Abstract
Backgrouand and aim
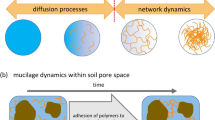
Myxospermous seeds become bound by mucilage upon hydration and this trait is ecologically important. Major impacts could be enhancing seed-soil contact and improving water retention, which we quantify in this study.
Methods
Myxospermous or demucilaged seeds of Capsella bursa-pastoris L. Medik. (shepherd’s purse) were added to a test sandy clay loam at seed : soil densities of 5 and 10 % [w/w]. The soil water retention and hydraulic conductivity were assessed. Soil rheology was also assessed using extracted mucilage only amendment at 0.5 and 1 % [w/w].
Results
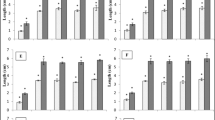
Shepherd’s purse seeds increased soil water retention and reduced soil hydraulic conductivity for myxospermous and demucilaged seeds. Soil rheological properties (complex shear modulus, viscosity and yield stress) increased in response to seed mucilage addition, and became more pronounced as soil dried. The mucilage had greatest impact on the yield stress compared to the other rheology parameters.
Conclusions
The densities of myxospermous and non-myxospermous seeds, and mucilage tested here reflect that may be found naturally in soil seedbanks. The findings provide the first evidence that the soil seedbank provided from a wild arable species may regulate the soil water retention and enhance soil stability, and that this capacity is greater for myxospermous seeds.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LVR:
-
linear viscoelastic region
References
Akhter J, Mahmood K, Malik KA, Mardan A, Ahmad M, Iqbal MM (2004) Effects of hydrogel amendment on water storage of sandy loam and loam soils and seedling growth of barley, wheat and chickpea. Plant Soil Environ 50:463–469
Al-Darby AM (1996) The hydraulic properties of a sandy soil treated with gel-forming soil conditioner. Soil Technol 9:15–28
Andry H, Yamamoto T, Irie T, Moritani S, Inoue M, Fujiyama H (2009) Water retention, hydraulic conductivity of hydrophilic polymers in sandy soil as affected by temperature and water quality. J Hydrol 373:177–183
Barré P, Hallett PD (2009) Rheological stabilization of wet soils by model root and fungal exudates depends on clay mineralogy. Eur J Soil Sci 60:525–538
Begg GS, Wishart J, Young MW, Squire GR, Iannetta PPM (2011) Genetic structure among arable populations of Capsella bursa-pastoris is linked to functional traits and in-field conditions. Ecography 35:446–457
Bhardwaj AK, Shainberg I, Goldstein D, Warrington DN, Levy GJ (2007) Water retention and hydraulic conductivity of cross-linked polyacrylamides in sandy soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:406–412
Boult S, Hand VL, Lloyd JR, Vaughan DJ, Wilkins MJ (2008) Experimental studies of the influence of grain size, oxygen availability and organic carbon availability on bioclogging in porous media. Environ Sci Technol 42:1485–1491
Caesar-Tonthat TC (2002) Soil binding properties of mucilage produced by a basidiomycete fungus in a model system. Mycol Res 106:930–937
Deng W, Jeng D-S, Toorop PE, Squire GR, Iannetta PPM (2012) A mathematical model of mucilage expansion in myxospermous seeds of Capsella bursa-pastoris (shepherd’s purse). Ann Bot-Lond 109:419–427
Deng W, Iannetta PPM, Hallett PD, Toorop PE, Squire GR, Jeng D-S (2013) The rheological properties of the seed coat mucilage of Capsella bursa-pastoris L. Medik. (shepherd’s purse). Biorheology 50:57–67
Engelbrecht M, Bochet E, García-Fayos P (2014) Mucilage secretion: an adaptive mechanism to reduce seed removal by soil erosion? Biol J Linn Soc 111:241–251
Ghezzehei TA, Or D (2001) Rheological properties of wet soils and clays under steady and oscillatory stresses. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:624–637
Grubert M (1974) Studies on the distribution of myxospermy among seeds and fruits of angiospermae and its ecological importance. Acta Biol Venez 8:315–551
Grubert M (1981) Mucilage or gum in seeds and fruits of angiosperms: A review. Minerva Publikation, Műnchen
Gutterman Y (1993) Seed germination in desert plants (adaptations of desert organisms). Springer, Berlin
Hallett PD, Young IM (1999) Changes to water repellence of soil aggregates caused by substrate-induced microbial activity. Eur J Soil Sci 50:35–40
Hawes C, Begg GS, Squire GR, Iannetta PPM (2005) Individuals as the basic accounting unit in studies of ecosystem function: functional diversity in shepherd’s purse, Capsella. Oikos 109:521–534
Hurka H, Haase R (1982) Seed ecology of Capsella bursa-pastoris (Cruciferae): dispersal mechanisms and the soil seed bank. Flora 172:35–46
Iannetta PPM (2010) Capsella. In: Kole C (ed) Wild crop relatives: Genomic and breeding resources—oilseeds. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 37–62
Iannetta PPM, Begg GS, Valentine TA, Wishart J (2010) Sustainable disease control using weeds as indicators: Capsella bursa-pastoris and tobacco rattle virus. Weed Res 50:511–514
Jani GK, Shah DP, Prajaoati VD, Jain V (2009) Gums and mucilages: versatile excipients for pharmaceutical formulations. Asian J Pharma Sci 4:309–323
Karmakar S, Kushwaha RL (2007) Development and laboratory evaluation of a rheometer for soil visco-plastic parameters. J Terrramech 44:197–204
Leeds-Harrison PB, Youngs EG (1997) Estimating the hydraulic conductivity of aggregates conditioned by different tillage treatments from sorption measurements. Soil Tillage Res 41:141–147
Leeds-Harrison PB, Youngs EG, Uddin B (1994) A device for determining the sorptivity of soil aggregates. Eur J Soil Sci 45:269–272
McGovern HJ, Deeks LK, Hallett PD, Ritz K, Young IM (2000) A sterile environment for growing, and monitoring, micro-organisms under a range of soil matric potentials. Soil Biol Biochem 33:689–691
Morel JL, Habib L, Plantureux S, Guckert A (1991) Influence of maize root mucilage on soil aggregate stability. Plant Soil 136:111–119
Mostafa MB (2009) Experimental and numerical investigations of conceptual models for biological clogging of unsaturated soils. Carleton University, Ottawa
O’Neal AM (1952) A key fore valuating soil permeability by means of certain field clues. Soil Sci Soc Am J 16:312–315
Or D, Phutane S, Dechesne A (2007) Extracellular polymeric substances affecting pore-scale hydrologic conditions for bacterial activity in unsaturated soils. Vadose Zone J 6:298–305
Penfield S, Meissner RC, Shoue DA, Carpita NC, Bevan MW (2001) MYB61 is required for mucilage deposition and extrusion in the Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant Cell 13:2777–2791
Peng X, Hallett PD, Zhang B, Horn R (2011) Physical response of rigid and non-rigid soils to analogues of biological exudates. Eur J Soil Sci 62:676–684
Prado MM, Ferreira MMP, Sartori DJM (2006) Drying of seeds and gels. Dry Technol 24:281–292
Rezayati Charani P, Dehghani-Firouzabadi M, Afra E, Shakeri A (2013) Rheological characterization of high concentrated MFC gel from kenaf unbleached pulp. Cellulose 20:727–740
Thullner M, Schroth MH, Zeyer J, Kinzelbach W (2004) Modeling of a microbial growth experiment with bioclogging in a two-dimensional saturated porous media flow field. J Contam Hydrol 70:37–62
Toorop PE, Campos Cuerva R, Begg GS, Locardi B, Squire GR, Iannetta PPM (2012) Co-adaptation of seed dormancy and flowering time in the arable weed Capsella bursa-pastoris (shepherd’s purse). Ann Bot-Lond 109:481–489
Torrance JK (1999) Physical, chemical and mineralogical influences on the rheology of remoulded low-activity sensitive marine clay. Appl Clay Sci 14:199–223
Van Rheede van Oudtshoorn K, Van Rooyen MW (1999) Dispersal biology of desert plants. Springer Verlag, Berlin
White I, Sully MJ (1987) Macroscopic and microscopic capillary length and time scales from field infiltration. Water Resour Res 23:1514–1522
Yang X, Dong M, Huang Z (2010) Role of mucilage in the germination of Artemisia sphaerocephala (Asteraceae) achenes exposed to osmotic stress and salinity. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:131–135
Yang X, Baskin CC, Baskin JM, Liu G, Huang Z (2012a) Seed mucilage improves seedling emergence of a sand desert shrub. Plos ONE 7:e34597
Yang X, Baskin CC, Baskin JM, Zhang W, Huang Z (2012b) Degradation of seed mucilage by soil microflora promotes early seedling growth of a desert sand dune plant. Plant Cell Environ 35:872–883
Yang X, Baskin JM, Baskin CC, Huang Z (2012c) More than just a coating: ecological importance, taxonomic occurrence and phylogenetic relationships of seed coat mucilage. Perspect Plant Ecol, Evol Syst 14:434–442
Acknowledgments
PPMI and GRS are funded by the Scottish Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jeffrey Walck.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, W., Hallett, P.D., Jeng, DS. et al. The effect of natural seed coatings of Capsella bursa-pastoris L. Medik. (shepherd’s purse) on soil-water retention, stability and hydraulic conductivity. Plant Soil 387, 167–176 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2281-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2281-8