Abstract
Aims
Subtropical ecosystems are receiving unprecedented changes in temperature as a consequence of anthropogenic activities, which potentially affects soil respiration (R s) and carbon (C) sequestration. Due to the large amounts of C store and cycle in subtropical forests, investigations about how R s and C sequestration respond to warming will be critical for our understanding of future global-scale climate and biogeochemical cycling.
Methods
In this study, we transferred soil samples and plant seedlings collected from a mixed forest to the growth chambers in two sites (300 m and 30 m a.s.l.), which induced an artificial warming of ca. 1 °C between the two corresponding forest mesocosms. We tested whether the modification of abiotic factors induced by the downward translocation could alter R s and soil C sequestration. We also investigated the effects on the biotic factors by including root biomass and soil microbial biomass.
Results
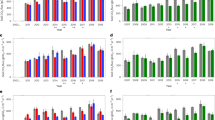
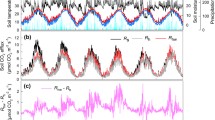
Our results showed that R s was greater in the warm site than in the control site, which were related to the higher aboveground biomass, litterfall and root biomass. R s showed a significantly positive exponential relationship with soil temperature. The downward translocation tended to decrease soil C sequestration, which was attributed to the decreased C use efficiency of soil microorganisms and increased root growth under downward translocation.
Conclusion
R s responded strongly to downward translocation, suggesting that climate warming exacerbated R s and tended to reduce soil C sequestration. The ability of subtropical forests to act as CO2 sink may be reduced under climate warming.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard V, Robin C, Newton PCD, Lieffering M, Soussana JF (2006) Short and long-term effects of elevated CO2 on Lolium perenne rhizodeposition and its consequences on soil organic matter turnover and plant N yield. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1178–1187
Allen LH, Vu JC (2009) Carbon dioxide and high temperature effects on growth of young orange trees in a humid, subtropical environment. Agric For Meteorol 149:820–830
Allison SD, Wallenstein MD, Bradford MA (2010) Soil-carbon response to warming dependent on microbial physiology. Nat Geosci 3:336–340
Antonarakis AS (2014) Uncertainty in initial forest structure and composition when predicting carbon dynamics in a temperate forest. Ecol Model 291:134–141
Bais HP, Weir TL, Perry LG, Gilroy S, Vivanco JM (2006) The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:233–266
Bardgett RD (2011) Plant-soil interactions in a changing world. F1000 biology reports 3: 16–16.
Bonan GB (2008) Forests and climate change: forcings, feedbacks, and the climate benefits of forests. Science 320:1444–1449
Buchmann N (2000) Biotic and abiotic factors controlling soil respiration rates in Picea abies stands. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1625–1635
Cavaleri MA, Reed SC, Smith WK, Wood TE (2015) Urgent need for warming experiments in tropical forests. Glob Chang Biol 21:2111–2121
Conant RT, Klopatek JM, Klopatek CC (2000) Environmental factors controlling soil respiration in three semiarid ecosystems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:383–390
Davidson EA, Janssens IA (2006) Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition and feedbacks to climate change. Nature 440:165–173
Deng Q, Zhou GY, Liu JX, Liu SZ, Duan HL, Zhang DQ (2010) Responses of soil respiration to elevated carbon dioxide and nitrogen addition in young subtropical forest ecosystems in China. Biogeosciences 7:315–328
Drake JE, Gallet-Budynek A, Hofmockel KS, Bernhardt ES, Billings SA, Jackson RB, Johnsen KS, Lichter J, McCarthy HR, McCormack ML (2011) Increases in the flux of carbon belowground stimulate nitrogen uptake and sustain the long-term enhancement of forest productivity under elevated CO2. Ecol Lett 14:349–357
Erhagen B, Ilstedt U, Nilsson MB (2015) Temperature sensitivity of heterotrophic soil CO2 production increases with increasing carbon substrate uptake rate. Soil Biol Biochem 80:45–52
Escolar C, Maestre FT, Rey A (2015) Biocrusts modulate warming and rainfall exclusion effects on soil respiration in a semi-arid grassland. Soil Biol Biochem 80:9–17
Fang X, Zhou GY, Li YL, Liu SZ, Chu GW, Xu ZH, Liu JX (2016) Warming effects on biomass and composition of microbial communities and enzyme activities within soil aggregates in subtropical forest. Biol Fertil Soils 52:353–365
Flanagan LB, Sharp EJ, Letts MG (2013) Response of plant biomass and soil respiration to experimental warming and precipitation manipulation in a Northern Great Plains grassland. Agric For Meteorol 173:40–52
Hagerty SB, van Groenigen KJ, Allison SD, Hungate BA, Schwartz E, Koch GW, Kolka RK, Dijkstra P (2014) Accelerated microbial turnover but constant growth efficiency with warming in soil. Nat Clim Chang 4:903–906
Hirsch AM, Bauer WD, Bird DM, Cullimore J, Tyler B, Yoder JI (2003) Molecular signals and receptors: controlling rhizosphere interactions between plants and other organisms. Ecology 84:858–868
Inclán R, De la Torre D, Benito M, Rubio A (2007) Soil CO2 efflux in a mixed pine-oak forest in Valsaín (Central Spain). Sci World J 7:166–174
Kirschbaum MU (1995) The temperature dependence of soil organic matter decomposition, and the effect of global warming on soil organic C storage. Soil Biol Biochem 27:753–760
Knorr W, Prentice IC, House JI, Holland EA (2005) Long-term sensitivity of soil carbon turnover to warming. Nature 433:298–301
Li YY, Liu JX, Zhou GY, Huang WJ, Duan HL (2016) Warming effects on photosynthesis of subtropical tree species: a translocation experiment along an altitudinal gradient. Sci Rep-UK 6. doi:10.1038/srep24895
Liang G, Liu X, Chen X, Qiu Q, Zhang D, Chu G, Liu J, Liu S, Zhou G (2013) Response of soil respiration to acid rain in forests of different maturity in southern China. PLoS One 8(4):e62207. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062207
Lin JJ, Zhu B, Cheng WX (2015) Decadally cycling soil carbon is more sensitive to warming than faster-cycling soil carbon. Glob Chang Biol 21:4602–4612
Liu L, King JS, Giardina CP, Booker FL (2009) The influence of chemistry, production and community composition on leaf litter decomposition under elevated atmospheric CO2 and tropospheric O3 in a northern hardwood ecosystem. Ecosystems 12:401–416
Liu L, Hu C, Yang P, Ju Z, Olesen JE, Tang J (2015) Effects of experimental warming and nitrogen addition on soil respiration and CH4 fluxes from crop rotations of winter wheat–soybean/fallow. Agric For Meteorol 207:38–47
Lloyd J, Taylor JA (1994) On the temperature-dependence of soil respiration. Funct Ecol 8:315–323
Luo Y (2007) Terrestrial carbon-cycle feedback to climate warming. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 38:683–712
Majdi H, öhrvik J (2004) Interactive effects of soil warming and fertilization on root production, mortality, and longevity in a Norway spruce stand in Northern Sweden. Glob Chang Biol 10:182–188
Manzoni S, Taylor P, Richter A, Porporato A, Ågren GI (2012) Environmental and stoichiometric controls on microbial carbon-use efficiency in soils. New Phytol 196:79–91
Mills RT, Gavazov KS, Spiegelberger T, Johnson D, Buttler A (2014) Diminished soil functions occur under simulated climate change in a sup-alpine pasture, but heterotrophic temperature sensitivity indicates microbial resilience. Sci Total Environ 473:465–472
Moyano FE, Kutsch WL, Rebmann C (2008) Soil respiration fluxes in relation to photosynthetic activity in broad-leaf and needle-leaf forest stands. Agric For Meteorol 148:135–143
Peng F, You QG, Xu MH, Zhou XH, Wang T, Guo J, Xue X (2015) Effects of experimental warming on soil respiration and its components in an alpine meadow in the permafrost region of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Eur J Soil Sci 66:145–154
Phillips RP, Finzi AC, Bernhardt ES (2011) Enhanced root exudation induces microbial feedbacks to N cycling in a pine forest under long-term CO2 fumigation. Ecol Lett 14:187–194
Rustad L, Campbell J, Marion G, Norby R, Mitchell M, Hartley A, Cornelissen J, Gurevitch J (2001) A meta-analysis of the response of soil respiration, net nitrogen mineralization, and aboveground plant growth to experimental ecosystem warming. Oecologia 126:543–562
Schindlbacher A, Rodler A, Kuffner M, Kitzler B, Sessitsch A, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S (2011) Experimental warming effects on the microbial community of a temperate mountain forest soil. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1417–1425
Schindlbacher A, Wunderlich S, Borken W, Kitzler B, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, Jandl R (2012) Soil respiration under climate change: prolonged summer drought offsets soil warming effects. Glob Chang Biol 18:2270–2279
Sheik CS, Beasley WH, Elshahed MS, Zhou X, Luo Y, Krumholz LR (2011) Effect of warming and drought on grassland microbial communities. ISME J 5:1692–1700
Shen ZX, Li YL, Fu G (2015) Response of soil respiration to short-term experimental warming and precipitation pulses over the growing season in an alpine meadow on the Northern Tibet. Appl Soil Ecol 90:35–40
Tang XL, Zhou GY, Liu SG, Zhang DQ, Liu SZ, Li J, Zhou CY (2006) Dependence of soil respiration on soil temperature and soil moisture in successional forests in southern China. J Integr Plant Biol 48:654–663
Vance E, Brookes P, Jenkinson D (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Wan S, Luo Y, Wallace L (2002) Changes in microclimate induced by experimental warming and clipping in tallgrass prairie. Glob Chang Biol 8:754–768
Wang LX, Niu SL, Good SP, Soderberg K, McCabe MF, Sherry RA, Luo YQ, Zhou XH, Xia JY, Caylor KK (2013) The effect of warming on grassland evapotranspiration partitioning using laser-based isotope monitoring techniques. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 111:28–38
Wang X, Liu L, Piao S, Janssens IA, Tang J, Liu W, Chi Y, Wang J, Xu S (2014) Soil respiration under climate warming: differential response of heterotrophic and autotrophic respiration. Glob Chang Biol 20:3229–3237
Wu J, Liu Z, Huang G, Chen D, Zhang W, Shao Y, Wan S, Fu S (2014) Response of soil respiration and ecosystem carbon budget to vegetation removal in eucalyptus plantations with contrasting ages. Sci Rep-UK 4:6262. doi:10.1038/srep06262
Yan J, Liu X, Tang X, Yu G, Zhang L, Chen Q, Li K (2012) Substantial amounts of carbon are sequestered during dry periods in an old-growth subtropical forest in South China. J For Res 18:21–30
Yan J, Zhang Y, Yu G, Zhou G, Zhang L, Li K, Tan Z, Sha L (2013) Seasonal and inter-annual variations in net ecosystem exchange of two old-growth forests in southern China. Agric For Meteorol 182:257–265
Yu G, Chen Z, Piao S, Peng C, Ciais P, Wang Q, Li X, Zhu X (2014) High carbon dioxide uptake by subtropical forest ecosystems in the east Asian monsoon region. P Natl Acad Sci USA 111:4910–4915
Zhou G, Wei X, Luo Y, Zhang M, Li Y, Qiao Y, Liu H, Wang C (2010) Forest recovery and river discharge at the regional scale of Guangdong Province, China. Water Resour Res 46:W09503
Zhou G, Wei X, Wu Y, Liu S, Huang Y, Yan J, Zhang D, Zhang Q, Liu J, Meng Z (2011a) Quantifying the hydrological responses to climate change in an intact forested small watershed in Southern China. Glob Chang Biol 17:3736–3746
Zhou Y, Tang J, Melillo JM, Butler S, Mohan JE (2011b) Root standing crop and chemistry after six years of soil warming in a temperate forest. Tree Physiol 31:707–717
Zhou G, Houlton BZ, Wang W, Huang W, Xiao Y, Zhang Q, Liu S, Cao M, Wang X, Wang S (2014) Substantial reorganization of China’s tropical and subtropical forests: based on the permanent plots. Glob Chang Biol 20:240–250
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31370530, 31570482 and 31400382).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Per Ambus.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhou, G., Huang, W. et al. Potential effects of warming on soil respiration and carbon sequestration in a subtropical forest. Plant Soil 409, 247–257 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2966-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2966-2