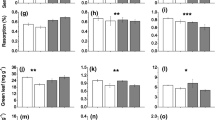
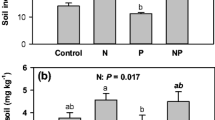
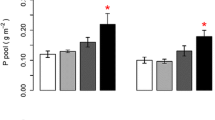
Abstract
Aims
Here we assessed N and P uptake of four grassland species grown together in response to a short-term drought event along a soil P gradient.
Methods
We used 15N and 32P tracers to examine uptake of N and P by the grasses Bothriochloa macra, Themeda triandra, Lolium perenne and Microlaena stipoides grown together in pots with initial available P levels of 3, 8, 12, 20 mg P kg−1 soil. Soil moisture in half the pots was reduced from 60 to 30% water holding capacity during a 7-day period to simulate drought.
Results
Plant P uptake was strongly reduced by drought in all species across all P levels, much more so than N uptake, indicating decoupling in N and P uptake. Soil available P (Bray method) was not affected by drought, suggesting that the reduced P uptake with drought was due to reduced soil P mobility. Plant competition for N and P changed with drought and soil P levels, where relatively more N and P was taken up with drought by M. stipoides at the lowest soil P level.
Conclusions
We showed that greater reductions in P than in N uptake and shifts in N and P uptake among species caused by a short-term drought have strong consequences for plant growth.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam SM (1999) Nutrient uptake by plants under stress conditions. In: Pessarakli M (ed) Handbook of plant and crop stress. Marcel Dekker, New York
Andresen L, Michelsen A, Jonasson S, Schmidt I, Mikkelsen T, Ambus P, Beier C (2010) Plant nutrient mobilization in temperate heathland responds to elevated CO2, temperature and drought. Plant Soil 328:381–396
Belnap J (2011) Biological phosphorus cycling in dryland regions. In: Bünemann EK, Oberson A, Frossard E (eds) Phosphorus in action. Springer, Berlin, pp 37–406
Campbell BD, Stafford Smith DM (2000) A synthesis of recent global change research on pasture and rangeland production: reduced uncertainties and their management implications. Agric Ecosyst Environ 82:39–55
Chapin FS III, Fetcher N, Kielland K, Everett KR, Linkins AE (1988) Productivity and nutrient cycling of Alaskan tundra: enhancement by flowing soil water. Ecology 69:693–702
Ciais P, Reichstein M, Viovy N, Granier A, Ogee J, Allard V, Aubinet M, Buchmann N, Bernhofer C, Carrara A, Chevallier F, De Noblet N, Friend AD, Friedlingstein P, Grunwald T, Heinesch B, Keronen P, Knohl A, Krinner G, Loustau D, Manca G, Matteucci G, Miglietta F, Ourcival JM, Papale D, Pilegaard K, Rambal S, Seufert G, Soussana JF, Sanz MJ, Schulze ED, Vesala T, Valentini R (2005) Europe-wide reduction in primary productivity caused by the heat and drought in 2003. Nature 437:529–533
Dijkstra FA, Pendall E, Morgan JA, Blumenthal DM, Carrillo Y, LeCain DR, Follett RF, Williams DG (2012) Climate change alters stoichiometry of phosphorus and nitrogen in a semiarid grassland. New Phytol 196:807–815
Dijkstra FA, He M, Johansen MP, Harrison JJ, Keitel C (2015) Plant and microbial uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus affected by drought using 15N and 32P tracers. Soil Biol Biochem 82:135–142
Elser JJ, Bracken MES, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 10:1135–1142
Güsewell S (2004) N : P ratios in terrestrial plants: variation and functional significance. New Phytol 164:243–266
Gustafsson JP, Mwamila LB, Kergoat K (2012) The pH dependence of phospate sorption and desoprtion in Swedish agriscultural soils. Geoderma 189-190:304–311
Harpole WS, Ngai JT, Cleland EE, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Bracken MES, Elser JJ, Gruner DS, Hillebrand H, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2011) Nutrient co-limitation of primary producer communities. Ecol Lett 14:852–862
He M, Dijkstra FA (2014) Drought effect on plant nitrogen and phosphorus: a meta-analysis. New Phytol 204:924–931
Heisler-White JL, Blair JM, Kelly EF, Harmoney K, Knapp AK (2009) Contingent productivity responses to more extreme rainfall regimes across a grassland biome. Glob Change Biol 15:2894–2904
Hill JO, Simpson RJ, Moore AD, Chapman DF (2006) Morphology and response of roots of pasture species to phosphorus and nitrogen nutrition. Plant Soil 286:7–19
Hinojosa MB, Parra A, Ramírez DA, Carreira JA, García-Ruiz R, Moreno JM (2012) Effects of drought on soil phosphorus availability and fluxes in a burned Mediterranean shrubland. Geoderma 191:61–69
Homyak PM, Allison SD, Huxman TE, Goulden ML, Treseder KK (2017) Effects of drought manipulation on soil nitrogen cycling: a meta-analysis. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 122:3260–3272
Isbell RF (2002) The Australian soil classification. CSIRO Pub, Collingwood, Vic, Aus
Jackson ML (1958) Soil chemical analsysis. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs
Jiao F, Shi XR, Han FP, Yuan ZY (2016) Increasing aridity, temperature and soil pH induce soil C-N-P imbalance in grasslands. Sci Rep 6:19601
Jung V, Albert CH, Violle C, Kunstler G, Loucougaray G, Spiegelberger T (2014) Intraspecific trait variability mediates the response of subalpine grassland communities to extreme drought events. J Ecol 102:45–53
Lambers H, Chapin FS III, Pons TL (2008) Plant physiological ecology. Springer Science, New York, NY, USA
L'Annuziata FM (2012) Handbook of radioactivity analysis. Academic Press, San Diego, USA
Li Y, Niu S, Yu G (2016) Aggravated phosphorus limitation on biomass production under increasing nitrogen loading: a meta-analysis. Glob Change Biol 22:934–943
Luo W, Elser JJ, Lü XT, Wang Z, Bai E, Yan C, Wang C, Li MH, Zimmermann NE, Han X, Xu Z, Li H, Wu Y, Jiang Y (2015) Plant nutrients do not covary with soil nutrients under changing climatic conditions. Glob Biogeochem Cycl 29:1298–1308
Luo W, Xu C, Ma W, Yue X, Liang X, Zuo X, Knapp AK, Smith MD, Sardans J, Dijkstra FA, Peñuelas J, Bai Y, Wang Z, Yu Q, Han X (2018) Effects of extreme drought on plant nutrient uptake and resorption in rhizomatous vs bunchgrass-dominated grasslands. Oecologia 188:633–643
Luo W, Zuo X, Griffin-Nolan RJ, Xu C, Ma W, Song L, Helsen K, Lin Y, Cai J, Yu Q, Wang Z, Smith MD, Han X, Knapp AK (2019) Long term experimental drought alters community plant trait variation, not trait means, across three semiarid grasslands. Plant Soil 442:343–353.
Mariotte P, Canarini A, Dijkstra FA (2017) Stoichiometric N:P flexibility and mycorrhizal symbiosis favour plant resistance against drought. J Ecol 105:958–967
Minoletti ML, Boerner REJ (1994) Drought and site fertility effects on foliar nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics and nutrient resorption by the forest understory shrub Viburnum acerifolium L. Am Midl Nat 131:109–119
Öhlinger R (2012) Methods in soil physics. In: Schinner F, Öhlinger R, Kandeler E, Margesin R (eds) Methods in soil biology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus. In: Pace AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis part 2 chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Inc., Madison
Peuke AD, Rennenberg H (2004) Carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and Sulphur concentration and partitioning in beech ecotypes (Fagus sylvatica L.): phosphorus most affected by drought. Trees 18:639–648
Ryalls JMW, Moore BD, Johnson SN, Connor M, Hiltpold I (2018) Root responses to domestication, precipitation and silicification: weeping meadow grass simplifies and alters toughness. Plant Soil 427:291–304
Sardans J, Peñuelas J (2004) Increasing drought decreases phosphorus availability in an evergreen Mediterranean forest. Plant Soil 267:367–377
Solaiman Z, Marschner P, Wang D, Rengel Z (2007) Growth, P uptake and rhizosphere properties of wheat and canola genotypes in an alkaline soil with low P availability. Biol Fert Soils 44:143–153
Stafford J (1996) Weeping rice-grass (Microlaena stipoides), species information sheet. Native Grass Resources Group Inc. September 1996. Mount lofty ranges catchment Centre, Mount Barker South Australia 5251
Stark JM, Hart SC (1996) Diffusion technique for preparing salt solutions, Kjeldahl digests, and persulfate digests for nitrogen-15 analysis. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60:1846–1855
Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological stoichiometry. The biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Suriyagoda LDB, Ryan MH, Renton M, Lambers H (2014) Plant responses to limited moisture and phosphorus availability: a meta-analysis. Adv Agron 124:143–200
Tezara W, Mitchell VJ, Driscoll SD, Lawlor DW (1999) Water stress inhibits plant photosynthesis by decreasing coupling factor and ATP. Nature 401:914–917
Vitra A, Deléglise C, Meisser M, Risch AC, Signarbieux C, Lamacque L, Delzon S, Buttler A, Mariotte P (2019) Responses of plant leaf economic and hydraulic traits mediate the effects of early- and late-season drought on grassland productivity. AoB PLANTS 11:plz023
Yu Q, Chen Q, Elser JJ, He N, Wu H, Zhang G, Wu J, Bai Y, Han X (2010) Linking stoichiometric homoeostasis with ecosystem structure, functioning and stability. Ecol Lett 13:1390–1399
Yu Q, Wilcox K, Pierre KL, Knapp AK, Han X, Smith MD (2015) Stoichiometric homeostasis predicts plant species dominance, temporal stability, and responses to global change. Ecology 96:2328–2335
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by an Australian Institute of Nuclear Science and Engineering Research Award (ALNGRA15209) awarded to FAD in 2015. PM was funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation (n°P300P3_154648).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Felipe E. Albornoz.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 484 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mariotte, P., Cresswell, T., Johansen, M.P. et al. Plant uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus among grassland species affected by drought along a soil available phosphorus gradient. Plant Soil 448, 121–132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04407-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04407-0