Abstract
Background and aims
It is known that the single and combined use of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) and silicon (Si) have the potential to improve the uptake of phosphorus (P) by plants in calcareous soils. However, it was unclear which form of Si in soil would have the most profound effects on the uptake of P by wheat plant inoculated with PSB. Here we investigated the effect of Si fertilizer on chemical forms of Si and P uptake by wheat plant inoculated with PSB in a calcareous soil. Determining different forms of Si in calcareous soils with a low P supply is essential to better understand the capacity of these forms to supply wheat plant with P in the presence of PSB.
Methods
A pot trial in a completely randomized design with factorial arrangement in 3 repetitions under greenhouse conditions was adopted to investigate the effect of Si fertilizer alone or in combination with PSB on the uptake of P and Si by wheat plant grown on a calcareous soil with low available P. Experimental treatments included: Si factor at four levels of 0, 150, 300, and 600 mg Si kg−1 from silicic acid source and PSB strains factor at three levels of B0 (control), Pseudomonas sp. FA1, and Bacillus simplex UT1. The impacts of Si levels and PSB on shoot and root dry weight and the wheat shoot uptake of Si and P were measured. Also, the chemical forms of Si in wheat rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil and the regression models of the variables were studied to better understand the mechanisms of this process.
Results
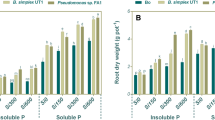
With increasing the levels of Si, the plant available Si with the lowest level, adsorbed Si, and amorphous Si with the highest level in both the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil increased. In addition, Si fertilization-mediated increase at level of the soil Si fractions was intensified in the presence of PSB strains. The highest plant available Si (75.50 mg Si kg−1 soil) was obtained from the treatment of 600 mg Si kg−1 soil in the presence of Pseudomonas sp. FA1. The combined application of Si and PSB strains also increased the wheat shoot dry weight by 3.5 times compared to the control treatments. The use of Si alone at level of 300 mg Si kg−1 also increased the wheat shoot content of P by 2.3 times compared to the control treatment. However, the combined application of Pseudomonas sp. FA1 and Si at level of 600 mg Si kg−1 increased the wheat shoot content of P by 4 times compared to the control treatment. According to the correlations among the studied parameters, in addition to the expected positive correlation between plant available Si of wheat rhizosphere soil and the measured parameters, a positive and significant correlation between adsorbed Si of wheat rhizosphere soil and the shoot uptake of Si (r2 = 0.84, P < 0.01) and the shoot uptake of P (r2 = 0.58, P < 0.05) was also observed in this study.
Conclusions
The information on the distribution of different forms of Si and the availability of P following the combined use of PSB strains and Si in this study (e.g., the role of rhizosphere adsorbed Si in increasing the wheat shoot uptake of P) may help in better management of P-fertilization in calcareous soils.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi D, Cade-Menun BJ, Ziadi N, Parent LÉ (2014) Long-term impact of tillage practices and phosphorus fertilization on soil phosphorus forms as determined by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Environ Qual 43(4):1431–1441
Alexandre A, Meunier J-D, Colin F, Koud J-M (1997) Plant impact on the biogeochemical cycle of silicon and related weathering processes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61(3):677–682
Alori ET, Glick BR, Babalola OO (2017) Microbial phosphorus solubilization and its potential for use in sustainable agriculture. Front Microbiol 8:971. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00971
Alovisi AMT, Furtini Neto AE, Carneiro LF, Curi N, Alovisi AA (2014) Silicon-phosphorus interactions in soils cultivated with bean plants. Acta Sci Agron 36(1):79–86
Alzoubi MM, Gaibore M (2012) The effect of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and organic fertilization on availability of Syrian rock phosphate and increase of triple superphosphate efficiency. World J Agric Sci 8(5):473–478
Argeaa HA, Nasseem MG, Mahmoud HA, Hussein MA (2016) Assessment of silicon status in calcareous soils of Banger Elsokkar Region, Egypt. Alex Sci Exch J 37(January-March):45–53
Babu T, Tubana B, Paye W, Kanke Y, Datnoff L (2016) Establishing soil silicon test procedure and critical silicon level for rice in Louisiana soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 47(12):1578–1597
Bahari SS, Pirdashti H, Yaghoubian Y (2012) The effects of nitrogen and silicon biofertilizers on powdery mildew disease, physiological parameters and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).
Barber SA (1995) Soil nutrient bioavailability: a mechanistic approach. Wiley, New York
Bayer C, Martin-Neto L, Mielniczuk J, Pillon CN, Sangoi L (2001) Changes in soil organic matter fractions under subtropical no-till cropping systems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65(5):1473–1478
Beheshti M, Alikhani HA, Pourbabaee AA, Etesami H, Asadi Rahmani H, Norouzi M (2021) Periphytic biofilm and rice rhizosphere phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and fungi: A possible use for activating occluded P in periphytic biofilms in paddy fields. Rhizosphere 19:100395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2021.100395
Bennett PC, Rogers JR, Choi WJ, Hiebert FK (2001) Silicates, silicate weathering, and microbial ecology. Geomicrobiol J 18(1):3–19
Berthelsen S, Noble AD, Kingston G, Hurney A, Rudd A, Garside A (2003) Improving yield and ccs in sugarcane through the application of silicon based amendments. Final Report, Sugar Research and Development Corporation Project CLW009
Bowman RA (1988) A rapid method to determine total phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52(5):1301–1304
Breuer J, Herrmann L (1999) Eignung der Extraktion mit Natriumbikarbonat für die Charakterisierung von bodenbildendenProzessen. Mitteilungen Der Deutschen Bodenkundlichen Gesellschaft 91:1375–1378
Brucker E, Kernchen S, Spohn M (2020) Release of phosphorus and silicon from minerals by soil microorganisms depends on the availability of organic carbon. Soil Biol Biochem 143:107737
Carey JC, Fulweiler RW (2016) Human appropriation of biogenic silicon–the increasing role of agriculture. Funct Ecol 30(8):1331–1339
Caubet M, Cornu S, Saby NPA, Meunier JD (2020) Agriculture increases the bioavailability of silicon, a beneficial element for crop, in temperate soils. Sci Rep 10(1):1–11
Chen Z, Ma S, Liu LL (2008) Studies on phosphorus solubilizing activity of a strain of phosphobacteria isolated from chestnut type soil in China. Biores Technol 99(14):6702–6707
Cornelis JT, Delvaux B, Georg RB, Lucas Y, Ranger J, Opfergelt S (2011) Tracing the origin of dissolved silicon transferred from various soil-plant systems towards rivers: a review. Biogeosciences 8(1):89–112
Crusciol CAC, de Arruda DP, Fernandes AM, Antonangelo JA, Alleoni LRF, Nascimento CACd, Rossato OB, McCray JM (2018) Methods and extractants to evaluate silicon availability for sugarcane. Sci Rep 8(1):916. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19240-1
Danilova A, Sauer D, Hermann L, Breuer J, Zarei M, Stahr K (2010) Development of a method for sequential extraction of Si-pools from soils. In: 19th world congress of soil science, soil solutions for a changing world, Brisbane, Australia, 1st-6th august. pp 31–34
El-Leboudi AE-S, El-Sebaay A-ES, Abd-Elrahman SH, El-Etr WM, Saad HY (2019) Effect of Silicon and Phosphorus Additions and Their Interactions on Wheat Plants Grown on a Clay Soil. Asian Soil Res J 1–10
Elhaissoufi W, Khourchi S, Ibnyasser A, Ghoulam C, Rchiad Z, Zeroual Y, Lyamlouli K, Bargaz A (2020) Phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria could have a stronger influence on wheat root traits and aboveground physiology than rhizosphere P solubilization. Front Plant Sci 11:979
Elliott CL, Snyder GH (1991) Autoclave-induced digestion for the colorimetric determination of silicon in rice straw. J Agric Food Chem 39(6):1118–1119
Epstein E (2009) Silicon: its manifold roles in plants. Ann Appl Biol 155(2):155–160
Etesami H (2018) Can interaction between silicon and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria benefit in alleviating abiotic and biotic stresses in crop plants? Agr Ecosyst Environ 253:98–112
Etesami H (2020) enhanced phosphorus fertilizer use efficiency with microorganisms. In: Nutrient dynamics for sustainable crop production. Springer, pp 215–245
Etesami H, Jeong BR (2018) Silicon (Si): Review and future prospects on the action mechanisms in alleviating biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:881–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.063
Etesami H, Adl SM (2020a) Can interaction between silicon and non–rhizobial bacteria help in improving nodulation and nitrogen fixation in salinity–stressed legumes? A review. Rhizosphere 15:100229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2020.100229
Etesami H, Adl SM (2020b) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and their action mechanisms in availability of nutrients to plants. Phyto-Microbiome in stress regulation, pp 147–203
Etesami H, Maheshwari DK (2018) Use of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) with multiple plant growth promoting traits in stress agriculture: Action mechanisms and future prospects. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 156:225–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.013
Etesami H, Jeong BR (2020) Importance of silicon in fruit nutrition: Agronomic and physiological implications. In: Fruit Crops. Elsevier, pp 255–277
Etesami H, Jeong BR, Glick BR (2021) Contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, phosphate-solubilizing bacteria, and silicon to P uptake by plant. Front Plant Sci 12(1355):699618. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.699618
Etesami H, Jeong BR, Rizwan M (2020) The use of silicon in stressed agriculture management: action mechanisms and future prospects. Metalloids in plants: advances and future prospects, pp 381–431
Fischer G (1992) Nutritional disorders of plants-development. Visual and Analytical Diagnosis, New York
Fraysse F, Pokrovsky OS, Schott J, Meunier J-D (2009) Surface chemistry and reactivity of plant phytoliths in aqueous solutions. Chem Geol 258(3–4):197–206
Gehlen M, Van Raaphorst W (2002) The role of adsorption–desorption surface reactions in controlling interstitial Si (OH) 4 concentrations and enhancing Si (OH) 4 turn-over in shallow shelf seas. Cont Shelf Res 22(10):1529–1547
Georgiadis A, Sauer D, Herrmann L, Breuer J, Zarei M, Stahr K (2013) Development of a method for sequential Si extraction from soils. Geoderma 209:251–261
Georgiadis A, Rinklebe J, Straubinger M, Rennert T (2017) Silicon fractionation in Mollic Fluvisols along the Central Elbe River, Germany. CATENA 153:100–105
Ghorchiani M, Etesami H, Alikhani HA (2018) Improvement of growth and yield of maize under water stress by co-inoculating an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and a plant growth promoting rhizobacterium together with phosphate fertilizers. Agr Ecosyst Environ 258:59–70
Glick BR (2012) Plant growth-promoting bacteria: mechanisms and applications. Scientifica 2012
Golmohammad H, Ramezanpour H, Rezapour S (2016) Study on some soil properties as affected by different slope position and aspect in mountainous landform with different parent materials in Masouleh. Water Soil Sci 26(2–2):53–66
Guntzer F, Keller C, Meunier J-D (2012) Benefits of plant silicon for crops: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 32(1):201–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-011-0039-8
Haluschak P (2006) Laboratory methods of soil analysis. Canada-Manitoba soil survey, pp 3–133
Hameed A, Sheikh MA, Jamil A, Basra SMA (2013) Seed priming with sodium silicate enhances seed germination and seedling growth in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under water deficit stress induced by polyethylene glycol. Pak J Life Soc Sci 11(1):19–24
Hattori T, Inanaga S, Araki H, An P, Morita S, Luxová M, Lux A (2005) Application of silicon enhanced drought tolerance in Sorghum bicolor. Physiol Plant 123(4):459–466. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2005.00481.x
Haynes RJ (2014) A contemporary overview of silicon availability in agricultural soils. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 177(6):831–844
Haynes RJ, Zhou Y-F (2020) Silicate sorption and desorption by a Si-deficient soil–Effects of pH and period of contact. Geoderma 365:114204
Henriet C, De Jaeger N, Dorel M, Opfergelt S, Delvaux B (2008) The reserve of weatherable primary silicates impacts the accumulation of biogenic silicon in volcanic ash soils. Biogeochemistry 90(2):209–223
Hiemstra T, Barnett MO, van Riemsdijk WH (2007) Interaction of silicic acid with goethite. J Colloid Interface Sci 310(1):8–17
Hinsinger P (1998) How do plant roots acquire mineral nutrients? Chemical processes involved in the rhizosphere. Adv Agron 64:225–266
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Circular California agricultural experiment station 347 (2nd edit)
Jalali M, Sajadi Tabar S (2011) Chemical fractionation of phosphorus in calcareous soils of Hamedan, western Iran under different land use. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174(4):523–531
Jones LHP, Handreck KA (1965) Studies of silica in the oat plant. Plant Soil 23(1):79–96
Karimzadeh J, Alikhani HA, Etesami H, Pourbabaei AA (2020) Improved Phosphorus Uptake by Wheat Plant (Triticum aestivum L.) with rhizosphere fluorescent pseudomonads strains under water-deficit stress. J Plant Growth Regul 1–17
Kaur G, Reddy MS (2015) Effects of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria, Rock Phosphate and Chemical Fertilizers on Maize-Wheat Cropping Cycle and Economics. Pedosphere 25(3):428–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(15)30010-2
Kim YH, Khan AL, Waqas M, Shim JK, Kim DH, Lee KY, Lee IJ (2014) Silicon application to rice root zone influenced the phytohormonal and antioxidant responses under salinity stress. J Plant Growth Regul 33(2):137–149
Korndörfer GH, Coelho NM, Snyder GH, Mizutani CT (1999) Avaliação de métodos de extração de silício em solos cultivados com arroz de sequeiro. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 23:101–106
Koski-Vähälä J, Hartikainen H, Tallberg P (2001) Phosphorus mobilization from various sediment pools in response to increased pH and silicate concentration. J Environ Qual 30(2):546–552
Kostic L, Nikolic N, Bosnic D, Samardzic J, Nikolic M (2017) Silicon increases phosphorus (P) uptake by wheat under low P acid soil conditions. Plant Soil 419(1):447–455
Kowalska J, Tyburski J, Jakubowska M, Krzymińska J (2020) Effect of different forms of silicon on growth of spring wheat cultivated in organic farming system. Silicon:1–7
Li Z, Delvaux B (2019) Phytolith-rich biochar: a potential Si fertilizer in desilicated soils. Gcb Bioenergy 11(11):1264–1282
Li Z, Unzué-Belmonte D, Cornelis J-T, Vander Linden C, Struyf E, Ronsse F, Delvaux B (2019) Effects of phytolithic rice-straw biochar, soil buffering capacity and pH on silicon bioavailability. Plant Soil 438(1):187–203
Li Z, Cornelis J-T, Vander Linden C, Van Ranst E, Delvaux B (2020a) Neoformed aluminosilicate and phytogenic silica are competitive sinks in the silicon soil–plant cycle. Geoderma 368:114308
Li Z, Guo F, Cornelis J-T, Song Z, Wang X, Delvaux B (2020b) Combined silicon-phosphorus fertilization affects the biomass and phytolith stock of rice plants. Front Plant Sci 11:67
Liu D, Liu M, Liu X-L, Cheng X-G, Liang Z-W (2018) Silicon Priming Created an Enhanced Tolerance in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Seedlings in Response to High Alkaline Stress. Frontiers in Plant Science 9 (716). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00716
Loeppert RH, Suarez DL (1996) Carbonate and gypsum. Methods of soil analysis Part 3, pp 437–474
Lugtenberg BJJ, Chin-A-Woeng TFC, Bloemberg GV (2002) Microbe–plant interactions: principles and mechanisms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81(1):373–383
Mahmood S, Daur I, Al-Solaimani SG, Ahmad S, Madkour MH, Yasir M, Hirt H, Ali S, Ali Z (2016) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and silicon synergistically enhance salinity tolerance of mung bean. Front Plant Sci 7:876
Mali M, Aery, Naresh C (2008) Silicon effects on nodule growth, dry-matter production, and mineral nutrition of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 171(6):835–840
Matichenkov VV, Bocharnikova EA (2001) The relationship between silicon and soil physical and chemical properties. In: Studies in plant science, vol 8. Elsevier, pp 209–219
Meunier J-D, Sandhya K, Prakash NB, Borschneck D, Dussouillez P (2018) pH as a proxy for estimating plant-available Si? A case study in rice fields in Karnataka (South India). Plant Soil 432(1):143–155
Miles N, Manson AD, Rhodes R, van Antwerpen R, Weigel A (2014) Extractable silicon in soils of the South African sugar industry and relationships with crop uptake. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 45(22):2949–2958
Milnes AR, Twidale CR (1983) An overview of silicification in Cainozoic landscapes of arid central and southern Australia. Soil Research 21(4):387–410
Morsy MA (2008) Silicon in agriculture conference. Wild Coast Sun, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, 26–31 October
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Narayanaswamy C, Prakash NB (2009) Calibration and categorization of plant available silicon in rice soils of South India. J Plant Nutr 32(8):1237–1254
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of Soil Analysis Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 403–430
Pati S, Pal B, Badole S, Hazra GC, Mandal B (2016) Effect of silicon fertilization on growth, yield, and nutrient uptake of rice. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 47(3):284–290
Puppe D, Kaczorek D, Wanner M, Sommer M (2014) Dynamics and drivers of the protozoic Si pool along a 10-year chronosequence of initial ecosystem states. Ecol Eng 70:477–482
Rai D, Kittrick JA (1989) Mineral equilibria and the soil system. Minerals in soil environments 1, pp 161–198
Rangaraj S, Gopalu K, Rathinam Y, Periasamy P, Venkatachalam R, Narayanasamy K (2014) Effect of silica nanoparticles on microbial biomass and silica availability in maize rhizosphere. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 61(6):668–675
Ranjbar SS, Motesharezadeh B, Moshiri F, Hosseini HM, Alikhani HA (2019) Silicon utilization efficiency of different wheat cultivars in a calcareous soil. Silicon 11(4):2159–2168
Rezakhani L, Motesharezadeh B, Tehrani MM, Etesami H, Mirseyed Hosseini H (2019) Phosphate–solubilizing bacteria and silicon synergistically augment phosphorus (P) uptake by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plant fertilized with soluble or insoluble P source. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 173:504–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.060
Rezakhani L, Motesharezadeh B, Tehrani MM, Etesami H, Mirseyed Hosseini H (2020) Effect of Silicon and Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Improved Phosphorus (P) Uptake Is Not Specific to Insoluble P-Fertilized Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Plants. J Plant Growth Regul 39(1):239–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-09978-x
Richard Drees L, Wilding LP, Smeck NE, Senkayi AL (1989) Silica in soils: quartz and disordered silica polymorphs. Minerals in Soil Environments 1, pp 913–974
Riotte J, Meunier J-D, Zambardi T, Audry S, Barboni D, Anupama K, Prasad S, Chmeleff J, Poitrasson F, Sekhar M (2018) Processes controlling silicon isotopic fractionation in a forested tropical watershed: Mule Hole Critical Zone Observatory (Southern India). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 228:301–319
Ryan J, Estefan G, Rashid A (2001) Soil and plant analysis laboratory manual. ICARDA
Saccone L, Conley DJ, Koning E, Sauer D, Sommer M, Kaczorek D, Blecker SW, Kelly EF (2007) Assessing the extraction and quantification of amorphous silica in soils of forest and grassland ecosystems. Eur J Soil Sci 58(6):1446–1459
Schaller J, Faucherre S, Joss H, Obst M, Goeckede M, Planer-Friedrich B, Peiffer S, Gilfedder B, Elberling B (2019) Silicon increases the phosphorus availability of Arctic soils. Sci Rep 9(1):1–11
Schwertmann U, Taylor RM (1989) Iron oxides. Minerals in soil environments 1, pp 379–438
Shamshiripour M, Motesharezadeh B, Rahmani HA, Alikhani HA, Etesami H (2021) Optimal concentrations of silicon enhance the growth of soybean (Glycine Max L.) cultivars by improving nodulation, root system architecture, and soil biological properties. Silicon 1–13
Sharif M, Khattak RA, Sarir MS (2002) Effect of different levels of lignitic coal derived humic acid on growth of maize plants. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 33(19–20):3567–3580
Sharma SB, Sayyed RZ, Trivedi MH, Gobi TA (2013) Phosphate solubilizing microbes: sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. Springerplus 2(1):587. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-2-587
Shirmohammadi E, Alikhani HA, Pourbabaei AA, Etesami H (2020) Improved phosphorus (P) uptake and yield of rainfed wheat fed with P fertilizer by drought-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing fluorescent pseudomonads strains: a field study in drylands. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20(4):2195–2211
Snyder GH (2001) Methods for silicon analysis in plants, soils, and fertilizers. In: Studies in plant science, vol 8. Elsevier, pp 185–196
Sommer M, Kaczorek D, Kuzyakov Y, Breuer J (2006) Silicon pools and fluxes in soils and landscapes—a review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 169(3):310–329
Song A, Li Z, Liao Y, Liang Y, Wang E, Wang S, Li X, Bi J, Si Z, Lu Y (2021a) Soil bacterial communities interact with silicon fraction transformation and promote rice yield after long-term straw return. Soil Ecol Lett 1–14
Song A, Li Z, Wang E, Xu D, Wang S, Bi J, Wang H, Jeyakumar P, Li Z, Fan F (2021) Supplying silicon alters microbial community and reduces soil cadmium bioavailability to promote health wheat growth and yield. Sci Total Environ 796:148797
Swift RS, Sparks DL (1996) Methods of soil analysis: Part 3. Chemical methods. Soil Science Society of America Book Series 5, pp 1018–1020
Tavakkoli E, Lyons G, English P, Guppy CN (2011) Silicon nutrition of rice is affected by soil pH, weathering and silicon fertilisation. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174(3):437–446
Uroz S, Calvaruso C, Turpault M-P, Frey-Klett P (2009) Mineral weathering by bacteria: ecology, actors and mechanisms. Trends Microbiol 17(8):378–387
Valizadeh-rad K, Motesharezadeh B, Alikhani HA, Jalali M (2021) Direct and residual effects of water deficit stress, different sources of silicon and plant-growth promoting bacteria on silicon fractions in the soil. Silicon 1–13
Waling I, Van Vark W, Houba VJG, Van der Lee JJ (1989) Soil and plant analysis, a series of syllabi: Part 7. Plant analysis procedures. Wageningen Agriculture University
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37(1):29–38
Wang S, Liu P, Chen D, Yin L, Li H, Deng X (2015) Silicon enhanced salt tolerance by improving the root water uptake and decreasing the ion toxicity in cucumber. Front Plant Sci 6:759
Wang D, Xie Y, Jaisi DP, Jin Y (2016) Effects of low-molecular-weight organic acids on the dissolution of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Environ Sci Nano 3(4):768–779
Yadav H, Fatima R, Sharma A, Mathur S (2017) Enhancement of applicability of rock phosphate in alkaline soils by organic compost. Appl Soil Ecol 113:80–85
Yan G-c, Nikolic M, Ye M-j, Xiao Z-x, Liang Y-c (2018) Silicon acquisition and accumulation in plant and its significance for agriculture. J Integr Agric 17(10):2138–2150
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the financial support of the University of Tehran for doing this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed equally to this study.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Christopher Guppy.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezakhani, L., Motesharezadeh, B., Tehrani, M.M. et al. The effect of silicon fertilization and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on chemical forms of silicon and phosphorus uptake by wheat plant in a calcareous soil. Plant Soil 477, 259–280 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-05274-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-05274-4