Abstract
Background and aims
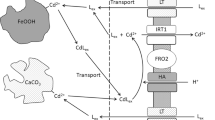
Chelant-enhanced phytoextraction has given variable and often unexplained experimental results. This work was carried out to better understand the mechanisms of Cd plant uptake in the presence of EDTA and to evaluate the contributions of Cd-EDTA complexes to the uptake.
Method
A 1-D mechanistic model was implemented, which described the free Cd2+ root absorption, the dissociation and the direct absorption of the Cd-EDTA complexes. It was used to explain Cd uptake by maize in hydroponics and in soil.
Results
In hydroponics, the addition of EDTA caused a decrease in Cd uptake by maize, particularly when the ratio of total EDTA ([EDTA] T ) to total Cd ([Cd] T ) was greater than 1. At [Cd] T = 1 μM, when [EDTA] T /[Cd] T < 1, the model indicated that Cd uptake was predominantly due to the absorption of free Cd2+, whose pool was replenished by the dissociation of Cd-EDTA. When [EDTA] T /[Cd] T > 1, the low Cd uptake was mostly due to Cd-EDTA absorption. In soil spiked with 5 mg Cd kg−1, Cd uptake was not affected by the various EDTA additions, because of the buffering capacity of the soil solid phase.
Conclusions
Addition of EDTA to soil increases Cd solubility but dissociation of Cd-EDTA limits the availability of the free Cd2+ at the root surface, which finally reduces the plant uptake of the metal.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- NTA:
-
Nitrilotriacetic acid
- EDDS:
-
Ethylenediamine disuccinic acid
- MES:
-
Morpholinoethane sulfonic acid
References
Barber SA (1995) Soil nutrient bioavailability. A mechanistic approach. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Barber SA, Cushman JH (1981) Nitrogen uptake model for agronomic crops. In: Iskandar JK (ed) Modeling waste water renovation-land treatment, 1st edn. J. Wiley Inter-Science, New York
Barber SA, Mackay AD (1986) Root growth and phosphorus and potassium uptake by two corn genotypes in the field. Fertil Res 10:217–230
Blaylock MJ, Salt DE, Dushenkov S, Zakharova O, Gussman C, Kapulnik Y, Ensley BD, Raskin I (1997) Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environ Sci Technol 31:860–865
Borggaard OK (1976) Selective extraction of amorphous iron oxide by edta from a mixture of amorphous iron oxide, goethite, and hematite. J Soil Sci 27:478–486
Bucheli-Witschel M, Egli T (2001) Environmental fate and microbial degradation of aminopolycarboxylic acids. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:69–106
Clemens S (2001) Molecular mechanisms of plant metal tolerance and homeostasis. Planta 212:475–486
Collins RN, Merrington G, McLaughlin MJ, Knudsen C (2002) Uptake of intact zinc-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid from soil is dependent on plant species and complex concentration. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1940–1945
Cushman JH (1979) An analytical solution to solute transport near root surfaces for low initial concentration: I. Equations development. Soil Sci Soc Am J 43:1087–1090
Darrah PR, Jones DL, Kirk GJD, Roose T (2006) Modelling the rhizosphere: a review of methods for ‘upscaling’ to the whole-plant scale. Eur J Soil Sci 57:13–25
Degryse F, Smolders E, Merckx R (2006) Labile Cd complexes increase Cd availability to plants. Environ Sci Technol 40:830–836
Degryse F, Shahbazi A, Verheyen L, Smolders E (2012) Diffusion limitations in root uptake of cadmium and zinc, but not nickel, and resulting bias in the Michaelis constant. Plant Physiol 160:1097–1109. doi:10.1104/pp. 112.202200
Hong PKA, Li C, Banerji SK, Regmi T (1999) Extraction, recovery, and biostability of EDTA for remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil. J Soil Contam 8:81–103
Huang JW, Cunningham SD (1996) Lead phytoextraction: species variation in lead uptake and translocation. New Phytol 134:75–84
Kos B, Le tan D (2003) Influence of a biodegradable ([S, S]-EDDS) and nondegradable (EDTA) chelate and hydrogel modified soil water sorption capacity on Pb phytoextraction and leaching. Plant Soil 253:403–411
Kulli B, Balmer M, Krebs R, Lothenbach B, Geiger G, Schulin R (1999) The Influence of nitrilotriacetate on heavy metal uptake of lettuce and ryegrass. J Environ Qual 28:1699–1705. doi:10.2134/jeq1999.00472425002800060002x
Kumar M, Bijo AJ, Baghel RS, Reddy CRK, Jha B (2011) Selenium and spermine alleviate cadmium induced toxicity in the red seaweed Gracilaria dura by regulating antioxidants and DNA methylation. Plant Physiol Biochem 51:129–138
Lai H-Y, Chen Z-S (2004) Effects of EDTA on solubility of cadmium, zinc, and lead and their uptake by rainbow pink and vetiver grass. Chemosphere 55:421–430
Luo C, Shen Z, Li X, Baker AJM (2006) Enhanced phytoextraction of Pb and other metals from artificially contaminated soils through the combined application of EDTA and EDDS. Chemosphere 63:1773–1784
Mullins GL, Sommers LE (1986) Cadmium and zinc influx characteristics by intact corn (Zea mays L.) seedlings. Plant Soil 96:153–164
Nascimento CWA (2006) Organic acids effects on desorption of heavy metals from a contaminated soil. Sci Agric 63:276–280
Niu L, Shen Z, Luo C, Deng Y-e, Wang C (2012) Accumulation mechanisms and subcellular distribution of Cu in maize grown on soil treated with [S, S]-ethylenediamine disuccinic acid. Plant Soil 351:237–247
Nowack B, Sigg L (1996) Adsorption of EDTA and Metal-EDTA complexes onto goethite. J Colloid Interface Sci 177:106–121
Nowack B, Sigg L (1997) Dissolution of Fe(III) (hydr) oxides by metal-EDTA complexes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:951–963
Nowack B, Schulin R, Robinson BH (2006) Critical assessment of chelant-enhanced metal phytoextraction. Environ Sci Technol 40:5225–5232
Nye PH (1973) The relation between the radius of a root and its nutrient-absorbing power. J Exp Bot 24:783–786
Nye PH, Marriott FHC (1969) A theoretical study of the distribution of substances around roots resulting from simultaneous diffusion and mass flow. Plant Soil 30:459–473
Panfili F, Schneider A, Vives A, Perrot F, Hubert P, Pellerin S (2009) Cadmium uptake by durum wheat in presence of citrate. Plant Soil 316:299–309
Parker DR, Pedler JF (1997) Reevaluating the free-ion activity model of trace metal availability to higher plants. Plant Soil 196:223–228
Perriguey J, Sterckeman T, Morel J-L (2008) Effect of rhizosphere and plant-related factors on the cadmium uptake by maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Exp Bot 63:333–341
Redjala T, Zelko I, Sterckeman T, Legué V, Lux A (2011) Relationship between root structure and root cadmium uptake in maize. Environ Exp Bot 71:241–248
Roose T, Kirk G (2009) The solution of convection–diffusion equations for solute transport to plant roots. Plant Soil 316:257–264
Roose T, Fowler AC, Darrah PR (2001) A mathematical model of plant nutrient uptake. J Math Biol 42:347–360
Sarret G, Vangronsveld J, Manceau A, Musso M, D’Haen J, Menthonnex J-J, Hazemann J-L (2001) Accumulation forms of Zn and Pb in Phaseolus vulgaris in the presence and absence of EDTA. Environ Sci Technol 35:2854–2859
Satroutdinov AD, Dedyukhina EG, Chistyakova TI, Witschel M, Minkevich IG, Eroshin VK, Egli T (2000) Degradation of metal-EDTA complexes by resting cells of the bacterial strain DSM 9103. Environ Sci Technol 34:1715–1720
Schaider L, Parker D, Sedlak D (2006) Uptake of EDTA-complexed Pb, Cd and Fe by solution- and sand-cultured Brassica juncea. Plant Soil 286:377–391
Schneider A, Nguyen C, Denaix L (2009) Estimation of the association and dissociation rate constants of Cd complexes with various aminopolycarboxylic acids by an exchange method. Environ Chem 6:334–340
Shen Z-G, Li X-D, Wang C-C, Chen H-M, Chua H (2002) Lead phytoextraction from contaminated soil with high-biomass plant species. J Environ Qual 31:1893–1900. doi:10.2134/jeq2002.1893
Sterckeman T, Perriguey J, Caël M, Schwartz C, Morel JL (2004) Applying a mechanistic model to cadmium uptake by Zea mays and Thlaspi caerulescens: Consequences for the assessment of the soil quantity and capacity factors. Plant Soil 262:289–302
Sterckeman T, Carignan J, Srayeddin I, Baize D, Cloquet C (2009) Availability of soil cadmium using stable and radioactive isotope dilution. Geoderma 153:372–378
Tandy S, Schulin R, Nowack B (2006a) The influence of EDDS on the uptake of heavy metals in hydroponically grown sunflowers. Chemosphere 62:1454–1463
Tandy S, Schulin R, Nowack B (2006b) Uptake of metals during chelant-assisted phytoextraction with EDDS related to the solubilized metal concentration. Environ Sci Technol 40:2753–2758
Vassil AD, Kapulnik Y, Raskin I, Salt DE (1998) The role of EDTA in lead transport and accumulation by Indian mustard. Plant Physiol 117:447–453
von Wirén N, Marschner H, Römheld V (1996) Roots of iron-efficient maize also absorb phytosiderophore-chelated zinc. Plant Physiol 111:1119–1125
Wang P, Zhou D, Luo X, Li L (2009) Effects of Zn-complexes on zinc uptake by wheat (Triticum aestivum) roots: a comprehensive consideration of physical, chemical and biological processes on biouptake. Plant Soil 316:177–192
Wenger K, Gupta SK, Furrer G, Schulin R (2003) The role of nitrilotriacetate in copper uptake by tobacco. J Environ Qual 32:1669–1676
Wu LH, Luo YM, Christie P, Wong MH (2003) Efects of EDTA and low molecular weight organic acids on soil solution properties of a heavy metal polluted soil. Chemosphere 50:819–822
Wu LH, Luo YM, Xing XR, Christie P (2004) EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil with Indian mustard and associated potential leaching risk. Agric Ecosyst Environ 102:307–318
Zhang Z, Buffle J, van Leeuwen HP (2007) Roles of dynamic metal speciation and membrane permeability in metal flux through lipophilic membranes: general theory and experimental validation with nonlabile complexes. Langmuir 23:5216–5226
Acknowledgments
This work was supported through a doctoral grant funded by the Région Lorraine and French National Institute for Agricultural Research (INRA). The authors thank Didier Stemmelen (Laboratoire d’Energétique et de Mécanique Théorique et Appliquée) and the technical staff of the Laboratoire Sols et Environnement for their precious help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Fangjie Zhao.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 928 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Custos, JM., Moyne, C., Treillon, T. et al. Contribution of Cd-EDTA complexes to cadmium uptake by maize: a modelling approach. Plant Soil 374, 497–512 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1906-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1906-7