophic and symbiotic diazotrophs dominate nitrogen-fixing communities in Tibetan grassland soils. Sci Total Environ 639:997–1006
Chen J, Moorhead DL (2022) Progressively decreased nitrogen-stimulation of soil phosphatase activity with long-term nitrogen addition. Appl Soil Ecol 169:104213
Chen WB, Peng SL (2020) Land-use legacy effects shape microbial contribution to N2O production in three tropical forests. Geoderma 358:113979
Chen Y, Jiang Y, Huang H, Mou L, Ru J, Zhao J, Xiao S (2018) Long-term and high-concentration heavy-metal contamination strongly influences the microbiome and functional genes in Yellow River sediments. Sci Total Environ 637–638:1400–1412
Chen J, Shen W, Xu H, Li Y, Luo T (2019a) The composition of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms correlates with soil nitrogen content during reforestation: A comparison between legume and non-legume plantations. Front Microbiol 10:508
Chen J, Wang PF, Wang C, Wang X, Miao LZ, Liu S, Yuan QS (2019b) Dam construction alters function and community composition of diazotrophs in riparian soils across an environmental gradient. Soil Biol Biochem 132:14–23
Coelho MR, de Vos M, Carneiro NP, Marriel IE, Paiva E, Seldin L (2008) Diversity of nifH gene pools in the rhizosphere of two cultivars of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) treated with contrasting levels of nitrogen fertilizer. FEMS Microbiol Lett 279:15–22
Coelho MRR, Marriel IE, Jenkins SN, Lanyon CV, Seldin L, O’Donnell AG (2009) Molecular detection and quantification of nifH gene sequences in the rhizosphere of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) sown with two levels of nitrogen fertilizer. Appl Soil Ecol 42:48–53
Cui X, Guo W, Chen X (2010) Enrichment characteristics of heavy metals by dominant plants in Siding Lead-zine Abandoned Mine area. Metal Mine 406:180–182 (in Chinese)
Dennis PG, Miller AJ, Hirsch PR (2010) Are root exudates more important than other sources of rhizodeposits in structuring rhizosphere bacterial communities? FEMS Microbiol Ecol 72:313–327
Drewniak L, Sklodowska A (2013) Arsenic-transforming microbes and their role in biomining processes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:7728–7739
Ge YY, Wang QL, Wang L, Liu WX, Liu XY, Huang YJ, Christie P (2018) Response of soil enzymes and microbial communities to root extracts of the alien Alternanthera philoxeroides. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64:708–717
Geng H, Wang F, Yan C, Ma S, Zhang Y, Qin Q, Tian Z, Liu R, Chen H, Zhou B, Yuan R (2022) Rhizosphere microbial community composition and survival strategies in oligotrophic and metal(loid) contaminated iron tailings areas. J Hazard Mater 436:129045
Gu Y, Wang P, Kong CH (2009) Urease, invertase, dehydrogenase and polyphenoloxidase activities in paddy soil influenced by allelopathic rice variety. Eur J Soil Biol 45:436–441
Guo H, Nasir M, Lv J, Dai Y, Gao J (2017) Understanding the variation of microbial community in heavy metals contaminated soil using high throughput sequencing. Ecotox Environ Saf 144:300–306
Haiming T, Xiaoping X, Chao L, Xiaochen P, Kaikai C, Weiyan L, Ke W (2020) Microbial carbon source utilization in rice rhizosphere and nonrhizosphere soils with short-term manure N input rate in paddy field. Sci Rep 10:6487
Hao J, Feng Y, Wang X, Yu Q, Zhang F, Yang G, Ren G, Han X, Wang X, Ren C (2022) Soil microbial nitrogen-cycling gene abundances in response to crop diversification: A meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 838:156621
Hassani MA, Duran P, Hacquard S (2018) Microbial interactions within the plant holobiont. Microbiome 6:58
Hou S, Ai C, Zhou W, Liang G, He P (2018) Structure and assembly cues for rhizospheric nirK- and nirS-type denitrifier communities in long-term fertilized soils. Soil Biol Biochem 119:32–40
Hu T, Chen A, Jiang Y, Sun C, Luo S, Shao J (2022) Application of a newly recorded diazotrophic cyanobacterium in acidified and Cd contaminated paddy soil: Promotes rice yield and decreases Cd accumulation. Sci Total Environ 814:152630
Khan S, Hesham AE-L, Qiao M, Rehman S, He J-Z (2010) Effects of Cd and Pb on soil microbial community structure and activities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:288–296
Khan AR, Ullah I, Waqas M, Park G-S, Khan AL, Hong S-J, Ullah R, Jung BK, Park CE, Ur-Rehman S, Lee I-J, Shin J-H (2017) Host plant growth promotion and cadmium detoxification in Solanum nigrum, mediated by endophytic fungi. Ecotox Environ Saf 136:180–188
Kim H, Lee DK, Voigt TB, Tian G, Yannarell AC (2022) Agricultural practices of perennial energy crops affect nitrogen cycling microbial communities. Appl Soil Ecol 172:104366
Kohda YH, Endo G, Kitajima N, Sugawara K, Chien MF, Inoue C, Miyauchi K (2022) Arsenic uptake by Pteris vittata in a subarctic arsenic-contaminated agricultural field in Japan: An 8-year study. Sci Total Environ 831:154830
Komárek M, Vaněk A, Ettler V (2013) Chemical stabilization of metals and arsenic in contaminated soils using oxides – A review. Environ Pollut 172:9–22
Kuypers MMM, Marchant HK, Kartal B (2018) The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:263
Lee JK, Park HJ, Cha SJ, Kwon SJ, Park JH (2021) Effect of pyroligneous acid on soil urease, amidase, and nitrogen use efficiency by Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris var. Pekinensis). Environ Pollut 291 118132
Li D, Voigt TB, Kent AD (2015) Plant and soil effects on bacterial communities associated with Miscanthus × giganteus rhizosphere and rhizomes. GCB Bioenergy 8:183–193
Li Y, Liu K, Zhu J, Jiang Y, Huang Y, Zhou Z, Chen C, Yu F (2019a) Manganese accumulation and plant physiology behavior of Camellia oleifera in response to different levels of nitrogen fertilization. Ecotox Environ Saf 184:109603
Li Y, Wu Z, Dong X, Jia Z, Sun Q (2019b) Dependency of biological nitrogen fixation on organic carbon in acidic mine tailings under light and dark conditions. Appl Soil Ecol 140:18–25
Li Y, Lin J, Huang Y, Yao Y, Wang X, Liu C, Liang Y, Liu K, Yu F (2020) Bioaugmentation-assisted phytoremediation of manganese and cadmium co-contaminated soil by Polygonaceae plants (Polygonum hydropiper L. and Polygonum lapathifolium L.) and Enterobacter sp. FM-1. Plant Soil 448:439–453
Li Y, Zhang HC, Liu Y, Wei JT, Wang C, Liang Y, Liu KH, Yu FM (2022) Characteristics on the community structure and abundance of diazotrophs from the soil profile in the Siding mine area. China Environ Sci 42:1819–1828 (in Chinese)
Lin H, Liu C, Li B, Dong Y (2021) Trifolium repens L. regulated phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by promoting soil enzyme activities and beneficial rhizosphere associated microorganisms. J Hazard Mater 402 123829
Liu WQ, Song YS, Wang B, Li JT, Shu WS (2012) Nitrogen fixation in biotic crusts and vascular plant communities on a copper mine tailings. Eur J Soil Biol 50:15–20
Lu C, Wang Y, Yang J (2010) Soil heavy metal pollution and dominant plants selection in Pb-Zn Mining areas of Guangxi. Chinese J Soil Sci 41:1471–1475 (in Chinese)
Ma X, Zarebanadkouki M, Kuzyakov Y, Blagodatskaya E, Pausch J, Razavi BS (2018) Spatial patterns of enzyme activities in the rhizosphere: Effects of root hairs and root radius. Soil Biol Biochem 118:69–78
Maarastawi SA, Frindte K, Bodelier PLE, Knief C (2019) Rice straw serves as additional carbon source for rhizosphere microorganisms and reduces root exudate consumption. Soil Biol Biochem 135:235–238
Mager DM, Thomas AD (2011) Extracellular polysaccharides from cyanobacterial soil crusts: A review of their role in dryland soil processes. J Arid Environ 75:91–97
Morugan-Coronado A, Garcia-Orenes F, McMillan M, Pereg L (2019) The effect of moisture on soil microbial properties and nitrogen cyclers in Mediterranean sweet orange orchards under organic and inorganic fertilization. Sci Total Environ 655:158–167
Navarro-Noya YE, Hernández-Mendoza E, Morales-Jiménez J, Jan-Roblero J, Martínez-Romero E, Hernández-Rodríguez C (2012) Isolation and characterization of nitrogen fixing heterotrophic bacteria from the rhizosphere of pioneer plants growing on mine tailings. Appl Soil Ecol 62:52–60
Olanrewaju OS, Ayangbenro AS, Glick BR, Babalola OO (2019) Plant health: feedback effect of root exudates-rhizobiome interactions. Appl Microbiol Biot 103:1155–1166
Olsen SR (1954) Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate. United States Department Of Agriculture, Washington
Qian F, Huang X, Su X, Bao Y (2022) Responses of microbial communities and metabolic profiles to the rhizosphere of Tamarix ramosissima in soils contaminated by multiple heavy metals. J Hazard Mater 438:129469
Quintela-Sabaris C, Auber E, Sumail S, Masfaraud JF, Faucon MP, Watteau F, Saad RF, van der Ent A, Repin R, Sugau J, Nilus R, Echevarria G, Leguedois S (2019) Recovery of ultramafic soil functions and plant communities along an age-gradient of the actinorhizal tree Ceuthostoma terminale (Casuarinaceae) in Sabah (Malaysia). Plant Soil 440:201–218
Rajkumar M, Sandhya S, Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2012) Perspectives of plant-associated microbes in heavy metal phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 30:1562–1574
Rathika R, Khalifa AYZ, Srinivasan P, Praburaman L, Kamala-Kannan S, Selvankumar T, Kim W, Govarthanan M (2020) Effect of citric acid and vermi-wash on growth and metal accumulation of Sorghum bicolor cultivated in lead and nickel contaminated soil. Chemosphere 243:125327
Razavi BS, Zarebanadkouki M, Blagodatskaya E, Kuzyakov Y (2016) Rhizosphere shape of lentil and maize: Spatial distribution of enzyme activities. Soil Biol Biochem 96:229–237
Saarathandra SU, Perrott KW, Upsdell MP (1984) Microbiological and biochemical characteristics of a range New Zealand soils under estabilised pasture. Soil Biol Biochem 16:177–183
Samaddar S, Chatterjee P, Truu J, Anandham R, Kim S, Sa T (2019) Long-term phosphorus limitation changes the bacterial community structure and functioning in paddy soils. Appl Soil Ecol 134:111–115
Sarria Carabalí MM, García-Oliva F, Cortés Páez LE, López-Lozano NE (2020) Effect of cadmium contamination on the rhizosphere bacterial diversity of Echinocactus platyacanthus. Rhizosphere 13
Schlatter DC, Reardon CL, Johnson-Maynard J, Brooks E, Kahl K, Norby J, Huggins D, Paulitz TC (2019) Mining the Drilosphere: Bacterial Communities and Denitrifier Abundance in a No-Till Wheat Cropping System. Front Microbiol 10:1339
Shah V, Daverey A (2020) Phytoremediation: A multidisciplinary approach to clean up heavy metal contaminated soil. Environ Technol Inno 18:100774
Shi L, Zhang P, He Y, Zeng F, Xu J, He L (2021) Enantioselective effects of cyflumetofen on microbial community and related nitrogen cycle gene function in acid-soil. Sci Total Environ 771:144831
Shu X, Zhang K, Zhang Q, Wang W (2019) Ecophysiological responses of Jatropha curcas L. seedlings to simulated acid rain under different soil types. Ecotox Environ Saf 185: 109705
Song Y, Li X, Yao S, Yang X, Jiang X (2020) Correlations between soil metabolomics and bacterial community structures in the pepper rhizosphere under plastic greenhouse cultivation. Sci Total Environ 728:138439
Sun X, Kong T, Haggblom MM, Kolton M, Li F, Dong Y, Huang Y, Li B, Sun W (2020) Chemolithoautotropic Diazotrophy Dominates the Nitrogen Fixation Process in Mine Tailings. Environ Sci Technol 54:6082–6093
Ullah A, Mushtaq H, Ali H, Munis MFH, Javed MT, Chaudhary HJ (2015) Diazotrophs-assisted phytoremediation of heavy metals: a novel approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:2505–2514
Wang C, Zheng M, Song W, Wen S, Wang B, Zhu C, Shen R (2017) Impact of 25 years of inorganic fertilization on diazotrophic abundance and community structure in an acidic soil in southern China. Soil Biol Biochem 113:240–249
Wang F, Kertesz MA, Feng G (2019a) Phosphorus forms affect the hyphosphere bacterial community involved in soil organic phosphorus turnover. Mycorrhiza 29:351–362
Wang S, Liu W, Zhao S, Wang C, Zhuang L, Liu L, Wang W, Lu Y, Li F, Zhu G (2019b) Denitrification is the main microbial N loss pathway on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau above an elevation of 5000 m. Sci Total Environ 696:133852
Wang X, Liu B, Ma J, Zhang Y, Hu T, Zhang H, Feng Y, Pan H, Xu Z, Liu G, Lin X, Zhu J, Bei Q, Xie Z (2019c) Soil aluminum oxides determine biological nitrogen fixation and diazotrophic communities across major types of paddy soils in China. Soil Biol Biochem 131:81–89
Wang J, Li Q, Shen C, Yang F, Wang J, Ge Y (2020b) Significant dose effects of fertilizers on soil diazotrophic diversity, community composition, and assembly processes in a long-term paddy field fertilization experiment. Land Degrad Dev 32:420–429
Wang C, Wei M, Wang S, Wu B, Du D (2020a) Cadmium influences the litter decomposition of Solidago canadensis L. and soil N-fixing bacterial communities. Chemosphere 246: 125717
Wang L, Pang X, Li N, Qi K, Huang J, Yin C (2020c) Effects of vegetation type, fine and coarse roots on soil microbial communities and enzyme activities in eastern Tibetan plateau. Catena 194
Wang G, Jin Z, Wang X, George TS, Feng G, Zhang L (2022a) Simulated root exudates stimulate the abundance of Saccharimonadales to improve the alkaline phosphatase activity in maize rhizosphere. Appl Soil Ecol 170
Wang L, Zhang H, Wang J, Wang J, Zhang Y (2022b) Long-term fertilization with high nitrogen rates decreased diversity and stability of diazotroph communities in soils of sweet potato. Appl Soil Ecol 170
Watanabe K, Hayano K (1995) Seasonal variation of soil protease activities and their relation to proteolytic bacteria and Bacillus spp in paddy field soil. Soil Biol Biochem 27:197–203
Weis JS, Weis P (2004) Metal uptake, transport and release by wetland plants: implications for phytoremediation and restoration. Environ Int 30:685–700
Wise BR, Roane TM, Mosier AC (2020) Community Composition of Nitrite Reductase Gene Sequences in an Acid Mine Drainage Environment. Microbial Ecol 79:562–575
Wu LS, Feng S, Nie YY, Zhou JH, Yang ZR, Zhang J (2015) Soil cellulase activity and fungal community responses to wetland degradation in the Zoige Plateau, China. J Mount Sci 12:471–482
Wu W, Dong C, Wu J, Liu X, Wu Y, Chen X, Yu S (2017) Ecological effects of soil properties and metal concentrations on the composition and diversity of microbial communities associated with land use patterns in an electronic waste recycling region. Sci Total Environ 601:57–65
Wu B, Luo S, Luo H, Huang H, Xu F, Feng S, Xu H (2022) Improved phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by Miscanthus floridulus under a varied rhizosphere ecological characteristic. Sci Total Environ 808:151995
Xiao E, Ning A, Xiao T, Sun W, Qiu Y, Zhang Y, Chen J, Gou Z, Chen Y (2019) Variation in rhizosphere microbiota correlates with edaphic factor in an abandoned antimony tailing dump. Environ Pollut 253:141–151
Xu L, Han Y, Yi M, Yi H, Guo E, Zhang A (2019) Shift of millet rhizosphere bacterial community during the maturation of parent soil revealed by 16S rDNA high-throughput sequencing. Appl Soil Ecol 135:157–165
Xue S, Wang J, Wu C, Li S, Hartley W, Wu H, Zhu F, Cui M (2018) Physiological response of Polygonum perfoliatum L. following exposure to elevated manganese concentrations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:132–140
Yang CL, Sun TH, He WX, Zhou QX, Chen S (2007) Single and joint effects of pesticides and mercury on soil urease. J Environ Sci 19:210–216
Yang Y, Ding J, Chi Y, Yuan J (2020) Characterization of bacterial communities associated with the exotic and heavy metal tolerant wetland plant Spartina alterniflora. Sci Rep 10:17985
Yang L, Cao XY, Chen XY, Deng QH, Wan LL, Li XW, Zhou YY, Song CL (2021) Community composition and functional genes explain different ecological roles of heterotrophic bacteria attached to two bloom-forming cyanobacterial genera. Sci Total Environ 758:143850
Yang Z, Chen X, Hou J, Liu H, Tan W (2022) Soil texture and pH exhibit important effects on biological nitrogen fixation in paddy soil. Appl Soil Ecol 178
Yin R, Luo Y, Li J, Zhu Y (2008) Evaluation of the Potential Ecological Risk of Heavy Metal Pollution in Soil and Bioaccumulation Characteristics of Dominant Plants in Siding Pb-Zn Mine. J Agro-Environ Sci 27:2158–2165 (in Chinese)
Yu F, Li C, Dai C, Liu K, Li Y (2020a) Phosphate: Coupling the functions of fertilization and passivation in phytoremediation of manganese-contaminated soil by Polygonum pubescens blume. Chemosphere 260:127651
Yu F, Lin J, Xie D, Yao Y, Wang X, Huang Y, Xin M, Yang F, Liu K, Li Y (2020b) Soil properties and heavy metal concentrations affect the composition and diversity of the diazotrophs communities associated with different land use types in a mining area. Appl Soil Ecol 155
Yu G, Jiang P, Fu X, Liu J, Sunahara GI, Chen Z, Xiao H, Lin F, Wang X (2020c) Phytoextraction of cadmium-contaminated soil by Celosia argentea Linn.: A long-term field study. Environ Pollut 266: 115408
Yuan J, Zhao J, Wen T, Zhao M, Li R, Goossens P, Huang Q, Bai Y, Vivanco JM, Kowalchuk GA, Berendsen RL, Shen Q (2018) Root exudates drive the soil-borne legacy of aboveground pathogen infection. Microbiome 6:156
Zeng P, Guo Z, Xiao X, Peng C, Feng W, Xin L, Xu Z (2019) Phytoextraction potential of Pteris vittata L. co-planted with woody species for As, Cd, Pb and Zn in contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 650:594–603
Zhan J, Sun Q (2011) Diversity of free-living nitrogen-fixing microorganisms in wastelands of copper mine tailings during the process of natural ecological restoration. J Environ Sci 23:476–487
Zhan J, Sun Q (2012) Diversity of free-living nitrogen-fixing microorganisms in the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere of pioneer plants growing on wastelands of copper mine tailings. Microbiol Res 167:157–165
Zhang Q, Jia X, Li T, Shao M, Yu Q, Wei X (2021) Decreased soil total phosphorus following artificial plantation in the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 385:114882
Zhao X, Huang J, Lu J, Sun Y (2019) Study on the influence of soil microbial community on the long-term heavy metal pollution of different land use types and depth layers in mine. Ecotox Environ Saf 170:218–226
Zhou T, Wang C, Zhou Z (2020) Impacts of forest thinning on soil microbial community structure and extracellular enzyme activities: A global meta-analysis. Soil Biol Biochem 149:107915
Acknowledgements
This paper is sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 41967019, 41907096), Guangxi Key Research and Development Program (AB21220057), Research Funds of The Guangxi Key Laboratory of Landscape Resources Conservation and Sustainable Utilization in Lijiang River Basin, Guangxi Normal University (grant number LRCSU21Z0210, LRCSU21Z0211) and Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (grant number 2021GXNSFAA220024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL: Writing-original draft, Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition. XC: Investigation, Data curation. CT: Software, Validation, Data curation. MZ: Software, Investigation. SL: Data curation, Formal analysis. QL: Software, Data curation. KL: Writing- review & editing. JM: Funding acquisition. ST: Writing-original draft, Investigation, Data curation. FY: Supervision, Writing-review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Juan Barcelo.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Chen, X., Tang, C. et al. Variations on the diazotrophic community in the rhizosphere soil of three dominant plant species in a lead–zinc mine area. Plant Soil 489, 155–175 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06003-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06003-9