Abstract
Background and aims
The ionome (elemental composition) of grassland species has rarely been studied at the level of individual organs and little is known about effects of soil chemical properties on the ionome. Using the model oxalate plant Rumex obtusifolius, we asked how its biomass production and the distribution of elements between its organs is affected by soil chemical properties.
Methods
We established a pot experiment with R. obtusifolius planted in acidic non-contaminated control and in slightly acidic and alkaline soils anthropogenically contaminated by the risk elements As, Cd, Pb, and Zn. Both contaminated soils were untreated and treated by lime and superphosphate. We determined biomass production and the concentrations of elements in its organs.
Results
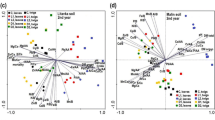
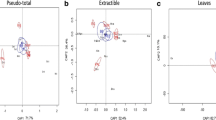
Biomass production was negatively related to the mobility of micro- and risk elements. Restricted transport of micro- and risk elements from belowground organs into leaves was recorded in untreated contaminated soils. In both lime-treated soils and in superphosphate-treated alkaline soil, elevated transport of micro- and risk elements from belowground organs into leaves was recorded in comparison to untreated contaminated soils. The lowest concentrations of micro- and risk elements were recorded in stems and seeds, followed by belowground organs and leaves.
Conclusions
R. obtusifolius is an As-, Cd-, Pb-, and Zn-excluder and is sensitive to high availability of micro- and risk elements in the soil. Soil chemical properties affect the distribution of essential elements within the plant greatly.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkorta I, Hernández-Allica J, Becerril JM, Amezaga I, Albizu I, Garbisu C (2004) Recent findings on the phytoremediation of soils contaminated with environmentally toxic heavy metals and metalloids such as zinc, cadmium, lead and arsenic. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 3:71–90
Allen SE (1989) Analysis of ecological materials, 2nd edn. Blackwell, Oxford
Alvarenga P, Goncalves AP, Fernandes RM, de Varennes A, Vallini G, Duarte E, Cunha-Queda AC (2008) Evaluation of composts and liming materials in the phytostabilization of a mine soil using perennial ryegrass. Sci Total Environ 406:43–56
Anonymous (1994) Public notice No. 13/1994 for the managemenet of soil protection. Czech Ministry of the Environment, Prague, In Czech
Anton A, Mathe-Gaspar G (2005) Factors affecting heavy metal uptake in plant selection for phytoremediation. Z Naturforsch C 60:244–246
Appenroth KJ, Gabrys H (2003) Ion antagonism between calcium and magnesium in phytochrome-mediated degradation of storage starch in Spirodela polyrhiza. Plant Sci 165:1261–1265
Baker AJM (1981) Accumulators and excluders—strategies in the response of plants to heavy-metals. J Plant Nutr 3:643–654
Barman SC, Sahu RK, Bhargava SK, Chaterjee C (2000) Distribution of heavy metals in wheat, mustard, and weed grown in field irrigated with industrial effluents. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 64:489–496
Barrutia O, Epelde L, Garcia-Plazaola JI, Garbisu C, Becerril JM (2009) Phytoextraction potential of two Rumex acetosa L. accessions collected from metalliferous and non-metalliferous sites: effect of fertilization. Chemosphere 74:259–264
Borůvka L, HuanWei C, Kozák J, Krištoufková S (1996) Heavy contamination of soil with cadmium, lead and zinc in the alluvium of the Litavka river. Rostl Výr 42:543–550
Bose S, Bhattacharyya AK (2008) Heavy metal accumulation in wheat plant grown in soil amended with industrial sludge. Chemosphere 70:1264–1272
Bose S, Chandrayan S, Rai V, Bhattacharyya AK, Ramanathan A (2008) Translocation of metals in pea plants grown on various amendment of electroplating industrial sludge. Bioresour Technol 99:4467–4475
Chen Q, Wong JWC (2006) Growth of Agropyron elongatum in a simulated nickel contaminated soil with lime stabilization. Sci Total Environ 366:448–455
Garcia-Salgado S, Garcia-Casillas D, Quijano-Nieto MA, Bonilla-Simon MM (2012) Arsenic and heavy metal uptake and accumulation in native plant species from soils polluted by mining activities. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:559–572
Gaweda M (2009) Heavy metal content in common sorrel plants (Rumex Acetosa L.) obtained from natural sites in Malopolska province. Pol J Environ Stud 18:213–218
Guleryuez G, Arslan H, Celik C, Gucer S, Kendall M (2008) Heavy metal content of plant species along Nilufer stream in industrialized Bursa City, Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut 195:275–284
Gupta S, Nayek S, Saha RN, Satpati S (2008) Assessment of heavy metal accumulation in macrophyte, agricultural soil, and crop plants adjacent to discharge zone of sponge iron factory. Environ Geol 55:731–739
Hann P, Trska C, Kromp B (2012) Effects of management intensity and soil chemical properties on Rumex obtusifolius in cut grasslands in Lower Austria. J Pest Sci 85:5–15
Hansch R, Mendel RR (2009) Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl). Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:259–266
Hejcman M, Strnad L, Hejcmanová P, Pavlů V (2012a) Response of plant species composition, biomass production and biomass chemical properties to high N, P and K application rates in Dactylis glomerata- and Festuca arundinacea-dominated grassland. Grass Forage Sci 67:488–506
Hejcman M, Vondráčková S, Müllerová V, Červená K, Száková J, Tlustoš P (2012b) Effect of quick lime and superphosphate additives on emergence and survival of Rumex obtusifolius seedlings in acid and alkaline soils contaminated by As, Cd, Pb, and Zn. Plant Soil Environ 58:561–567
Horák J, Hejcman M (2013) Use of trace elements from historical mining for alluvial sediment dating. Soil Water Res 8:77–86
Hrdličková J, Hejcman M, Křišťálová V, Pavlů V (2011) Production, size, and germination of broad-leaved dock seeds collected from mother plants grown under different nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium supplies. Weed Biol Manag 11:190–201
Hujerová R, Pavlů V, Hejcman M, Pavlů L, Gaisler J (2013) Effect of cutting frequency on above- and below-ground biomass production of Rumex alpinus, R. crispus, R. obtusifolius, and the Rumex hybrid (R. patienta x R. tianschanicus) in the seeding year. Weed Res 53:378–386
Jiang HM, Yang JC, Zhang JF (2007) Effects of external phosphorus on the cell ultrastructure and the chlorophyll content of maize under cadmium and zinc stress. Environ Pollut 147:750–756
Kabata-Pendias A (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Levy DB, Redente EF, Uphoff GD (1999) Evaluating the phytotoxicity of Pb-Zn tailings to big bluestem (Andropogon gerardii Vitman) and switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). Soil Sci 164:363–375
Lindström BEM, Frankow-Lindberg BE, Dahlin AS, Wivstad M, Watson CA (2013) Micronutrient concentrations in common and novel forage species and varieties grown on two contrasting soils. Grass Forage Sci 68:427–436
López-Lefebre LR, Rivero RM, Garcia PC, Sanches E, Ruiz JM, Romero L (2001) Effect of calcium on mineral nutrient uptake and growth of tobacco. J Sci Food Agric 81:1334–71338
Lorestani B, Cheraghi M, Yousefi N (2011) Accumulation of Pb, Fe, Mn, Cu and Zn in plants and choice of hyperaccumulator plant in the industrial town of Vian, Iran. Arch Biol Sci 63:739–745
Mahler RL (2004) Nutrients plants require for growth. CIS1124 Publishing University of Idaho College of Agricultural and Life Sciences. http://www.cals.uidaho.edu/edcomm/pdf/CIS/CIS1124.pdf. Accessed 16 Feb 2014
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic, London
Mehlich A (1984) Mehlich-3 soil test extractant—a modification of Mehlich-2 extractant. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 15:1409–1416
Miyagi A, Uchimiya M, Kawai-Yamada M, Uchimiya H (2013) Impact of aluminium stress on oxalate and other metabolites in Rumex obtusifolius. Weed Res 53:30–41
Pugh RE, Dick DG, Fredeen AL (2002) Heavy metal (Pb, Zn, Cd, Fe, and Cu) contents of plant foliage near the anvil range lead/zinc mine, Faro, Yukon Territory. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 52:273–279
Qiu Q, Wang YT, Yang ZY, Yuan JG (2011) Effects of phosphorus supplied in soil on subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in two Chinese flowering cabbage (Brassica parachinensis L.) cultivars differing in cadmium accumulation. Food Chem Toxicol 49:2260–2267
Quevauviller P (1998) Operationally defined extraction procedures for soil and sediment analysis—I. standardization. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 17:289–298
Salt DE, Baxter I, Lahner B (2008) Ionomics and the study of the plant ionome. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:709–733
Schwertfeger DM, Hendershot WH (2009) Determination of effective cation exchange capacity and exchange acidity by a one-step BaCl2 method. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73:737–743
Šrek P, Hejcman M, Kunzová E (2012) Effect of long-term cattle slurry and mineral N, P and K application on concentration of N, P, K, Ca, Mg, As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn in peeled potato tubers and peels. Plant Soil Environ 58:167–173
Strnad L, Hejcman M, Hejcmanová P, Křišťálová V, Pavlů V (2012) Performance and mortality of Rumex obtusifolius and R. crispus in managed grasslands are affected by nutrient availability. Folia Geobotanica 47:293–304
Sytar O, Kumar A, Latowski D, Kuczynska P, Strzalka K, Prasad MNV (2013) Heavy metal-induced oxidative damage, defense reactions, and detoxification mechanisms in plants. Acta Physiol Plant 35:985–999
ter Braak CJF, Smilauer P (2002) CANOCO reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user’s guide: software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). Microcomputer Power, Ithaca
Thompson K, Parkinson JA, Band SR, Spencer RE (1997) A comparative study of leaf nutrient concentrations in a regional herbaceous flora. New Phytol 136:679–689
Tlustoš P, van Dijk D, Száková J, Pavlíková D (1994) Cd and Zn release through the selected extractants. Rostl Výr 40:1107–1121
Tlustoš P, Száková J, Kořínek K, Pavlíková D, Hanč A, Balík J (2006) The effect of liming on cadmium, lead, and zinc uptake reduction by spring wheat grown in contaminated soil. Plant Soil Environ 53:16–24
Tolra RP, Poschenrieder C, Luppi B, Barcelo J (2005) Aluminium-induced changes in the profiles of both organic acids and phenolic substances underlie Al tolerance in Rumex acetosa L. Environ Exp Bot 54:231–238
Tyler G, Ström L (1995) Differing organic-acid exudation pattern explains calcifuge and acidifuge behaviour of plants. Ann Bot 75:75–78
Vondráčková S, Hejcman M, Tlustoš P, Száková J (2013) Effect of quick lime and dolomite application on mobility of elements (Cd, Zn, Pb, As, Fe, and Mn) in contaminated soils. Pol J Environ Stud 22:577–589
Vondráčková S, Hejcman M, Tlustoš P, Száková J (2014) Effect of rock phosphate and superphosphate application on mobility of elements (Cd, Zn, Pb, As, Fe, Mn) in contaminated soils. Environ Eng Manag J. In press.
White PJ, Broadley MR (2003) Calcium in plants. Ann Bot 92:487–511
White PJ, Veneklaas EJ (2012) Nature and nurture: the importance of seed phosphorus content. Plant Soil 357:1–8
White PJ, Broadley MR, Thompson JA, McNicol JW, Crawley MJ, Poulton PR, Johnston AE (2012) Testing the distinctness of shoot ionomes of angiosperm families using the Rothamsted Park grass continuous hay experiment. New Phytol 196:101–109
Zhang XH, Liu J, Huang HT, Chen J, Zhu YN, Wang DQ (2007) Chromium accumulation by the hyperaccumulator plant Leersia hexandra Swartz. Chemosphere 67:1138–1143
Zhang XF, Xia HP, Lia ZA, Zhuang P, Gao B (2010) Potential of four forage grasses in remediation of Cd and Zn contaminated soils. Bioresour Technol 101:2063–2066
Zhao FJ, Lombi E, McGrath SP (2003) Assessing the potential for zinc and cadmium phytoremediation with the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Soil 249:37–43
Zhao H, Guo B, Wei Y, Zhang B (2013) Multi-element composition of wheat grain and provenance soil and their potentialities as fingerprints of geographical origin. J Cereal Sci 57:391–397
Zhuang P, Yang QW, Wang HB, Shu WS (2007) Phytoextraction of heavy metals by eight plant species in the field. Water Air Soil Pollut 184:235–242
Acknowledgments
The finalisation of this manuscript was supported by projects NAZV QJ 1210211 and by the project CIGA 20124205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philip John White.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vondráčková, S., Hejcman, M., Száková, J. et al. Soil chemical properties affect the concentration of elements (N, P, K, Ca, Mg, As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn) and their distribution between organs of Rumex obtusifolius . Plant Soil 379, 231–245 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2058-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2058-0