Abstract
Aims
Water use efficiency (WUE) of crop plants is an important plant trait for maintaining high yield in water limited areas. By influencing osmoregulation of plants, potassium (K) plays a critical role in stress avoidance and adaptation. However, whole plant physiological mechanisms modulated by K supply in respect of plant drought tolerance and water use efficiency are not well understood. In the present study, growth, development and transpiration dynamics of two barley cultivars were evaluated with and without PEG-induced osmotic stress using an automated balance system and image based leaf area determination.
Methods
Experiments were conducted to study the effects of varied K supply under different osmotic stress treatments on a wide range of morphological, biochemical and physiological characteristics of barley plants such as leaf area development, daily whole plant transpiration rate (DTR), stomatal conductance (gs), assimilation rate (AN), biomass and leaf water use efficiency (WUE) as well as foliar abscisic acid (ABA) concentrations. Two barley cultivars (cv. Sahin-91 and cv. Milford) were treated with two K supply levels (0.04 and 0.8 mM K) and osmotic stress induced by polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG) for a period of 9 days (in total 48 days experiment) in the hydroponic plant culture (non-PEG and + 20% PEG ).
Results
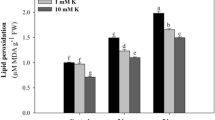
Without PEG, low-K supply depressed dry matter (DM) by almost 60% averaged across both cultivars. Under osmotic stress (+PEG), total leaf area was reduced by almost 70% in low-K compared to adequate-K plants. Low K concentration under PEG stress was correlated with higher ABA concentration and was correlated with lower leaf- and whole plant transpiration rate. Biomass-WUE under low K supply decreased significantly in both barley cultivars, to a greater extent in cv. Milford under osmotic stress. However, leaf-WUE was not affected by K supply in the absence of osmotic stress.
Conclusions
It was suggested that reduced biomass-WUE in low-K treated barley plants was not related to inefficient stomatal control under K deficiency, but instead due to reduced assimilation rate. It was further hypothesized that under low K supply, a number of energy consuming activities reduce biomass-WUE, which are not distinguished by measuring leaf-WUE. This study showed that low K supply under osmotic stress increases foliar ABA concentration thereby decreasing plant transpiration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amtmann A, Armengaud P (2009) Effects of N, P, K and S on metabolism: new knowledge gained from multi-level analysis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:275–283. Physiology and Metabolism Edited by David E Salt and Lorraine Williams. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.04.014
Andersen MN, Jensen CR, Lösch R (1992) The interaction effects of potassium and drought in field-grown barley. I. Yield, water-use efficiency and growth. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica B-Plant SoilSciences 42:34–44
Ashraf M, Ahmad A, McNeilly T (2001) Growth and photosynthetic characteristics in pearl millet under water stress and different potassium supply. Photosynthetica 39:389–394. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015182310754
Battie-Laclau P, Delgado-Rojas JS, Christina M, Nouvellon Y, Bouillet J-P, Piccolo M d C, Moreira MZ, Gonçalves JL d M, Roupsard O, Laclau J-P (2016) Potassium fertilization increases water-use efficiency for stem biomass production without affecting intrinsic water-use efficiency in Eucalyptus grandis plantations. For Ecol Manag 364:77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.01.004
Bednarz CW, Oosterhuis DM, Evans RD (1998) Leaf photosynthesis and carbon isotope discrimination of cotton in response to potassium deficiency. Environ Exp Bot 39:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-8472(97)00039-7
Benlloch-Gonzalez M, Arquero O, Maria Fournier J, Barranco D, Benlloch M (2008) K+ starvation inhibits water-stress-induced stomatal closure. J Plant Physiol 165:623–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2007.05.010
Benlloch-González M, Romera J, Cristescu S, Harren F, Fournier JM, Benlloch M (2010) K+ starvation inhibits water-stress-induced stomatal closure via ethylene synthesis in sunflower plants. J Exp Bot 61:1139–1145. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp379
Bottrill DE, Possingham JV, Kriedemann PE (1970) The effect of nutrient deficiencies on phosynthesis and respiration in spinach. Plant Soil 32:424–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01372881
Brag H (1972) The influence of potassium on the transpiration rate and stomatal opening in Triticum aestivum and Pisum sativum. Physiol Plant 26:250–257. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1972.tb03577.x
Cakmak I (1994) Activity of ascorbate-dependent H2O2-scavenging enzymes and leaf chlorosis are enhanced in magnesium-and potassium-deficient leaves, but not in phosphorus-deficient leaves. J Exp Bot 45:1259–1266
Cakmak I, Kirkby EA (2008) Role of magnesium in carbon partitioning and alleviating photooxidative damage. Physiol Plant 133:692–704. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2007.01042.x
Cernusak LA, Winter K, Turner BL (2009) Physiological and isotopic ( δ 13 C and δ 18 O) responses of three tropical tree species to water and nutrient availability. Plant Cell Environ 32:1441–1455. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02010.x
Chen L, Dodd IC, Davies WJ, Wilkinson S (2013) Ethylene limits abscisic acid- or soil drying-induced stomatal closure in aged wheat leaves. Plant Cell Environ 36:1850–1859. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12094
Daszkowska-Golec A, Szarejko I (2013) Open or close the gate - stomata action under the control of phytohormones in drought stress conditions. Front Plant Sci 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00138
Duncan DB (1955) Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 11:1. https://doi.org/10.2307/3001478
Egilla JN, Davies FT, Drew MC (2001) Effect of potassium on drought resistance of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis cv. Leprechaun: plant growth, leaf macro- and micronutrient content and root longevity. Plant Soil 229:213–224. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004883032383
Egilla JN, Davies FT, Boutton TW (2005) Drought stress influences leaf water content, photosynthesis, and water-use efficiency of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis at three potassium concentrations. Photosynthetica 43:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-005-5140-2
Farquhar GD, Sharkey TD (1982) Stomatal conductance and photosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 33:317–345. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.33.060182.001533
Farquhar GD, Ehleringer JR, Hubick KT (1989) Carbon isotope discrimination and photosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 40:503–537. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.40.060189.002443
Fournier JM, Roldán ÁM, Sánchez C, Alexandre G, Benlloch M (2005) K+ starvation increases water uptake in whole sunflower plants. Plant Sci 168:823–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.10.015
Gattward JN, Almeida A-AF, Souza JO, Gomes FP, Kronzucker HJ (2012) Sodium–potassium synergism in Theobroma cacao: stimulation of photosynthesis, water-use efficiency and mineral nutrition. Physiol Plant 146:350–362. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01621.x
Gerardeaux E, Jordan-Meille L, Constantin J, Pellerin S, Dingkuhn M (2010) Changes in plant morphology and dry matter partitioning caused by potassium deficiency in Gossypium hirsutum (L.). Environ Exp Bot 67:451–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.09.008
Gupta AS, Berkowitz GA, Pier PA (1989) Maintenance of photosynthesis at low leaf water potential in wheat role of potassium status and irrigation history. Plant Physiol 89:1358–1365. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.89.4.1358
Häffner E, Karlovsky P, Splivallo R, Traczewska A, Diederichsen E (2014) ERECTA, salicylic acid, abscisic acid, and jasmonic acid modulate quantitative disease resistance of Arabidopsis thaliana to Verticillium longisporum. BMC Plant Biol 14:85. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-85
Hafsi C, Romero-Puertas MC, del Río LA, Abdelly C, Sandalio LM (2011) Antioxidative response of Hordeum maritimum L. to potassium deficiency. Acta Physiol Plant 33:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0537-3
Hsiao TC, Lauchli A (1986) Role of potassium in plant-water relations. Advances in plant nutrition (USA)
Jákli B, Tavakol E, Tränkner M, Senbayram M, Dittert K (2016a) Quantitative limitations to photosynthesis in K deficient sunflower and their implications on water-use efficiency. J Plant Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2016.11.010
Jákli B, Tränkner M, Senbayram M, Dittert K (2016b) Adequate supply of potassium improves plant water-use efficiency but not leaf water-use efficiency of spring wheat. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci. n/a-n/a. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201600340
Jordan-Meille L, Pellerin S (2004) Leaf area establishment of a maize (Zea Mays L.) field crop under potassium deficiency. Plant Soil 265:75–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-0695-z
Kanai S, Moghaieb RE, El-Shemy HA, Panigrahi R, Mohapatra PK, Ito J, Nguyen NT, Saneoka H, Fujita K (2011) Potassium deficiency affects water status and photosynthetic rate of the vegetative sink in green house tomato prior to its effects on source activity. Plant Sci 180(2):368–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.10.011
Law BE, Falge E, Gu L, Baldocchi DD, Bakwin P, Berbigier P, Davis K, Dolman AJ, Falk M, Fuentes JD, Goldstein A, Granier A, Grelle A, Hollinger D, Janssens IA, Jarvis P, Jensen NO, Katul G, Mahli Y, Matteucci G, Meyers T, Monson R, Munger W, Oechel W, Olson R, Pilegaard K, Paw U KT, Thorgeirsson H, Valentini R, Verma S, Vesala T, Wilson K, Wofsy S (2002) Environmental controls over carbon dioxide and water vapor exchange of terrestrial vegetation. Agric For Meteorol, FLUXNET 2000 Synthesis 113:97–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1923(02)00104-1
Lim CW, Baek W, Jung J, Kim J-H, Lee SC (2015) Function of ABA in stomatal defense against biotic and drought stresses. Int J Mol Sci 16:15251–15270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160715251
Lösch R, Jensen CR, Andersen MN (1992) Diurnal courses and factorial dependencies of leaf conductance and transpiration of differently potassium fertilized and watered field grown barley plants. Plant Soil 140:205–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010598
Lu Z, Lu J, Pan Y, Lu P, Li X, Cong R, Ren T (2016) Anatomical variation of mesophyll conductance under potassium deficiency has a vital role in determining leaf photosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ 39:2428–2439. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12795
Lynch J, Läuchli A (1984) Potassium transport in salt-stressed barley roots. Planta 161:295–301
Marschner H (2012) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Elsevier, London
Martineau E, Domec JC, Bosc A, Denoroy P, Fandino VA, Lavres Jr J, Jordan-Meille L (2017) The effects of potassium nutrition on water use in field-grown maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Exp Bot 134:62–71
Martin-Vertedor AI, Dodd IC (2011) Root-to-shoot signalling when soil moisture is heterogeneous: increasing the proportion of root biomass in drying soil inhibits leaf growth and increases leaf abscisic acid concentration. Plant Cell Environ 34:1164–1175. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02315.x
Medrano H, Tomás M, Martorell S, Flexas J, Hernández E, Rosselló J, ... & Bota J (2015) From leaf to whole-plant water use efficiency (WUE) in complex canopies: limitations of leaf WUE as a selection target. The Crop Journal 3(3):220–228
Mengel K, Kirkby EA, Kosegarten H, Appel T (2001) Potassium. In: Mengel K, Kirkby EA, Kosegarten H, Appel T (eds) Principles of plant nutrition. springer netherlands, pp 481–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-1009-2_10
Michel BE, Kaufmann MR (1973) The osmotic potential of polyethylene glycol 6000. Plant Physiol 51:914–916
Pi Z, Stevanato P, Sun F, Yang Y, Sun X, Zhao H, Geng G, Yu L (2016) Proteomic changes induced by potassium deficiency and potassium substitution by sodium in sugar beet. J Plant Res 129:527–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-016-0800-9
Rasband WS (1997) ImageJ. US National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD
R Core Team 2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
Ratzinger A, Riediger N, von Tiedemann A, Karlovsky P (2009) Salicylic acid and salicylic acid glucoside in xylem sap of Brassica napus infected with Verticillium longisporum. J Plant Res 122:571–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-009-0237-5
Seibt U, Rajabi A, Griffiths H, Berry JA (2008) Carbon isotopes and water use efficiency: sense and sensitivity. Oecologia 155:441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-007-0932-7
Senbayram M, Tränkner M, Dittert K, Brück H (2015) Daytime leaf water use efficiency does not explain the relationship between plant N status and biomass water-use efficiency of tobacco under non-limiting water supply. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 178:682–692. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201400608
Smith BN, Epstein S (1971) Two caterogies of 13C/12C ratios for higher plants. Plant Physiol 47:380–384
Tambussi E a, Bort J, Araus J l (2007) Water use efficiency in C3 cereals under Mediterranean conditions: a review of physiological aspects. Ann Appl Biol 150:307–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2007.00143.x
Tränkner M, Jákli B, Tavakol E, Geilfus C-M, Cakmak I, Dittert K, Senbayram M (2016) Magnesium deficiency decreases biomass water-use efficiency and increases leaf water-use efficiency and oxidative stress in barley plants. Plant Soil 406:409–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2886-1
Vishwakarma K, Upadhyay N, Kumar N, Yadav G, Singh J, Mishra RK, Kumar V, Verma R, Upadhyay RG, Pandey M, Sharma S (2017) Abscisic acid signaling and abiotic stress tolerance in plants: a review on current knowledge and future prospects. Front Plant Sci 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00161
Von Caemmerer SV, Farquhar GD (1981) Some relationships between the biochemistry of photosynthesis and the gas exchange of leaves. Planta 153:376–387
Wang M, Zheng Q, Shen Q, Guo S (2013) The critical role of potassium in plant stress response. Int J Mol Sci 14:7370–7390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14047370
White PJ, Broadley MR (2003) Calcium in plants. Ann Bot 92:487–511. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcg164
Yamburenko MV, Zubo YO, Börner T (2015) Abscisic acid affects transcription of chloroplast genes via protein phosphatase 2C-dependent activation of nuclear genes: repression by guanosine-3′-5′-bisdiphosphate and activation by sigma factor 5. Plant J 82:1030–1041. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12876
Zhang J, Jia W, Yang J, Ismail AM (2006) Role of ABA in integrating plant responses to drought and salt stresses. Field Crop Res, Preparing Rice for a Water-Limited Future: from Molecular to Regional Scale. International Rice Research Congress 97:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2005.08.018
Zörb C, Senbayram M, Peiter E (2014) Potassium in agriculture – status and perspectives. J Plant Physiol 171:656–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2013.08.008
Acknowledgements
The research performed for this paper was financed by K+S KALI GmbH, Germany. We would also like to thank the staff of IAPN and the plant nutrition group of Göttingen University for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ian Dodd.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tavakol, E., Jákli, B., Cakmak, I. et al. Optimized potassium nutrition improves plant-water-relations of barley under PEG-induced osmotic stress. Plant Soil 430, 23–35 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3704-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3704-8