Abstract
Background and aims
Nitrogen mineralization of lupine seeds and seedlings to be used as flexible leguminous N source in organic vegetable production was investigated. It was hypothesized that changes in seed chemical composition during germination are associated with increased fertilizer efficiency of seed N.
Methods
Net N mineralization of seed meal and seedlings varying in age was determined in pot and field experiments. The temporal mineralization pattern was quantified by fitting first-order kinetics.
Results
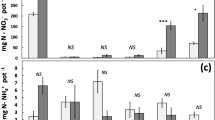
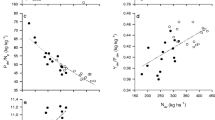
In the pot experiment, seedling C:N ratio declined within 2 weeks from initially 8.8 to a minimum of 6.2 prior to a re-increase. Maximum net N mineralization increased strongly with decreasing C:N ratio being up to 44% higher for seedlings compared to seed meal. Time course of net N mineralization in the field showed initial peaks partly exceeding the amount of applied lupine seed N. Ignoring mineralization peaks, the relationship between maximum net N mineralization and C:N ratio was in close agreement with pot experimental data. The critical C:N ratio of the pooled data was 13.
Conclusions
Nitrogen mineralization of field-sown lupine seeds can be manipulated by varying seedling growing time until incorporation. High fertilizer efficiency provided by high net N mineralization is associated with early seedling incorporation and high germination rates.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ågren GI, Bosatta E (1996) Theoretical ecosystem ecology: understanding element cycles. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Asmar F, Eiland F, Nielsen NE (1994) Effect of extracellular-enzyme activities on solubilization rate of soil organic nitrogen. Biol Fertil Soils 17:32–38
Aulakh MS, Walters DT, Doran JW, Francis DD, Mosier AR (1991) Crop residue type and placement effects on denitrification and mineralization. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55:1020–1025
Baijukya FP, de Ridder N, Giller KE (2006) Nitrogen release from decomposing residues of leguminous cover crops and their effect on maize yield on depleted soils of Bukoba District, Tanzania. Plant Soil 279:77–93
Bending GD, Turner MK, Burns IG (1998) Fate of nitrogen from crop residues as affected by biochemical quality and the microbial biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 30:2055–2065
Blagodatskaya E, Kuzyakov Y (2008) Mechanisms of real and apparent priming effects and their dependence on soil microbial biomass and community structure: critical review. Biol Fertil Soils 45:115–131
Cadisch G, Handayanto E, Malama C, Seyni F, Giller KE (1998) N recovery from legume prunings and priming effects are governed by the residue quality. Plant Soil 205:125–134
Cardon ZG (1996) Influence of rhizodeposition under elevated CO2 on plant nutrition and soil organic matter. Plant Soil 187:277–288
Chapin FS III, Matson PA, Mooney HA, Chapin MC (2002) Principles of terrestrial ecosystem ecology. Springer, New York
Chaves B, De Neve S, Hofman G, Boeckx P, Van Cleemput O (2004) Nitrogen mineralization of vegetable root residues and green manures as related to their (bio)chemical composition. Eur J Agron 21:161–170
Cheng W (2009) Rhizosphere priming effect: its functional relationships with microbial turnover, evapotranspiration, and C:N budgets. Soil Biol Biochem 41:180–1795
Cleveland CC, Liptzin D (2007) C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 85:235–252
Dagnia SG, Petterson DS, Bell RB, Flanagan VF (1992) Germination alters the chemical composition and protein quality of lupin seeds. J Sci Food Agr 60:419–423
Dalenberg JW, Jager G (1981) Priming effect of small glucose additions to 14C-labeled soil. Soil Biol Biochem 13:219–223
Dalenberg JW, Jager G (1989) Priming effect of some organic additions to 14C-labeled soil. Soil Biol Biochem 21:443–448
De Neve S, Hofman G (1996) Modelling N mineralization of vegetable crop residues during laboratory incubations. Soil Biol Biochem 28:1451–1457
Del Prado A, Merino P, Estavillo J, Pinto M, González-Murua C (2006) N2O and NO emissions from different N sources and under a range of soil water contents. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 74:229–243
Dijkstra FA, Bader NE, Johnson DW, Cheng W (2009) Does accelerated soil organic matter decomposition in the presence of plants increase plant N availability? Soil Biol Biochem 41:1080–1087
Dinesh R, Suryanarayana MA, Nair AK, Ghoshal Chaudhuri S (2001) Leguminous cover crop effects on nitrogen mineralization rates and kinetics in soils. J Agron Crop Sci 187:161–166
Fernandez-Orozco R, Piskula MK, Zielinski H, Kozlowska H, Frias J, Vidal-Valverde C (2006) Germination as a process to improve the antioxidant capacity of Lupinus angustifolius L. var. Zapaton. Eur Food Res Technol 223:495–502
Fontaine S, Bardoux G, Abbadie L, Mariotti A (2004) Carbon input to soil may decrease soil carbon content. Ecol Lett 7:314–320
Fox RH, Myers RJK, Vallis I (1990) The nitrogen mineralization rate of legume residues in soil as influenced by their polyphenol, lignin, and nitrogen contents. Plant Soil 129:251–259
Frank DA, Groffman PM (2009) Plant rhizospheric N processes: what we don’t know and why we should care. Ecology 90:1512–1519
Frankenberger W, Abdelmagid H (1985) Kinetic parameters of nitrogen mineralization rates of leguminous crops incorporated into soil. Plant Soil 87:257–271
Ghavidel RA, Prakash J (2007) The impact of germination and dehulling on nutrients, antinutrients, in vitro iron and calcium bioavailability and in vitro starch and protein digestibility of some legume seeds. LWT Food Sci Technol 40:1292–1299
Handayanto E, Giller KE, Cadisch G (1997) Regulating N release from legume tree prunings by mixing residues of different quality. Soil Biol Biochem 29:1417–1426
Ibewiro B, Sanginga N, Vanlauwe B, Merckx R (2000) Nitrogen contributions from decomposing cover crop residues to maize in a tropical derived savanna. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 57:131–140
Jarvis SC, Stockdale EA, Shepherd MA, Powlson DS (1996) Nitrogen mineralization in temperate agricultural soils: processes and measurement. Adv Agron 57:187–235
Jenkinson DS, Fox RH, Rayner JH (1985) Interactions between fertilizer nitrogen and soil nitrogen—the so-called ‘priming’ effect. J Soil Sci 36:425–444
Kuzyakov Y (2002) Review: factors affecting rhizosphere priming effects. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 165:382–396
Kuzyakov Y (2010) Priming effects: interactions between living and dead organic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1363–1371
Kuzyakov Y, Friedel JK, Stahr K (2000) Review of mechanisms and quantification of priming effects. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1485–1498
Kuzyakov Y, Hill PW, Jones DL (2007) Root exudate components change litter decomposition in a simulated rhizosphere depending on temperature. Plant Soil 290:293–305
Laber H (2003) N-Freisetzung aus organischen Handelsdüngern–Übersicht und eigene Versuchsergebnisse im ökologischen Gemüsebau. In: Rahmann G, Nieberg H (eds) Ressortforschung für den ökologischen Landbau 2002. Landbauforschung Völkenrode, Special Issue 259. Braunschweig, pp 17–20
Li Z, Schulz R, Müller T (2009) Short term nitrogen availability from lupin seed meal as organic fertilizer is affected by seed quality at low temperatures. Biol Agric Hortic 26:337–352
Liljeroth E, Van Veen JA, Miller HJ (1990) Assimilate translocation to the rhizosphere of two wheat lines and subsequent utilization by rhizosphere microorganisms at two soil nitrogen concentrations. Soil Biol Biochem 22:1015–1021
Liu XJ, Mosier AR, Halvorson AD, Reule CA, Zhang FS (2007) Dinitrogen and N2O emissions in arable soils: effect of tillage, N source and soil moisture. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2362–2370
Lopez-Amoros ML, Hernandez T, Estrella I (2006) Effect of germination on legume phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity. J Food Compos Anal 19:277–283
Mafongoya PL, Nair PKR, Dzowela BH (1998) Mineralization of nitrogen from decomposing leaves of multipurpose trees as affected by their chemical composition. Biol Fertil Soils 27:143–148
Manzoni S, Jackson RB, Trofymow JA, Porporato A (2008) The global stoichiometry of litter nitrogen mineralization. Science 321:684–686
Manzoni S, Trofymow JA, Jackson RB, Porporato A (2010) Stoichiometric controls on carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus dynamics in decomposing litter. Ecol Monogr 80:89–106
Müller T, von Fragstein und Niemsdorff P (2006a) Organic fertilizers derived from plant materials part I: turnover in soil at low and moderate temperatures. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 169:255–264
Müller T, von Fragstein und Niemsdorff P (2006b) Organic fertilizers derived from plant materials part II: turnover in field trials. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 169:265–273
Oglesby K, Fownes J (1992) Effects of chemical composition on nitrogen mineralization from green manures of seven tropical leguminous trees. Plant Soil 143:127–132
Parton W, Silver WL, Burke IC, Grassens L, Harmon ME, Currie WS, King JY, Adair EC, Brandt LA, Hart SC, Fasth B (2007) Global-scale similarities in nitrogen release patterns during long-term decomposition. Science 315:361–364
Passioura JB (2006) The perils of pot experiments. Funct Plant Biol 33:1075–1079
Rasch D, Verdooren R (2004) Grundlagen der Korrelationsanalyse und der Regressionsanalyse. Einführung in die Biometrie 4. Saphir, Ribbesbüttel
Rasmussen PE, Douglas CL, Collins HP, Albrecht SL (1998) Long-term cropping system effects on mineralizable nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1829–1837
Rodrigo A, Recous S, Neel C, Mary B (1997) Modelling temperature and moisture effects on C-N transformations in soils: comparison of nine models. Ecol Model 102:325–339
Sabahi H, Schulz R, Müller T, Li Z (2009) Nitrogen turnover of legume seed meals as affected by seed meal texture and quality at different temperatures. Arch Agron Soil Sci 55:671–682
Schmitz H-J, Fischer P (2003) Vegetabile Dünger in Substraten für den ökologischen Gemüsebau. Gemüse 2:18–22
Seneviratne G (2000) Litter quality and nitrogen release in tropical agriculture: a synthesis. Biol Fertil Soils 31:60–64
Stadler C, von Tucher S, Schmidhalter U, Gutser R, Heuwinkel H (2006) Nitrogen release from plant-derived and industrially processed organic fertilizers used in organic horticulture. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 169:549–556
Trinsoutrot I, Recous S, Bentz B, Lineres M, Cheneby D, Nicolardot B (2000) Biochemical quality of crop residues and carbon and nitrogen mineralization kinetics under nonlimiting nitrogen conditions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:918–926
Van Schöll L, Van Dam AM, Leffelaar PA (1997) Mineralisation of nitrogen from an incorporated catch crop at low temperatures: experiment and simulation. Plant Soil 188:211–219
Vigil MF, Kissel DE (1991) Equations for estimating the amount of nitrogen mineralized from crop residues. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55:757–761
Wu J, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1993) Formation and destruction of microbial biomass during the decomposition of glucose and ryegrass in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 25:1435–1441
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hans Lambers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katroschan, KU., Teixeira, G., Kahlen, K. et al. Decomposition of lupine seeds and seedlings as N fertilizer in organic vegetable production. Plant Soil 357, 59–71 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1144-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1144-4