Abstract
Aims
This study aimed to better understanding the mechanism underlying the interaction between boron and NaCl and may provide methods to improve sugar beet production in saline soils.
Methods
Sugar beet seedlings were treated with different concentrations of boron and NaCl. The flame photometer and ion chromatography were used to determine the ion content. And the uptake of Cl− by beet roots, was measured by non-invasive micro-test technology (NMT) and in vivo uptake system. The qPCR was used to measure the relative expression of the genes encoding ion transporters.
Results
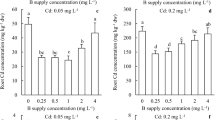
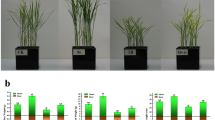
In this study, we demonstrate that application of 750 µM boron markedly mitigated the growth inhibition of sugar beet seedlings caused by 300 mM NaCl, as reflected in dry and fresh weight, leaf area, chlorophyll content, and net photosynthetic rates. Both Na+ and K+ in the plants were not affected by treatment with boron. However, boron markedly reduced the Cl− content of sugar beet seedlings. Boron profoundly upregulated the expression of CLC-b, CLC-c, CLC-f and downregulated the expression of NIP5, NIP6 and AKT1 under NaCl stress.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that exogenous boron reduced Cl− content of sugar beet seedlings by regulation of Cl− transport under NaCl stress, which is possibly involved in upregulation of BvCLC-b, BvCLC-c and BvCLC-f genes encoding Cl− transporters in a cell wall-dependent Ca2+ signal transduction process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi Z, Arzani A, Majidi MM, Rajabi A, Jalali A (2019) Genetic analysis of sugar yield and physiological traits in sugar beet under salinity stress conditions. Euphytica 215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-019-2422-5
Adler G, Blumwald E, Bar-Zvi D (2010) The sugar beet gene encoding the sodium/proton exchanger 1 (BvNHX1) is regulated by a MYB transcription factor. Planta 232:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1160-7
Ahmad M, Zahir ZA, Nazli F, Akram F, Arshad M, Khalid M (2013) Effectiveness of halo-tolerant, auxin producing Pseudomonas and Rhizobium strains to improve osmotic stress tolerance in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.). Braz J Microbiol 44:1341–1348. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-83822013000400045
Alpaslan M, Gunes A (2001) Interactive effects of boron and salinity stress on the growth, membrane permeability and mineral composition of tomato and cucumber plants. Plant Soil 236:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1011931831273
Arzani A, Ashraf M (2016) Smart engineering of genetic resources for enhanced salinity tolerance in crop plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 35:146–189. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2016.1245056
Ashraf M, Shahbaz M (2003) Assessment of genotypic variation in salt tolerance of early CIMMYT hexaploid wheat germplasm using photosynthetic capacity and water relations as selection criteria. Photosynthetica 41:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHOT.0000011961.33120.b6
Bernhard AE, Tucker J, Giblin AE, Stahl DA (2007) Functionally distinct communities of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria along an estuarine salinity gradient. Environ Microbiol 9:1439–1447. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01260.x
Biczak R, Pawlowska B, Feder-Kubis J (2017) The effect of ionic liquids with (-)-menthol derivative containing a chloride anion to weed. Ecol Chem Eng S 24:637–651. https://doi.org/10.1515/eces-2017-0042
Britto DT, Ruth TJ, Lapi S, Kronzucker HJ (2004) Cellular and whole-plant chloride dynamics in barley: insights into chloride-nitrogen interactions and salinity responses. Planta 218:615–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1137-x
Chartzoulakis K, Klapaki G (2000) Response of two greenhouse pepper hybrids to NaCl salinity during different growth stages. Sci Hortic 86:247–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-4238(00)00151-5
Chartzoulakis K, Psarras G (2005) Global change effects on crop photosynthesis and production in Mediterranean: the case of Crete. Greece Agriculture Ecosystems Environment 106:147–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2004.10.004
Chen P, Yan K, Shao H, Zhao S (2013) Physiological mechanisms for high salt tolerance in wild soybean (Glycine soja) from Yellow River Delta, China: photosynthesis, osmotic regulation, ion flux and antioxidant capacity. PLos One 8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083227
Chi Tam N, Agorio A, Jossier M, Depre S, Thomine S, Filleur S (2016) Characterization of the chloride channel-like, AtCLCg, involved in chloride tolerance in arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 57:764–775. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcv169
Cohen S, Offenbach R, Suriano S, Aloni B, Karni L, Bar-Tal A, Keinan M, Maduel A (2003) Managing of circulated nutrient solutions with saline water for pepper cultivation. Acta Hort 609:349–354. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-015-1114-6
Cubero-Font P, Maierhofer T, Jaslan J, Rosales MA, Espartero J, Diaz-Rueda P, Mueller HM, Huerter A-L, Al-Rasheid KAS, Marten I, Hedrich R, Colmenero-Flores JM, Geiger D (2016) Silent S-type anion channel subunit SLAH1 gates SLAH3 open for chloride root-to-shoot translocation. Curr Biol 26:2213–2220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2016.06.045
De Stefano S, Pusch M, Zifarelli G (2011) Extracellular determinants of anion discrimination of the Cl-/H + antiporter protein CLC-5. J Biol Chem 286:44134–44144. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.272815
Fedorova EE, Coba de la Pena T, Lara-Dampier V, Trifonova NA, Kulikova O, Pueyo JJ, Lucas MM (2021) Potassium content diminishes in infected cells of Medicago truncatula nodules due to the mislocation of channels MtAKT1 and MtSKOR/GORK. J Exp Bot 72:1336–1348. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa508
Ferreyra RE, Aljaro AU, Ruiz RS, Rojas LP, Oster JD (1997) Behavior of 42 crop species grown in saline soils with high boron concentrations. Agric Water Manag 34:111–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3774(97)00014-0
Flowers TJ (2004) Improving crop salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 55:307–319. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh003
Ghoulam C, Foursy A, Fares K (2002) Effects of salt stress on growth, inorganic ions and proline accumulation in relation to osmotic adjustment in five sugar beet cultivars. Environ Exp Bot 47:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0098-8472(01)00109-5
Gonzalez-Fontes A, Navarro-Gochicoa MT, Camacho-Cristobal JJ, Herrera-Rodriguez MB, Quiles-Pando C, Rexach J (2014) Is Ca2 + involved in the signal transduction pathway of boron deficiency? New hypotheses for sensing boron deprivation. Plant Sci 217:135–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.12.011
Grattan SR, Grieve CM (1999) Salinity mineral nutrient relations in horticultural crops. Sci Hortic 78:127–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4238(98)00192-7
Guo J, Li Y, Han G, Song J, Wang B (2018) NaCl markedly improved the reproductive capacity of the euhalophyte Suaeda salsa. Funct Plant Biol 45:350–361. https://doi.org/10.1071/fp17181
Guo J, Dong X, Han G, Wang B (2019) Salt-enhanced reproductive development of Suaeda salsa L. coincided with ion transporter gene upregulation in flowers and increased pollen K+ . Front Plant Sci 10:333. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00333
Gupta B, Huang B (2014) Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization. Int J Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/701596
Hamid M, Khalil Ur R, Ashraf MY (2010) Salicylic acid-induced growth and biochemical changes in salt-stressed wheat. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 41:373–389. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620903494343
Hasegawa PM (2013) Sodium (Na+) homeostasis and salt tolerance of plants. Environ Exp Bot 92:19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.03.001
Hedrich R, Geiger D (2017) Biology of SLAC1-type anion channels - from nutrient uptake to stomatal closure. New Phytol 216:46–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14685
Hocq L, Pelloux J, Lefebvre V (2017) Connecting homogalacturonan-type pectin remodeling to acid growth. Trends Plant Sci 22:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2016.10.009
Horie T, Kaneko T, Sugimoto G, Sasano S, Panda SK, Shibasaka M, Katsuhara M (2011) Mechanisms of water transport mediated by PIP aquaporins and their regulation via phosphorylation events under salinity stress in barley roots. Plant Cell Physiol 52:663–675. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcr027
Huang L-T, Zhao L-N, Gao L-W, Very A-A, Sentenac H, Zhang Y-D (2018) Constitutive expression of CmSKOR, an outward K + channel gene from melon, in Arabidopsis thaliana involved in saline tolerance. Plant Sci 274:492–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.07.005
Huetsch BW, Jung S, Schubert S (2015) Comparison of salt and drought-stress effects on maize growth and yield formation with regard to acid invertase activity in the kernels. J Agron Crop Sci 201:353–367. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12111
Jossier M, Kroniewicz L, Dalmas F, Le Thiec D, Ephritikhine G, Thomine S, Barbier-Brygoo H, Vavasseur A, Filleur S, Leonhardt N (2010) The Arabidopsis vacuolar anion transporter, AtCLCc, is involved in the regulation of stomatal movements and contributes to salt tolerance. Plant J 64:563–576. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04352.x
Kaiser WM, Schroppel-Meier G, Wirth E (1986) Enzyme activities in an artificial stroma medium: An experimental model for studying effects of dehydration on photosynthesis. Planta 167:292–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00391429
Lohse G (1982) Microanalytical azomethine-H method for boron determination in plant tissue. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 13:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103628209367251
Luo Q, Yu B, Liu Y (2002) Stress of Cl– is stronger than that of Na+ on glycine max seedlings under NaCl stress. Agric Sci China 12:1404–1409
Lv X, Chen S, Wang Y (2019) Advances in understanding the physiological and molecular responses of sugar beet to salt stress. Front Plant Sci 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01431
Maierhofer T, Lind C, Huettl S, Scherzer S, Papenfuss M, Simon J, Al-Rasheid KAS, Ache P, Rennenberg H, Hedrich R, Mueller TD, Geiger D (2014) A single-pore residue renders the arabidopsis root anion channel SLAH2 highly nitrate selective. Plant Cell 26:2554–2567. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.125849
Marmagne A, Vinauger-Douard M, Monachello D, de Longevialle AF, Charon C, Allot M, Rappaport F, Wollman F-A, Barbier-Brygoo H, Ephritikhine G (2007) Two members of the Arabidopsis CLC (chloride channel) family, AtCLCe and AtCLCf, are associated with thylakoid and Golgi membranes, respectively. J Exp Bot 58:3385–3393. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erm187
Martinez-Ballesta MdC, Bastias E, Zhu C, Schaeffner AR, Gonzalez-Moro B, Gonzalez-Murua C, Carvajal M (2008) Boric acid and salinity effects on maize roots. Response of aquaporins ZmPIP1 and ZmPIP2, and plasma membrane H+-ATPase, in relation to water and nutrient uptake. Physiol Plant 132:479–490. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2007.01045.x
Masood S, Wimmer MA, Witzel K, Zoerb C, Muehling KH (2012) Interactive effects of high boron and NaCl stresses on subcellular localization of chloride and boron in wheat leaves. J Agron Crop Sci 198:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2011.00501.x
Miwa K, Fujiwara T (2010) Boron transport in plants: co-ordinated regulation of transporters. Ann Bot 105:1103–1108. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq044
Moghadam NK, Lajayer BA, Ghorbanpour M (2020) Boron tolerance in plants. Metalloids in Plants
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Nable ROJP, Soil (1988) Resistance to boron toxicity amongst several barley and wheat cultivars: A preliminary examination of the resistance mechanism. 112:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02181751
Ochiai K, Uemura S, Shimizu A, Okumoto Y, Matoh T (2008) Boron toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). I. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis of tolerance to boron toxicity. Theor Appl Genet 117:125–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0758-7
Oh D-H, Leidi E, Zhang Q, Hwang S-M, Li Y, Quintero FJ, Jiang X, D’Urzo MP, Lee SY, Zhao Y, Bahk JD, Bressan RA, Yun D-J, Pardo JM, Bohnert HJ (2009) Loss of halophytism by interference with SOS1 expression. Plant Physiol 151:210–222. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.137802
O’Neill MA, Ishii T, Albersheim P, Darvill AG (2004) Rhamnogalacturonan II: Structure and function of a borate cross-linked cell wall pectic polysaccharide. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:109–139. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141750
Pan T, Liu M, Kreslavski VD, Zharmukhamedov SK, Nie C, Yu M, Kuznetsov VV, Allakhverdiev SI, Shabala S (2020) Non-stomatal limitation of photosynthesis by soil salinity. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1735231
Qi G-N, Yao F-Y, Ren H-M, Sun S-J, Tan Y-Q, Zhang Z-C, Qiu B-S, Wang Y-F (2018) The S-type anion channel ZmSLAC1 plays essential roles in stomatal closure by mediating nitrate efflux in maize. Plant Cell Physiol 59:614–623. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy015
Qiu J, Henderson SW, Tester M, Roy SJ, Gilliham M (2016) SLAH1, a homologue of the slow type anion channel SLAC1, modulates shoot Cl- accumulation and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 67:4495–4505. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw237
Reid R (2014) Understanding the boron transport network in plants. Plant Soil 385:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2149-y
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ibrahim M, Farid M, Adrees M, Bharwana SA, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Qayyum MF, Abbas F (2015) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of drought and salt stress in plants: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:15416–15431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5305-x
Rubio F, Nieves-Cordones M, Horie T, Shabala S (2020) Doing ‘business as usual’ comes with a cost: evaluating energy cost of maintaining plant intracellular K + homeostasis under saline conditions. New Phytologist 225
Seemann JR, Critchley C (1985) Effects of salt stress on the growth, ion content, stomatal behaviour and photosynthetic capacity of a salt-sensitive species, Phaseolus vulgaris L. Planta 164:151–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00396077
Shabala S, Bose J, Fuglsang AT, Pottosin I (2016) On a quest for stress tolerance genes: membrane transporters in sensing and adapting to hostile soils. J Exp Bot 67:1015–1031. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv465
Smith TE, Grattan SR, Grieve CM, Poss JA, Suarez DL (2010) Salinity’s influence on boron toxicity in broccoli: I. Impacts on yield, biomass distribution, and water use. Agric Water Manag 97:777–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2010.01.014
Sun J, Chen S, Dai S, Wang R, Li N, Shen X, Zhou X, Lu C, Zheng X, Hu Z, Zhang Z, Song J, Xu Y (2009) NaCl-induced alternations of cellular and tissue ion fluxes in roots of salt-resistant and salt-sensitive poplar species. Plant Physiol 149:1141–1153. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.129494
Sun JK, Li T, Xia JB, Tian JY, Lu ZH, Wang RT (2011) Influence of salt stress on ecophysiological parameters of Periploca sepium Bunge. Plant Soil Environ 57:139–144. https://doi.org/10.17221/227/2010-pse
Tavakkoli E, Rengasamy P, McDonald GK (2010) High concentrations of Na + and Cl- ions in soil solution have simultaneous detrimental effects on growth of faba bean under salinity stress. J Exp Bot 61:4449–4459. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq251
Teakle NL, Tyerman SD (2010) Mechanisms of Cl- transport contributing to salt tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 33:566–589. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02060.x
Tripler E, Ben-Gal A, Shani U (2007) Consequence of salinity and excess boron on growth, evapotranspiration and ion uptake in date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L., cv. Medjool). Plant Soil 297:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9328-z
von der Fecht-Bartenbach J, Bogner M, Krebs M, Stierhof Y-D, Schumacher K, Ludewig U (2007) Function of the anion transporter AtCLC-d in the trans-Golgi network. Plant J 50:466–474. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03061.x
von der Fecht-Bartenbach J, Bogner M, Dynowski M, Ludewig U (2010) CLC-b-mediated NO3-/H + exchange across the tonoplast of arabidopsis vacuoles. Plant Cell Physiol 51:960–968. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcq062
White PJ, Broadley MR (2001) Chloride in soils and its uptake and movement within the plant: A review. Ann Bot 88:967–988. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.2001.1540
Wu YJ, Cosgrove DJ (2000) Adaptation of roots to low water potentials by changes in cell wall extensibility and cell wall proteins. J Exp Bot 51:1543–1553. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/51.350.1543
Wu H, Zhang X, Giraldo JP, Shabala S (2018) It is not all about sodium: revealing tissue specificity and signalling roles of potassium in plant responses to salt stress. Plant Soil 431:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3770-y
Wu X, Lu X, Riaz M, Yan L, Jiang C (2018) Boron deficiency and toxicity altered the subcellular structure and cell wall composition architecture in two citrus rootstocks. Sci Hortic 238:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.04.057
Wu G-Q, Wang J-L, Li S-J (2019) Genome-wide identification of Na+/H + antiporter (NHX) genes in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) and their regulated expression under salt stress. Genes 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10050401
Yao F-Y, Qi G-N, Hussain J (2017) Investigation of the regulation mechanism of Arabidopsis thaliana anion channel SLAH2. Turk J Bot 41:543-543+. https://doi.org/10.3906/bot-1702-23
Yermiyahu U, Ben-Gal A, Sarig P, Zipilevitch E (2007) Boron toxicity in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) in conjunction with salinity and rootstock effects. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 82:547–554. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2007.11512272
Yermiyahu U, Ben-Gal A, Keren R, Reid RJ (2008) Combined effect of salinity and excess boron on plant growth and yield. Plant Soil 304:73–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9522-z
Yuan H-J, Ma Q, Wu G-Q, Wang P, Hu J, Wang S-M (2015) ZxNHX controls Na + and K + homeostasis at the whole-plant level in Zygophyllum xanthoxylum through feedback regulation of the expression of genes involved in their transport. Ann Bot 115:495–507. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcu177
Yuan F, Leng B, Zhang H, Wang X, Han G, Wang B (2019) A WD40-repeat protein from the Recretohalophyte Limonium bicolor enhances trichome formation and salt tolerance in arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01456
Zhang XK, Zhou QH, Cao JH, Yu BJ (2011) Differential Cl-/Salt tolerance and NaCl-induced alternations of tissue and cellular ion fluxes in glycine max, glycine soja and their hybrid seedlings. J Agron Crop Sci 197:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2011.00467.x
Zhang X-W, Tan S-N, Meng Z, Wang B-S (2019) Exogenous boron affects the growth of beet by regulation of leaf area and stomatal conductance. Plant Physiol J 55. https://doi.org/10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2019.0288
Zhao C, Zhang H, Song C, Zhu J-K, Shabala S (2020) Mechanisms of plant responses and adaptation to soil salinity. Innovation 1:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2020.100017
Zheng X, He K, Kleist T, Chen F, Luan S (2015) Anion channel SLAH3 functions in nitrate-dependent alleviation of ammonium toxicity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 38:474–486. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12389
Zhu JK (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:441–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-5266(03)00085-2
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Research Foundation of China (Project Nos. 31570251; 31600200; 31770288), Natural Science Research Foundation of Shandong Province (Project Nos. ZR2020QC031), Post-doctorate program in China (Project Nos. 2020M672114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Yong Chao Liang.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Figure S1
Effect of different concentrations of NaCl for 15 days on plant growth of the three B. vulgaris varieties KWS3418, 10-43 and HK-3 (PNG 2553 kb)
Figure S2
Effect of different concentrations of NaCl for 14 days. (A) plant growth, (B) fresh weight of shoots and (C) roots of B. vulgaris. Control: half-strength Hoagland solution; 50 NaCl: half-strength Hoagland solution + 50 mM NaCl; 100 NaCl: half-strength Hoagland solution + 100 mM NaCl; 150 NaCl: half-strength Hoagland solution + 150 mM NaCl; 200 NaCl: half-strength Hoagland solution + 200 mM NaCl; 300 NaCl: half-strength Hoagland solution + 300 mM NaCl; (B, C) 0: half-strength Hoagland solution; 50: half-strength Hoagland solution + 50 mM NaCl; 100: half-strength Hoagland solution + 100 mM NaCl; 150: half-strength Hoagland solution + 150 mM NaCl; 200: half-strength Hoagland solution + 200 mM NaCl; 300: half-strength Hoagland solution + 300 mM NaCl. Data are average of 5 replicates ± SD; Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05. (PNG 3473 kb)
Figure S3
Effect of different concentrations of NaCl in B. vulgaris roots. (A) Continuous Cl– flux and (B) mean Cl– flux in B. vulgaris roots. Data are average of 6 replicates ± SD; Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05. (PNG 335 kb)
Figure S4
Effect of exogenous boron on plant growth of B. vulgaris under NaCl stress for 22 days. Control: half-strength Hoagland solution; NaCl: half-strength Hoagland + 300 mMNaCl; NaCl + B: half-strength Hoagland solution (without H3BO3) + 300 mM NaCl + 750 μMH3BO3. (PNG 3045 kb)
Figure S5
Treatment of B. vulgaris (PNG 3096 kb)
Table S1
(DOCX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, X., Sun, L., Guo, J. et al. Exogenous boron alleviates growth inhibition by NaCl stress by reducing Cl− uptake in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). Plant Soil 464, 423–439 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-04946-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-04946-5