Abstract
Aims
This study aimed to examine the effects of NaCl on Cd tolerance of two halophytes with contrasting salt-tolerance ability: the euhalophyte Suaeda glauca and the recretohalophyte Limonium aureum.
Methods
Plant growth, photosynthesis and physiological responses of two halophytes were measured in a pot experiment treated with 0, 3 and 6 mg kg−1 Cd in combination with 0 and 0.3% NaCl.
Results
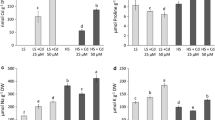
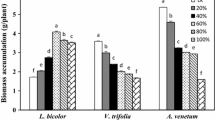
Both halophytes exhibited fair-level (moderate level) Cd tolerant ability. NaCl mitigated Cd-induced toxicity on the growth and photosynthesis of S. glauca, particularly under low Cd level, while a negative effect of NaCl was observed in L. aureum. Moreover, activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), catalase (CAT) and ascorbate peroxidase (APX) in leaves of S. glauca were boosted by Cd and/or salinity treatment. Although similar responses were observed, the overall increase of enzymatic activities in L. aureum was lower than in S. glauca. The soluble protein content in two species showed an opposite trend among treatments, whereas the proline accumulation in L. aureum was exceptionally higher than that in S. glauca under saline conditions. The nutrient concentrations of these two halophytes were only slightly affected by Cd excess, and NaCl significantly enhanced their Na accumulation, regardless of the plant’s organ and Cd level. In addition, Cd absorption and translocation were greatly enhanced by NaCl in the two halophytes.
Conclusions
Salt-induced alleviation of Cd toxicity in S. glauca might be mainly attributed to salt-triggered secondary metabolic strategy, which deffers from the energy-consuming adaptive strategy employed by L. aureum.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol Academic 105:121–126
Ali B, Qian P, Jin R et al (2014) Physiological and ultra-structural changes in Brassica napus seedlings induced by cadmium stress. Biol Plant 58:131–138
Anjum S, Wang L, Farooq M et al (2011) Brassinolide application improves the drought tolerance in maize through modulation of enzymatic antioxidants and leaf gas exchange. J Agron Crop Sci 197:177–185
Ashraf M, Foolad M (2007) Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot 59:206–216
Ashraf U, Hussain S, Anjum S, Abbas F, Tanveer M, Noor MA, Tang X (2017) Alterations in growth, oxidative damage, and metal uptake of five aromatic rice cultivars under lead toxicity. Plant Physiol Biochem 115:461–471
Bankaji I, Cacador I, Sleimi N (2016) Assessing of tolerance to metallic and saline stresses in the halophyte Suaeda fruticosa: the indicator role of antioxidative enzymes. Ecol Indic 64:297–308
Bates L, Waldren R, Teare I (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Ben Rejeb K, Abdelly C, Savouré A (2014) How reactive oxygen species and proline face stress together. Plant Physiol Biochem 80:278–284
Bose J, Rodrigo-Moreno A, Shabala S (2014) ROS homeostasis in halophytes in the context of salinity stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 65:1241–1257
Buege J, Aust S (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods in enzymology. Academic Press 52:302–310
Chen H, Zhang S, Wu K et al (2020) The effects of exogenous organic acids on the growth, photosynthesis and cellular ultrastructure of Salix variegata Franch. Under Cd stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 187:109790
Cheng M, Wang A, Liu Z, Gendall AR, Rochfort S, Tang C (2018) Sodium chloride decreases cadmium accumulation and changes the response of metabolites to cadmium stress in the halophyte Carpobrotus rossii. Ann Bot 122:373–385
Cherif J, Derbel N, Nakkach M et al (2012) Spectroscopic studies of photosynthetic responses of tomato plants to the interaction of zinc and cadmium toxicity. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 111:9–16
Conesa H, García G, Faz Á, Arnaldos R (2007) Dynamics of metal tolerant plant communities’ development in mine tailings from the Cartagena-La Unión Mining District (SE Spain) and their interest for further revegetation purposes. Chemosphere. 68:1180–1185
Das P, Samantaray S, Rout GR (1997) Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: a review. Environ Pollut 98:29–36
Ding F, Chen M, Sui N et al (2010) Ca2+ significantly enhanced development and salt-secretion rate of salt glands of Limonium bicolor under NaCl treatment. S Afr J Bot 76:95–101
Farquhar G, Sharkey T (1982) Stomatal conductance and photosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 33:317–345
Fischer R (1971) Role of potassium in stomatal opening in the leaf of Vicia faba. Plant Physiol 47:555–558
Flexas J, Medrano H (2002) Drought-inhibition of photosynthesis in C3 plants: stomatal and non-stomatal limitations revisited. Ann Bot 89:183–189
Flowers T, Colmer T (2008) Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol 179:945–963
Gallego S, Pena L, Barcia R et al (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46
Gupta B, Huang B (2014) Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization. International Journal of Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/701596
Habiba U, Ali S, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbasi GH, Hayat T, Ali B (2015) EDTA enhanced plant growth, antioxidant defense system, and phytoextraction of copper by Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1534–1544
Han R, Lefèvre I, Ruan C et al (2012) Effects of salinity on the response of the wetland halophyte Kosteletzkya virginica (L.) Presl. to copper toxicity. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:1137–1150
Idaszkin Y, Márquez F, Mateos-Naranjo E et al (2019) Multidimensional approach to evaluate Limonium brasiliense as source of early biomarkers for lead pollution monitoring under different saline conditions. Ecol Indic 104:567–575
Jiang H, Yang J, Zhang J (2007) Effects of external phosphorus on the cell ultrastructure and the chlorophyll content of maize under cadmium and zinc stress. Environ Pollut 147:750–756
Li L, Tu C, Peijnenburg W, Luo YM (2017) Characteristics of cadmium uptake and membrane transport in roots of intact wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings. Environ Pollut 221:351–358
Li B, Wang J, Yao L et al (2019) Halophyte Halogeton glomeratus, a promising candidate for phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated saline soils. Plant Soil 442:323–331
Liang L, Liu W, Sun Y et al (2016) Phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated saline soils using halophytes: current progress and future perspectives. Environ Rev 25:269–281
Lichtenthaler H, Wellburn A (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592
Limón-Pacheco J, Gonsebatt M (2009) The role of antioxidants and antioxidant-related enzymes in protective responses to environmentally induced oxidative stress. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 674:137–147
Liu X, Zhang S, Shan X, Christie P (2007) Combined toxicity of cadmium and arsenate to wheat seedlings and plant uptake and antioxidative enzyme responses to cadmium and arsenate co-contamination. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 68:305–313
Liu Y, Yang Y, Li C et al (2018) Assessing soil metal levels in an industrial environment of northwestern China and the phytoremediation potential of its native plants. Sustainability. 10:2686
Lutts S, Lefèvre I (2015) How can we take advantage of halophyte properties to cope with heavy metal toxicity in salt-affected areas? Ann Bot 115:509–528
Manousaki E, Galanaki K, Papadimitriou L, Kalogerakis N (2014) Metal phytoremediation by the halophyte Limoniastrum monopetalum (L.) Boiss: two contrasting ecotypes. International Journal of Phytoremediation 16:755–769
Mariem W, Kilani B, Benet G, Abdelbasset L, Stanley L, Charlotte P, Chedly A, Tahar G (2014) How does NaCl improve tolerance to cadmium in the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum? Chemosphere. 117:243–250
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Munns R, Passioura J, Colmer T et al (2019) Osmotic adjustment and energy limitations to plant growth in saline soil. New Phytol. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15862
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Nawaz I, Iqbal M, Bliek M, Schat H (2017) Salt and heavy metal tolerance and expression levels of candidate tolerance genes among four extremophile Cochlearia species with contrasting habitat preferences. Sci Total Environ 584-585:731–741
Nikalje G, Suprasanna P (2018) Coping with metal toxicity - cues from halophytes. Front Plant Sci 9:1–11
Ouni Y, Mateos-Naranjo E, Abdelly C et al (2016) Interactive effect of salinity and zinc stress on growth and photosynthetic responses of the perennial grass, Polypogon monspeliensis. Ecol Eng 95:171–179
Pandey P, Ramegowda V, Senthil-Kumar M (2015) Shared and unique responses of plants to multiple individual stresses and stress combinations: physiological and molecular mechanisms. Front Plant Sci 6:723
Parraga-Aguado I, González-Alcaraz M, Álvarez-Rogel J et al (2014) Assessment of the employment of halophyte plant species for the phytomanagement of mine tailings in semiarid areas. Ecol Eng 71:598–604
Perfus-Barbeoch L, Leonhardt N, Vavasseur A, Forestier C (2002) Heavy metal toxicity: cadmium permeates through calcium channels and disturbs the plant water status. Plant J 32:539–548
Redondo-Gómez S, Mateos-Naranjo E, Vecino-Bueno I, Feldman SR (2011) Accumulation and tolerance characteristics of chromium in a cordgrass Cr-hyperaccumulator, Spartina argentinensis. J Hazard Mater 185:862–869
Romero-Puertas M, Rodríguez-Serrano M, Corpas F et al (2004) Cadmium-induced subcellular accumulation of O2·− and H2O2 in pea leaves. Plant Cell Environ 27:1122–1134
Roth U, von Roepenack-Lahaye E, Clemens S (2006) Proteome changes in Arabidopsis thaliana roots upon exposure to Cd2+. J Exp Bot 57:4003–4013
Rozema J, Schat H (2013) Salt tolerance of halophytes, research questions reviewed in the perspective of saline agriculture. Environ Exp Bot 92:83–95
Sagardoy R, Vázquez S, Florez-Sarasa I, Albacete A, Ribas-Carbó M, Flexas J, Abadía J, Morales F (2010) Stomatal and mesophyll conductances to CO2 are the main limitations to photosynthesis in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) plants grown with excess zinc. New Phytol 187:145–158
Shahid M, Pourrut B, Dumat C et al (2014) Heavy-metal-induced reactive oxygen species: phytotoxicity and physicochemical changes in plants. In: reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. Springer International Publishing 232:1–44
Sharma S, Dietz K (2006) The significance of amino acids and amino acid-derived molecules in plant responses and adaptation to heavy metal stress. J Exp Bot 57:711–726
Snyder J, Desborough S (1978) Rapid estimation of potato tuber total protein content with coomassie brilliant blue G-250. Theoretical & Applied Genetics 52:135–139
Tauqeer H, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ali Q, Saeed R, Iftikhar U, Ahmad R, Farid M, Abbasi GH (2016) Phytoremediation of heavy metals by Alternanthera bettzickiana: growth and physiological response. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:138–146
Velikova V, Tsonev T, Loreto F, Centritto M (2011) Changes in photosynthesis, mesophyll conductance to CO2, and isoprenoid emissions in Populus nigra plants exposed to excess nickel. Environ Pollut 159:1058–1066
Wali M, Gunsè B, Llugany M et al (2016) High salinity helps the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum in defense against Cd toxicity by maintaining redox balance and photosynthesis. Planta 244:333–346
Wiszniewska A, Koźmińska A, Hanus-Fajerska E et al (2019) Insight into mechanisms of multiple stresses tolerance in a halophyte Aster tripolium subjected to salinity and heavy metal stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:12–22
Yang Q, Li Z, Lu X, Duan Q, Huang L, Bi J (2018a) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: pollution and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 642:690–700
Yang L, Zhu J, Wang P, Zeng J, Tan R, Yang YZ, Liu ZM (2018b) Effect of Cd on growth, physiological response, Cd subcellular distribution and chemical forms of Koelreuteria paniculata. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 160:10–18
Ying R, Qiu R, Tang Y, Hu PJ, Qiu H, Chen HR, Shi TH, Morel JL (2010) Cadmium tolerance of carbon assimilation enzymes and chloroplast in Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Picris divaricata. J Plant Physiol 167:81–87
Yuan F, Guo J, Shabala S et al (2019) Reproductive physiology of halophytes: current standing. Front Plant Sci 9:1954
Zhang X (1992) The measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation and SOD, POD and CAT activities in biological system. In research methodology of crop physiology (in Chinese). Agriculture press. Pp 208-211
Zhang X, Li M, Yang H, Li X, Cui Z (2018) Physiological responses of Suaeda glauca and Arabidopsis thaliana in phytoremediation of heavy metals. J Environ Manag 223:132–139
Zhang S, Ni X, Arif M et al (2020) Salinity influences Cd accumulation and distribution characteristics in two contrasting halophytes, Suaeda glauca and Limonium aureum. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110230
Zhao K, Fan H, Ungar I (2002) Survey of halophyte species in China. Plant Sci 163:491–498
Zhao K, Li F, Zhang F (2013) Salt-tolerance mechanisms of different types of halophytes. In halophytes in China (in Chinese). Science press. Pp 70-98
Zhao F, Ma Y, Zhu Y, Tang Z, McGrath S (2015) Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies. Environ Sci Technol 49:750–759
Zhou M, Han R, Ghnaya T, Lutts S (2018a) Salinity influences the interactive effects of cadmium and zinc on ethylene and polyamine synthesis in the halophyte plant species Kosteletzkya pentacarpos. Chemosphere. 209:892–900
Zhou M, Dailly H, Renard M, Han RM, Lutts S (2018b) NaCl impact on Kosteletzkya pentacarpos seedlings simultaneously exposed to cadmium and zinc toxicities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:17444–17456
Zhou M, Renard M, Quinet M et al (2019) Effect of NaCl on proline and glycinebetaine metabolism in Kosteletzkya pentacarpos exposed to Cd and Zn toxicities. Plant Soil 441:525–542
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Chongqing Municipality Key Forestry Research Project (No. TD2019-2), Chongqing Municipality Housing and Urban Construction Committee (No. Chengkezi 2019-1-4-2), Forestry Extension Project of China Central Finance (No. Yulinketui 2017-12) and International Sci-Tech Cooperation Project of Ministry of Science and Technology (No. 2015DFA90900). We are grateful to Ms. Ying Wu for her technical assistance during the tests and also to Mr. Yusheng Liang for his valuable suggestions on the manuscript. The two anonymous reviewers and Editor Dr. Antony van der Ent are greatly appreciated for their thoughtful and insightful comments that helped us improve our manuscript significantly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: C.L., X.N., S.Z.; Methodology: X.N., S.Z.; Formal analysis and investigation: X.N., S.Z., M.A., J.Z.; Writing - original draft preparation: S.Z., M.A.; Writing - review and editing: C.L., S.Z., M.A., J.Z., A.S.; Funding acquisition: C.L.; Resources: C.L., X.N.; Supervision: C.L..
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Antony Van der Ent.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Ni, X., Arif, M. et al. NaCl improved Cd tolerance of the euhalophyte Suaeda glauca but not the recretohalophyte Limonium aureum. Plant Soil 449, 303–318 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04475-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04475-7