Abstract
Background and aims
Phosphorus (P) deficiency is a major problem for alfalfa (Medicago sativa) productivity on alkaline soils on the Loess Plateau, China. Our aim was to investigate growth, morphological and physiological responses of alfalfa to P supply in two alkaline soils when water supply is limited.
Methods
A pot experiment was carried out to grow alfalfa in two alkaline soils supplied with different rates of P. Parameters of plant growth and root morphology, rhizosphere pH and carboxylates, and plant concentrations of mineral nutrients were measured.
Results
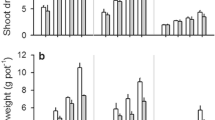
Plant growth and nutrient uptake were enhanced by supplying P, but shoot growth was not further increased when P supply was >20 μg P g−1 soil. Specific root length was only responsive to changes in soil P when P supply was low in the loessial soil. The rhizosphere carboxylate amount was significantly greater when no P was supplied than when P was supplied to the loessial soil. The rhizosphere pH was lower than the bulk soil pH, but did not vary with soil P.
Conclusions
A P supply of 20 μg P g−1 soil was optimal for alfalfa growth. The responses of specific root length and rhizosphere carboxylates depended on soil type.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahao A, Lambers H, Sawaya A, Mazzafera P, Oliveira RS (2014) Convergence of a specialized root trait in plants from nutrient-impoverished soils: phosphorus-acquisition strategy in a nonmycorrhizal cactus. Oecologia 176:345–355
Aziz T, Lambers H, Nicol D, Ryan MH (2015) Mechanisms for tolerance of very high tissue phosphorus concentrations in Ptilotus polystachyus. Plant Cell Environ 38:790–799
Bolan NS, Adriano DC, Curtin D (2003) Soil acidification and liming interactions with nutrient and heavy metal transformation and bioavailability. Adv Agron 78:215–272
Broadley MR, Rose T, Frei M, Pariasca-Tanaka J, Yoshihashi T, Thomson M, Hammond JP, Aprile A, Close TJ, Ismail AM, Wissuwa M (2010) Response to zinc deficiency of two rice lines with contrasting tolerance is determined by root growth maintenance and organic acid exudation rates, and not by zinc-transporter activity. New Phytol 186:400–414
Carpenter SR (2005) Eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems: Bistability and soil phosphorus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:10002–10005
Carvalhais LC, Dennis PG, Fedoseyenko D, Hajirezaei M-R, Borriss R, von Wirén N (2011) Root exudation of sugars, amino acids, and organic acids by maize as affected by nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and iron deficiency. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174:3–11
Cawthray GR (2003) An improved reversed-phase liquid chromatographic method for the analysis of low-molecular mass organic acids in plant root exudates. J Chromatogr A 1011:233–240
Conn S, Gilliham M (2010) Comparative physiology of elemental distributions in plants. Ann Bot 105:1081–1102
Cordell D, White S (2015) Tracking phosphorus security: indicators of phosphorus vulnerability in the global food system. Food Secur 7:337–350
Cordell D, Drangert J-O, White S (2009) The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Glob Environ Change-Human Policy 19:292–305
Dakora FD, Phillips DA (2002) Root exudates as mediators of mineral acquisition in low-nutrient environments. Plant Soil 245:35–47
Deng L, Wang KB, Li JP, Shangguan ZP, Sweeney S (2014) Carbon storage dynamics in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) fields in the hilly-gully region of the Loess Plateau, China. Clean-Soil Air Water 42:1253–1262
Dong DF, Peng XX, Yan XL (2004) Organic acid exudation induced by phosphorus deficiency and/or aluminium toxicity in two contrasting soybean genotypes. Physiol Plant 122:190–199
Elser JJ, Bracken MES, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 10:1135–1142
Fan JW, Du YL, Turner NC, Wang BR, Fang Y, Xi Y, Guo XR, Li FM (2015) Changes in root morphology and physiology to limited phosphorus and moisture in a locally-selected cultivar and an introduced cultivar of Medicago sativa L. growing in alkaline soil. Plant Soil 392:215–226
Fang Z, Shao C, Meng Y, Wu P, Chen M (2009) Phosphate signaling in Arabidopsis and Oryza sativa. Plant Sci 176:170–180
Fixen PE, Johnston AM (2012) World fertilizer nutrient reserves: a view to the future. J Sci Food Agric 92:1001–1005
Hassan HM, Marschner P, McNeill A, Tang CX (2012) Growth, P uptake in grain legumes and changes in rhizosphere soil P pools. Biol Fertil Soils 48:151–159
He H, Veneklaas EJ, Kuo J, Lambers H (2014) Physiological and ecological significance of biomineralization in plants. Trends Plant Sci 19:166–174
Hinsinger P (2001) Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: a review. Plant Soil 237:173–195
Hinsinger P, Plassard C, Tang CX, Jaillard B (2003) Origins of root-mediated pH changes in the rhizosphere and their responses to environmental constraints: a review. Plant Soil 248:43–59
Hoffland E, Wei C, Wissuwa M (2006) Organic anion exudation by lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.) at zinc and phosphorus deficiency. Plant Soil 283:155–162
Hossner LR, Freeouf JA, Folsom BL (1973) Solution phosphorus concentration and growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in flooded soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 37:405–408
Johnston AE, Poulton PR, Fixen PE, Curtin D (2014) Phosphorus: its efficient use in agriculture. Adv Agron 123:177–228
Kabir ME, Johansen C, Bell RW (2015) Subsoil rhizosphere modification by chickpea under a dry topsoil: implications for phosphorus acquisition. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 178:904–913
Kereszt A, Li D, Indrasumunar A, Nguyen CDT, Nontachaiyapoom S, Kinkema M, Gresshoff PM (2007) Agrobacterium rhizogenes - mediated transformation of soybean to study root biology. Nat Protoc 2:948–952
Kidd DR, Ryan MH, Haling RE, Lambers H, Sandral GA, Yang ZJ, Culvenor RA, Cawthray GR, Stefanski A, Simpson RJ (2016) Rhizosphere carboxylates and morphological root traits in pasture legumes and grasses. Plant Soil 402:77–89
Lambers H, Juniper D, Cawthray GR, Veneklaas EJ, Martinez-Ferri E (2002) The pattern of carboxylate exudation in Banksia Grandis (Proteaceae) is affected by the form of phosphate added to the soil. Plant Soil 238:111–122
Lambers H, Shane MW, Cramer MD, Pearse SJ, Veneklaas EJ (2006) Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits. Ann Bot 98:693–713
Lambers H, Thijs LP, Chapin FS (2008) Plant physiological ecology. Springer, New York
Lambers H, Hayes PE, Laliberte E, Oliveira RS, Turner BL (2015) Leaf manganese accumulation and phosphorus-acquisition efficiency. Trends Plant Sci 20:83–90
Li J, Copeland L (2000) Role of malonate in chickpeas. Phytochemistry 54:585–589
Little IP (1992) The relationship between soil pH measurements in calcium chloride and water suspensions. Aust J Soil Res 30:587–592
Lomonte C, Gregory D, Baker AJM, Kolev SD (2008) Comparative study of hotplate wet digestion methods for the determination of mercury in biosolids. Chemosphere 72:1420–1424
Lynch JP (2007) Roots of the second green revolution. Aust J Bot 55:493–512
Lynch JP, Ho MD (2005) Rhizoeconomics: carbon costs of phosphorus acquisition. Plant Soil 269:45–56
Marschner P, Rengel Z (2012) Nutrient availability in soils. In: Marschner P (ed) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Mimmo T, Hann S, Jaitz L, Cesco S, Gessa CE, Puschenreiter M (2011) Time and substrate dependent exudation of carboxylates by Lupinus albus L. and Brassica napus L. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:1272–1278
Nunes FC, Miyazawa M, Pavan MA (2009) Organic acid effect on calcium uptake by the wheat roots. Braz Arch Biol Techn 52:11–15
Oburger E, Kirk GJD, Wenzel WW, Puschenreiter M, Jones DL (2009) Interactive effects of organic acids in the rhizosphere. Soil Biol Biochem 41:449–457
Page V, Weisskopf L, Feller U (2006) Heavy metals in white lupin: uptake, root-to-shoot transfer and redistribution within the plant. New Phytol 171:329–341
Pang JY, Ryan MH, Tibbett M, Cawthray GR, Siddique KHM, Bolland MDA, Denton MD, Lambers H (2010a) Variation in morphological and physiological parameters in herbaceous perennial legumes in response to phosphorus supply. Plant Soil 331:241–255
Pang JY, Tibbett M, Denton MD, Lambers H, Siddique KHM, Bolland MDA, Revell CK, Ryan MH (2010b) Variation in seedling growth of 11 perennial legumes in response to phosphorus supply. Plant Soil 328:133–143
Pang JY, Yang JY, Lambers H, Tibbett M, Siddique KHM, Ryan MH (2015) Physiological and morphological adaptations of herbaceous perennial legumes allow differential access to sources of varyingly soluble phosphate. Physiol Plant 154:511–525
Rengel Z, Marschner P (2005) Nutrient availability and management in the rhizosphere: exploiting genotypic differences. New Phytol 168:305–312
Richardson AE, Lynch JP, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Smith FA, Smith SE, Harvey PR, Ryan MH, Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H, Oberson A, Culvenor RA, Simpson RJ (2011) Plant and microbial strategies to improve the phosphorus efficiency of agriculture. Plant Soil 349:121–156
Ron Vaz MD, Edwards AC, Shand CA, Cresser MS (1993) Phosphorus fractions in soil solution: influence of soil acidity and fertiliser additions. Plant Soil 148:175–183
Ryan MH, Tibbett M, Edmonds-Tibbett T, Suriyagoda LDB, Lambers H, Cawthray GR, Pang J (2012) Carbon trading for phosphorus gain: the balance between rhizosphere carboxylates and arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in plant phosphorus acquisition. Plant Cell Environ 35:2170–2180
Sastre J, Sahuquillo A, Vidal M, Rauret G (2002) Determination of cd, cu, Pb and Zn in environmental samples: microwave-assisted total digestion versus aqua regia and nitric acid extraction. Anal Chim Acta 462:59–72
van Scholl L, Hoffland E, van Breemen N (2006) Organic anion exudation by ectomycorrhizal fungi and Pinus sylvestris in response to nutrient deficiencies. New Phytol 170:153–163
Simpson RJ, Oberson A, Culvenor RA, Ryan MH, Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H, Lynch JP, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Smith FA, Smith SE, Harvey PR, Richardson AE (2011) Strategies and agronomic interventions to improve the phosphorus-use efficiency of farming systems. Plant Soil 349:89–120
Simpson RJ, Stefanski A, Marshall DJ, Moore AD, Richardson AE (2015) Management of soil phosphorus fertility determines the phosphorus budget of a temperate grazing system and is the key to improving phosphorus efficiency. Agric Ecosyst Environ 212:263–277
Suriyagoda LDB, Ryan MH, Renton M, Lambers H (2010) Multiple adaptive responses of Australian native perennial legumes with pasture potential to grow in phosphorus- and moisture-limited environments. Ann Bot 105:755–767
Suriyagoda LDB, Lambers H, Renton M, Ryan MH (2012a) Growth, carboxylate exudates and nutrient dynamics in three herbaceous perennial plant species under low, moderate and high phosphorus supply. Plant Soil 358:100–112
Suriyagoda LDB, Ryan MH, Renton M, Lambers H (2012b) Adaptive shoot and root responses collectively enhance growth at optimum temperature and limited phosphorus supply of three herbaceous legume species. Ann Bot 110:959–968
Suriyagoda LDB, Ryan MH, Renton M, Lambers H (2014) Plant responses to limited moisture and phosphorus availability: a meta-analysis. Adv Agron 124:143–200
Ulrich AE, Malley DF, Watts PD (2016) Lake Winnipeg Basin: advocacy, challenges and progress for sustainable phosphorus and eutrophication control. Sci Total Environ 542:1030–1039
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157:423–447
Veneklaas EJ, Stevens J, Cawthray GR, Turner S, Grigg AM, Lambers H (2003) Chickpea and white lupin rhizosphere carboxylates vary with soil properties and enhance phosphorus uptake. Plant Soil 248:187–197
Vu DT, Tang C, Armstrong RD (2008) Changes and availability of P fractions following 65 years of P application to a calcareous soil in a Mediterranean climate. Plant Soil 304:21–33
Wang L, Ruiz-Agudo E, Putnis CV, Menneken M, Putnis A (2012) Kinetics of calcium phosphate nucleation and growth on calcite: implications for predicting the fate of dissolved phosphate species in alkaline soils. Environ Sci Technol 46:834–842
Wang X, Tang C, Mahony S, Baldock JA, Butterly CR (2015) Factors affecting the measurement of soil pH buffer capacity: approaches to optimize the methods. Eur J Soil Sci 66:53–64
Wouterlood M, Cawthray GR, Scanlon TT, Lambers H, Veneklaas EJ (2004a) Carboxylate concentrations in the rhizosphere of lateral roots of chickpea (Cicer arietinum) increase during plant development, but are not correlated with phosphorus status of soil or plants. New Phytol 162:745–753
Wouterlood M, Cawthray GR, Turner S, Lambers H, Veneklaas EJ (2004b) Rhizosphere carboxylate concentrations of chickpea are affected by genotype and soil type. Plant Soil 261:1–10
Yanai RD (1991) Soil solution phosphorus dynamics in a whole-tree-harvested northern hardwood forest. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55:1746–1752
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41301570), the West Light Foundation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tim S. George.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 12.7 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Peng, Q., Wang, X. et al. Growth, morphological and physiological responses of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) to phosphorus supply in two alkaline soils. Plant Soil 416, 565–584 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3242-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3242-9