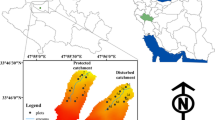
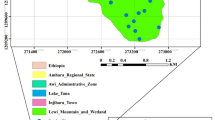
Abstract
Aims
Shelter forest communities in the Yellow River Delta (YRD) have been disturbed, withering, or even dying, showing ecosystem degradation. It is challenging to systematically analyze the relationship between forest dynamics and factors since multiple simultaneous drivers of degradation may interact and have confounding effects in different phenophases.
Methods
The vegetation indexes (VI), groundwater, soil water content (SWC), and electrical conductivity (EC) dynamics of the 0–260 cm soil layers were investigated in 3 health levels of shelter forests from May to October 2015, as well as the root distribution and topography. The Geodetector model was used to detect the factors affecting the forests in different phenophases.
Results
The kernel normalized difference vegetation index (kNDVI), normalized difference infrared index (NDII), and leaf area index (LAI) can monitor the growing season of shelter forests. SWC in the 60–220 cm soil layers had better explanatory power for NDII (\(\overline{Q }\)=0.74) and kNDVI (\(\overline{Q }\)=0.76) in the leaf expansion, full leaf and discoloration periods. LAI was sensitive to SWC in the 60–180 cm soil layers (\(\overline{Q }\)=0.85) during the fruit development and ripening period. The interaction of topography, soil texture, and groundwater influenced the dynamics and distribution of SWC (\(\overline{Q }\)=0.40–0.98) and EC (\(\overline{Q }\)=0.31–0.90).
Conclusions
SWC was the leading cause of degradation of shelter forests in the YRD during the growing season, and EC synergistically enhanced forest degradation with SWC in leaf expansion and discoloration periods. Differences in topography, soil texture and groundwater contribute to the different distribution and dynamics of SWC and EC.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrends A, Bulling M, Platts P et al (2021) Detecting and predicting forest degradation: a comparison of ground surveys and remote sensing in Tanzanian forests. Plants People Planet 3:268–281. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppp3.10189
Barbato D, Benocci A, Manganelli G (2020) Does forest age affect soil biodiversity? Case study of land snails in Mediterranean secondary forests. For Ecol Manage 455:117693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2019.117693
Behdad A, Mohsenzadeh S, Azizi M (2021) Growth, leaf gas exchange and physiological parameters of two Glycyrrhiza glabra L. populations subjected to salt stress condition. Rhizosphere 17:100319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2021.100319
Brooks R, Corey A (1964) Hydraulic properties of porous media and their relationship to drainage design. Trans ASAE 7:26–28
Bryk M, Kolodziej B (2019) Monitoring heterogeneous urban and rural area using Normalised Difference Infrared Index - a case study from SE Poland. Eur J Remote Sens 52:308–321. https://doi.org/10.1080/22797254.2019.1604080
Bustamante M, Roitman I, Aide T et al (2016) Toward an integrated monitoring framework to assess the effects of tropical forest degradation and recovery on carbon stocks and biodiversity. Glob Chang Biol 22:92–109. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13087
Buzmakov S, Khotyanovskaya Y (2020) Degradation and pollution of lands under the influence of oil resources exploitation. Appl Geochem 113:104443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.104443
Cabrera V, Stavast L, Baker T et al (2009) Soil and runoff response to dairy manure application on New Mexico rangeland. Agric Ecosyst Environ 131:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2009.01.022
Camps-Valls G, Campos-Taberner M, Moreno-Martinez A et al (2021) A unified vegetation index for quantifying the terrestrial biosphere. Sci Adv 7:eabc7447. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abc7447
Dai X, Xie Y, Simmons C et al (2021) Understanding topography-driven groundwater flow using fully-coupled surface-water and groundwater modeling. J Hydrol 594:125950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125950
Davies K, Chesson P, Harrison S et al (2005) Spatial heterogeneity explains the scale dependence of the native-exotic diversity relationship. Ecology 86:1602–1610. https://doi.org/10.1890/04-1196
De Reu J, Bourgeois J, Bats M et al (2013) Application of the topographic position index to heterogeneous landscapes. Geomorphology 186:39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.12.015
Du J, Jin M, Ouyang Z, Liu Y (2008) Characteristics of soil salinity profiles and relationship between salinity and soil particle composition in Yanqi Basin of Xinjiang, China. Earth Sci 33:131–136. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2008.01.018
Du X, He W, Wang Z et al (2021) Raised bed planting reduces waterlogging and increases yield in wheat following rice. Field Crop Res 265:108119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108119
Du Z, Liu F, Ma B et al (2014) Root distribution and fine root growth in mixed plantation of Robinia pseudoacacia and Fraxinus velutina in coastal Saline-Alkali area. Sci Silvae Sinicae 50:10–15
Dyderski M, Paź S, Frelich L, Jagodziński A (2018) How much does climate change threaten European forest tree species distributions? Glob Chang Biol 24:1150–1163. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13925
Fan X, Pedroli B, Liu G et al (2012) Soil salinity development in the yellow river delta in relation to groundwater dynamics. Land Degrad Dev 23:175–189. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.1071
Findlay A (2021) Climate mitigation through Indigenous forest management. Nat Clim Chang 11:371–373. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-021-01042-5
Flynn D, Wolkovich E (2018) Temperature and photoperiod drive spring phenology across all species in a temperate forest community. New Phytol 219:1353–1362. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15232
Gao S, Zheng Z, Wang Y et al (2018) Drought and grazing drive the retrogressive succession by changing the plant–plant interaction of the main species in Inner Mongolia Steppe. Ecol Evol 8:11954–11963. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.4652
Gitelson A, Merzlyak M (1998) Remote sensing of chlorophyll concentration in higher plant leaves. Adv Space Res 22:689–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1177(97)01133-2
Gressler E, Jochner S, Capdevielle-Vargas RM et al (2015) Vertical variation in autumn leaf phenology of Fagus sylvatica L. in southern Germany. Agric for Meteorol 201:176–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2014.10.013
Grossiord C, Buckley TN, Cernusak LA et al (2020) Plant responses to rising vapor pressure deficit. New Phytol 226:1550–1566. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16485
Huang S, Kong J (2016) Assessing Land Degradation Dynamics and Distinguishing Human-Induced Changes from Climate Factors in the Three-North Shelter Forest Region of China. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inf 5:158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi5090158
Huete A, Didan K, Miura T et al (2002) Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens Environ 83:195–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00096-2
Jackson T, Chen D, Cosh M et al (2004) Vegetation water content mapping using Landsat data derived normalized difference water index for corn and soybeans. Remote Sens Environ 92:475–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.10.021
Jancewicz K, Migoń P, Kasprzak M (2019) Connectivity patterns in contrasting types of tableland sandstone relief revealed by Topographic Wetness Index. Sci Total Environ 656:1046–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.467
Jenness J, Brost B, Beier P (2011) Land Facet Corridor Designer: extension for ArcGIS. Jenness Enterprises
Kimball J (2014) Vegetation Phenology. In: Njoku EG (ed) Encyclopedia of Remote Sensing. Springer, New York, pp 886–890
Klisz M, Puchałka R, Netsvetov M et al (2021) Variability in climate-growth reaction of Robinia pseudoacacia in Eastern Europe indicates potential for acclimatisation to future climate. For Ecol Manage 492:119194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119194
Laird D, Fleming P, Davis D et al (2010) Impact of biochar amendments on the quality of a typical Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 158:443–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.05.013
Li X, Han G, Eller F et al (2021a) Acclimation of coastal wetland vegetation to salinization results in the asymmetric response of soil respiration along an experimental precipitation gradient. Agric For Meteorol 310:108626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108626
Li X, Shao X, Li R et al (2021b) Optimization of tobacco water-fertilizer coupling scheme under effective microorganisms biochar-based fertilizer application condition. Agron J 113:1653–1663. https://doi.org/10.1002/agj2.20568
Li X, Xia J, Zhao X, Chen Y (2019) Effects of planting Tamarix chinensis on shallow soil water and salt content under different groundwater depths in the Yellow River Delta. Geoderma 335:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.08.017
Liu J, Li S, Yang X et al (2022) Effects of soil drought and vapour pressure deficit (VPD) on water use efficiency of tomato plants with contrasting endogenous ABA levels. Sci Hortic 295:110797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110797
Liu Z, Jia G, Yu X (2020) Variation of water uptake in degradation agroforestry shelterbelts on the North China Plain. Agr Ecosyst Environ 287:106697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2019.106697
Mantovani D, Veste M, Böhm C et al (2015) Spatial and temporal variation of drought impact on black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) water status and growth. iForest 8:743. https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor1299-008
Mao P, Mu H, Cao B et al (2016) Dynamic characteristics of soil properties in a Robinia pseudoacacia vegetation and coastal eco-restoration. Ecol Eng 92:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.03.037
Mao P, Tang Q, Cao B et al (2017) Eco-physiological adaptability in mixtures of Robinia pseudoacacia and Fraxinus velutina and coastal eco-engineering. Ecol Eng 106:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.05.021
Matsushita B, Xu M, Onda Y et al (2010) Detecting forest degradation in Kochi, Japan: ground-based measurements versus satellite (Terra/ASTER) remote sensing. Hydrol Processes 24:588–595. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7553
Nadal-Sala D, Hartig F, Gracia C, Sabaté S (2019) Global warming likely to enhance black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) growth in a Mediterranean riparian forest. For Ecol Manage 449:117448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2019.117448
Nguyen L, Osanai Y, Anderson I et al (2018) Impacts of waterlogging on soil nitrification and ammonia-oxidizing communities in farming system. Plant Soil 426:299–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3584-y
Nicolai V (2005) The Invasive Leaf Miner Phyllonorycter robiniella Feeding on Black Locust, Robinia pseudoacacia, in Central Europe (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae). Entomol Gen 28:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1127/entom.gen/28/2005/193
Paavilainen E, Päivänen J (1995) Forest Drainage. In: Paavilainen E, Päivänen J (eds) Peatland Forestry: Ecology and Principles. Springer, Berlin, pp 103–124
Qi S, Liu H (2017) Natural and anthropogenic hazards in the Yellow River Delta, China. Nat Hazards 85:1907–1911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2638-9
Reichardt S, Piepho H-P, Stintzi A, Schaller A (2020) Peptide signaling for drought-induced tomato flower drop. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaz5641
Rocha-Santos L, Pessoa M, Cassano C et al (2016) The shrinkage of a forest: landscape-scale deforestation leading to overall changes in local forest structure. Biol Conserv 196:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2016.01.028
Rouse J, Haas R, Schell J, Deering D (1974) Monitoring vegetation systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. NASA, pp 309–317
Rousseeuw P (1987) Silhouettes: a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J Comput Appl Math 20:53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-0427(87)90125-7
Roy D, Kovalskyy V, Zhang H et al (2016) Characterization of Landsat-7 to Landsat-8 reflective wavelength and normalized difference vegetation index continuity. Remote Sens Environ 185:57–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2015.12.024
Schaap M, Leij F, van Genuchten M (2001) ROSETTA: a computer program for estimating soil hydraulic parameters with hierarchical pedotransfer functions. J Hydrol 251:163–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00466-8
Schomaker M, Zarnoch S, Bechtold W et al (2007) Crown-condition classification: a guide to data collection and analysis. Gen Tech Rep SRS-102: US Department of Agriculture, Forest Services
Shi Z, Fang N, Wu F et al (2012) Soil erosion processes and sediment sorting associated with transport mechanisms on steep slopes. J Hydrol 454–455:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.06.004
Sun L, Chang X, Yu X et al (2019) Precipitation and soil water thresholds associated with drought-induced mortality of farmland shelter forests in a semi-arid area. Agric Ecosyst Environ 284:106595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2019.106595
Sun S, He C, Qiu L et al (2018) Stable isotope analysis reveals prolonged drought stress in poplar plantation mortality of the Three-North Shelter Forest in Northern China. Agric For Meteorol 252:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.12.264
van Genuchten M (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:892–898. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
Wallace R, Painter R (2002) Phenological patterns in a southern Amazonian tropical forest: implications for sustainable management. For Ecol Manage 160:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(00)00723-4
Wang B, Tian C, Liang Y (2021) Mixed effects of landscape structure, tree diversity and stand’s relative position on insect and pathogen damage in riparian poplar forests. For Ecol Manage 479:118555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2020.118555
Wang H, Pu R, Zhu Q et al (2015) Mapping health levels of Robinia pseudoacacia forests in the Yellow River delta, China, using IKONOS and Landsat 8 OLI imagery. Int J Remote Sens 36:1114–1135. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2015.1007253
Wang J, Haining R, Cao Z (2010a) Sample surveying to estimate the mean of a heterogeneous surface: reducing the error variance through zoning. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 24:523–543. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810902873512
Wang J, Li X, Christakos G et al (2010b) Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 24:107–127. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810802443457
Wang J, Xu C (2017) Geodetector: principle and prospective. Acta Geogr Sin 72:116–134. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlxb201701010
Wang J, Zhang T, Fu B (2016) A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol Indic 67:250–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.02.052
Wang J, Fu B, Lu N, Zhang L (2017) Seasonal variation in water uptake patterns of three plant species based on stable isotopes in the semi-arid Loess Plateau. Sci Total Environ 609:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.133
Williams A, Allen C, Macalady A et al (2013) Temperature as a potent driver of regional forest drought stress and tree mortality. Nat Clim Chang 3:292–297. https://doi.org/10.1038/NCLIMATE1693
Wilson M, O’Connell B, Brown C et al (2007) Multiscale Terrain Analysis of Multibeam Bathymetry Data for Habitat Mapping on the Continental Slope. Mar Geod 30:3–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490410701295962
Wu L, He D, Ji Z et al (2017) Protection efficiency assessment and quality of coastal shelterbelt for Dongshan Island at the coastal section scale. J for Res 28:577–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-016-0325-z
Xia J, Ren R, Chen Y et al (2020) Multifractal characteristics of soil particle distribution under different vegetation types in the Yellow River Delta chenier of China. Geoderma 368:114311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114311
Xie T, Liu X, Sun T (2011) The effects of groundwater table and flood irrigation strategies on soil water and salt dynamics and reed water use in the Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol Model 222:241–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2010.01.012
Xu M, Jian J, Wang J et al (2021) Response of root nutrient resorption strategies to rhizosphere soil microbial nutrient utilization along Robinia pseudoacacia plantation chronosequence. For Ecol Manage 489:119053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119053
Yando E, Sloey T, Dahdouh-Guebas F et al (2021) Conceptualizing ecosystem degradation using mangrove forests as a model system. Biol Conserv 263:109355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2021.109355
Yang H, Xia J, Cui Q et al (2021) Effects of different Tamarix chinensis-grass patterns on the soil quality of coastal saline soil in the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci Total Environ 772:145501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145501
Yang J, Feng Z, Luo X, Chen Y (2010) Numerically quantifying the relative importance of topography and buoyancy in driving groundwater flow. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci 53:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-009-0185-x
Ye Q, Liu G, Tian G et al (2004a) Geospatial-temporal analysis of land-use changes in the Yellow River Delta during the last 40 years. Sci China Ser D 47:1008–1024. https://doi.org/10.1360/03yd0151
Ye Q, Tian G, Liu G et al (2004b) Tupu methods of spatial-temporal pattern on land use change. J Geogr Sci 14:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02837528
Zhang Y, Liu G, Dong H, Li C (2021) Waterlogging stress in cotton: damage, adaptability, alleviation strategies, and mechanisms. Crop J 9:257–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2020.08.005
Zhao Y, Wang L (2018) Plant water use strategy in response to spatial and temporal variation in precipitation patterns in China: a stable isotope analysis. Forests 9:123. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9030123
Zhao X, Guo Q, Su Y, Xue B (2016) Improved progressive TIN densification filtering algorithm for airborne LiDAR data in forested areas. ISPRS-J Photogramm Remote Sens 117:79–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2016.03.016
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers 41471419 and 31971579). Author Hong Wang has received research support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Janusz J. Zwiazek.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Wang, H., Qin, S. et al. Yellow river delta shelter forest dynamic and degradation factors detection in different phenophases. Plant Soil 479, 233–250 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05512-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05512-3