Abstract
Aims
This study of a maize-white lupin model cropping system was conducted to investigate the effects of rhizosphere-sharing of white lupin, a P-efficient plant, on growth and P accumulation of maize under different P rates and forms in two contrasting soils.
Methods
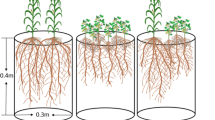
With Regosol and Andosol, a 42-day pot experiment was conducted for 0P (no P addition), 50Pi, 100Pi (50 and 100 mg P kg−1 soil by NaHPO4⋅2H2O respectively), and 100Po (100 mg P kg−1 soil by phytate). Plant growth, P uptake, rhizosphere pH, and different P fractions were investigated.
Results
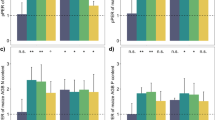
Complementary effects of intercropping for maize were observed in Regosol, but not in Andosol. Total P uptake by intercropped maize in 0P, 50Pi, and 100Po was elevated by 46, 37, and 65 %, respectively, compared to when it was grown as a monoculture. White lupin mobilized P from sparingly soluble forms. Thereby, maize plant enhanced its P accumulation as a result of access to these two fractions in mixed culture in Regosol, where strong root intermingling occurred among intercropped plants.
Conclusions
Results suggest that the P mobilization strategy of white lupin from sparingly soluble P pools in soil can enhance the P acquisition efficiency of coexisting maize with P facilitation in this intercropping occurring in the direction of white lupin to maize. Achieving enhanced growth and P uptake by P-inefficient species in intercropping with white lupin is dependent on the type of soil in which those plants are grown.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MA, Pate JS (1992) Availability of organic and inorganic forms of phosphorus to lupins (Lupinus spp.). Plant Soil 145:107–113
Ae N, Arihara J, Okada K, Yoshihara T, Johansen C (1990) Phosphorus uptake by pigeon pea and its role in cropping systems of the Indian subcontinent. Science 248:477–480
Bowman RA, Cole CV (1978) Transformation of organic phosphorus substrates in soil as evaluated by NaHCO3 extractions. Soil Sci 125:49–54. doi:10.1097/00010694-197801000-00008
Cordell D, Drangert JO, White S (2009) The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Global Environ Chang 19:292–305
Cu S, Hutson J, Schuller KA (2005) Mixed culture of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with white lupin (Lupinus albus L.) improves the growth and phosphorus nutrition of the wheat. Plant Soil 272:143–151. doi:10.1007/s11104-004-4336-8
Dawson CJ, Hilton J (2011) Fertiliser availability in a resource-limited world: production and recycling of nitrogen and phosphorus. Food Policy 36:14–22
Dinkelaker B, Romheld V, Marschner H (1989) Citric acid excretion and precipitation of calcium citrate in the rhizosphere of white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Plant Cell Environ 12:285–292. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.1989.tb01942.x
Gardner WK, Boundy KA (1983) The acquisition of phosphorus by Lupinus albus L. IV. The effect of interplanting wheat and white lupin on the growth and mineral composition of the two species. Plant Soil 70:391–402
Gardner WK, Parbery DG, Barber DA (1981) Proteoid root morphology and function in Lupinus albus. Plant Soil 60:143–147
Gardner WK, Barber DA, Parbery DG (1983) The acquisition of phosphorus by Lupinus albus L. III. The probable mechanism by which phosphorus movement in the soil/root interface is enhanced. Plant Soil 70:107–124
George TS, Grogory PJ, Robinson JS, Buresh RJ (2002a) Changes in phosphorus concentrations and pH in the rhizosphere of some agroforestry and crop species. Plant Soil 246:65–73
George TS, Gregory PJ, Wood M, Read D, Buresh RJ (2002b) Phosphatase activity and organic acids in the rhizosphere of potential agroforestry species and maize. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1487–1494
George TS, Turner BL, Gregory PJ, Cade-Menun BJ, Richardson AE (2006) Depletion of organic phosphorus from oxisols in relation to phosphatase activities in the rhizosphere. Eur J Soil Sci 57:47–57. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2006.00767.x
Gerke J (1992) Phosphate, aluminium and iron in the soil solution of three different soils in relation to varying concentration of citric acid. Z PflansBodenkunde 155:339–343. doi:10.1002/jpln.19921550417
Gerke J, Romer W, Junk A (1994) The excretion of citric and malic acid by proteoid roots of Lupinusalbus L.: effects of soil solution concentration of phosphate, iron, and aluminium in the proteoid rhizosphere samples of an oxisol and luvisol. Z PflansBodenkunde 157:289–294. doi:10.1002/jpln.19941570408
Gilbert N (2009) The disappearing nutrient. Nature 461:716–718. doi:10.1038/461716a
Gunes A, Bagci EG, Inal A (2007) Interspecific facilitative root interactions and rhizosphere effects on phosphorus and iron nutrition between mixed grown chickpea and barley. J Plant Nutr 30:1455–1469. doi:10.1080/01904160701555648
Hajabbasi MA, Schumacher TE (1994) Phosphorus effects on root growth and development in two maize genotypes. Plant Soil 158:39–46
Hassan HM, Marschner P, McNeill A, Tang C (2012) Growth P uptake in grain legumes and changes in rhizosphere soil P pools. Biol Fertil Soils 48:151–159. doi:10.1007/s00374-011-0612-y
Hedley MJ, Stewart JWB, Chauhan BS (1982) Changes in inorganic and organic soil phosphorus fractions by cultivation practices and by laboratory incubation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46:970–976. doi:10.2136/sssaj1982.03615995004600050017x
Hinsinger P (2001) Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: a review. Plant Soil 237:173–195
Hinsinger P, Plassard C, Tang C, Jaillard B (2003) Origins of root mediated pH changes in the rhizosphere and their responses to environmental constraints: a review. Plant Soil 248:43–59
Hinsinger P, Betencourt E, Bernard L, Brauman A, Plassard C, Shen J, Tang X, Zhang F (2011) P for two, sharing a scarce resource - soil phosphorus acquisition in the rhizosphere of intercropped species. Plant Physiol 156:1078–1086
Hirata H, Watanabe K, Fukushima K, Aoki M, Imamura R, Takahashi M (1999) Effect of continues application of farmyard manure and inorganic fertilizer for 9 years on changes in phosphorus compounds in plow layer of an upland Andosol. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 45:577–590
Hocking PJ, Randall PJ (2001) Better growth and phosphorus nutrition of sorghum and wheat following organic acid secreting crops. In: Horst WJ, Schenk MK, Burkert A, Claassen N, Flessa H, Frommer WB, Goldbach H, Olfs HW, Romheld V, Sattlemacher B, Schmidhalter U, Schubert S, Wiren NV, Wittenmayer L (eds) Plant nutrition food security and sustainability of agro-ecosystems through basic and applied research. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 548–549
Kamh M, Horst WJ, Amer F, Mostafa H, Maier P (1999) Mobilization of soil and fertilizer phosphate by cover crops. Plant Soil 211:19–27
Keerthisinghe G, Hocking PJ, Ryan PR, Delhaize E (1998) Effect of phosphorus supply on the formation and function of proteoid roots of white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Plant Cell Environ 21:467–478. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3040.1998.00300.x
Lambers H, Chapin FS III, Pons TL (1998) Plant physiological ecology. Springer, New York
Lambers H, Shane MW, Cramer MD, Pearse S, Veneklaas E (2006) Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits. Ann Bot 98:693–713. doi:10.1093/aob/mcl114
Lambers H, Clements JC, Nelson MN (2013) How a phosphorus-acquisition strategy based on carboxylate exudation powers the success and agronomic potential of lupines (Lupinus, Fabaceae). Am J Bot 100:263–288. doi:10.3732/ajb.1200474
Li CJ, Liang RX (2005) Root cluster formation and citrate exudation of white lupin (Lupinus albus L.) as related to phosphorus availability. J Integr Plant Biol 47:172–177. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7909.2005.00012.x
Li M, Shinano T, Tadano T (1997) Distribution of exudates of lupin roots in the rhizosphere under phosphorus deficient conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 43:237–245. doi:10.1080/00380768.1997.10414731
Li L, Tang C, Rengel Z, Zhang F (2003) Chickpea facilitates phosphorus uptake by intercropped wheat from an organic phosphorus source. Plant Soil 248:297–303
Li SM, Li L, Zhang FS, Tang C (2004) Acid phosphatase role in chickpea/maize intercropping. Ann Bot 94:297–303
Li L, Li S, Sun J, Zhou L, Bao X, Zhang H, Zhang F (2007) Diversity enhances agricultural productivity via rhizosphere phosphorus facilitation on phosphorus-deficient soils. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:11192–11196
Li H, Shen J, Zhang F, Clairotte M, Drevon JJ, Le Cadre E, Hinsinger P (2008) Dynamics of phosphorus fractions in the rhizosphere of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and durum wheat (Triticum turgidum durum L.) grown in monocropping and intercropping systems. Pant Soil 312:139–150. doi:10.1007/s11104-007-9512-1
Lukito HP, Kouno K, Ando T (1998) Phosphorus requirements of microbial biomass in a Regosol and an Andosol. Soil Biol Biochem 30:865–872
Mollier A, Pellerin S (1999) Maize root system growth and development as influenced by phosphorus deficiency. J Exp Bot 50:487–497
Murphy J, Reley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Neumann G, Römheld V (1999) Root excretion of carboxylic acids and protons in phosphorus-deficient plants. Plant Soil 211:121–130
Neumann G, Massonneau A, Martinoia E, Römheld V (1999) Physiological adaptations to phosphorus deficiency during proteoid root development in white lupin. Planta 208:373–382
Neumann G, Massonneau A, Langlade N, Dinkelaker B, Hengeler C, Römheld V, Martinoia E (2000) Physiological aspects of cluster root function and development in phosphorus-deficient white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Ann Bot 85:909–919. doi:10.1006/anbo.2000.1135
Nuruzzaman M, Lambers H, Bolland MDA, Veneklaas EJ (2006) Distribution of carboxylates and acid phosphatase and depletion of different phosphorus fractions in the rhizosphere of a cereal and three grain legumes. Plant Soil 281:109–120. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-3936-2
Ozawa K, Osaki M, Matsui H, Honma M, Tadano T (1995) Purification and properties of acid phosphatase secreted from lupin roots under phosphorus-deficiency conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 41:461–469. doi:10.1080/00380768.1995.10419608
Pearse SJ, Veneklaas EJ, Cawthray G, Bolland MDA, Lambers H (2006) Carboxylate release of wheat, canola and 11 grain legume species as affected by phosphorus status. Plant Soil 288:127–139. doi:10.1007/s11104-006-9099-y
Raghothama KG (1999) Phosphate acquisition. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:665–693
Richardson AE, Hadobas PA, Hayes JE (2001) Extracellular secretion of Aspergillus phytase from Arabidopsis roots enables plants to obtain phosphorus from phytate. Plant J 25:641–649
Richardson AE, Barea JM, McNeill AM, Prigent-Combaret C (2009) Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil 321:305–339. doi:10.1007/s11104-009-9895-2
Richardson AE, Lynch JP, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Smith FA, Smith SE, Harvey PR, Ryan MH, Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H, Oberson A, Culvenor RA, Simpson RJ (2011) Plant and microbial strategies to improve the phosphorus efficiency of agriculture. Plant Soil 349:121–156. doi:10.1007/s11104-011-0950-4
Sekiya K (1970) Phosphoric acid. In: Ishizawa S (ed) Analysis methods for measuring soil fertility. Yokendo Co. Ltd, Tokyo, pp 251–253
Shane MW, De Vos M, De Roock S, Lambers H (2003) Shoot P status regulates cluster-root growth and citrate exudation in Lupinus albus grown with a divided root system. Plant Cell Environ 26:265–273. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3040.2003.00957.x
Shen J, Li H, Neumann G, Zhang F (2005) Nutrient uptake, cluster root formation and exudation of protons and citrate in Lupinus albus as affected by localized supply of phosphorus in a split-root system. Plant Sci 168:837–845
Simpson RJ, Oberson A, Culvenor RA, Ryan MH, Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H, Lynch JP, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Smith FA, Smith SE, Harvey PR, Richardson AE (2011) Strategies and agronomic interventions to improve the phosphorus-use efficiency of farming systems. Plant Soil 349:89–120. doi:10.1007/s11104-011-0880-1
Song YN, Zhang FS, Marschner P, Fan FL, Gao HM, Bao XG, Sun JH, Li L (2007) Effect of intercropping on crop yield and chemical and microbiological properties in rhizosphere of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), maize (Zea mays L.), and faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Biol Fertil Soils 43:565–574. doi:10.1007/s00374-006-0139-9
Stewart JWB, Tiessen H (1987) Dynamics of soil organic phosphorus. Biogeochemistry 4:41–60
Tadano T, Sakai H (1991) Secretion of acid phosphatase by the roots of several crop species under phosphorus-deficient conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 37:129–140. doi:10.1080/00380768.1991.10415018
Tang C, Barton L, Rapheal C (1997) Pasture legume species differ in their capacity to acidify a low-buffer soil. Aust J Agric Res 49:53–58
Tiessen H, Moir JO (1993) Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. In: Carter MR (ed) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp 104–107
Tiessen H, Salcedo IH, Sampio EVSB (1992) Nutrient and soil organic matter dynamics under shifting cultivation in semi arid northeastern Brazil. Agric Ecosyst Environ 38:139–151
Vance CP (2001) Symbiotic nitrogen fixation and phosphorus acquisition. Plant nutrition in a world of declining renewable resources. Plant Physiol 127:390–397
Veneklaas EJ, Stevens J, Cawthray GR, Turner S, Grigg AM, Lambers H (2003) Chickpea and white lupin rhizosphere carboxylates vary with soil properties and enhance phosphorus uptake. Plant Soil 248:187–197
Wang Z, Shen J, Zhang F (2006) Cluster roots formation, carboxylate exudation and proton release of Lupinus pilosus Murr. as affected by medium pH and P deficiency. Plant Soil 287:247–256. doi:10.1007/s11104-006-9071-x
Wang Y, Marschner P, Zhang F (2012) Phosphorus pools and other soil properties in the rhizosphere of wheat and legumes growing in three soils in monoculture or as a mixture of wheat and legume. Plant Soil 354:283–298. doi:10.1007/s11104-011-1065-7
Wasaki J, Yamamura T, Shinano T, Osaki M (2003) Secreted acid phosphatase is expressed in cluster roots of lupin in response to phosphorus deficiency. Plant Soil 248:129–136
Acknowledgments
This research was partly supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF), Japan through a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (23688010) and a research project entitled: “Development of technologies for mitigation and adaptation to climate change in Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Hammond.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dissanayaka, D.M.S.B., Maruyama, H., Masuda, G. et al. Interspecific facilitation of P acquisition in intercropping of maize with white lupin in two contrasting soils as influenced by different rates and forms of P supply. Plant Soil 390, 223–236 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2392-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2392-x