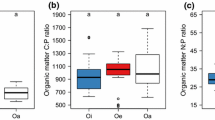
Abstract
Soil C and N dynamics were evaluated in five eucalypt plantations within a precipitation gradient (500–2,000 mm) in Portugal. Soil physical and chemical properties, total and labile (particulate organic matter, hydrolyzable, hot water soluble and microbial) soil C and N pools, and C and N mineralization were measured to characterize the C and N dynamics and their controlling factors within this gradient. Contents of total and labile soil organic C and N were positively correlated with the mean annual precipitation. A similar relationship was observed for net N mineralization (anaerobic and long-term aerobic incubation), gross N mineralization (15N isotope dilution technique) and C mineralization. In contrast, rates of C and N mineralization (per unit of C and N) were higher in the driest sites due to their higher proportion of particulate organic matter C. Net and gross N mineralization were strongly correlated and showed similar controlling factors (mean annual precipitation, total and labile C and N and extractable P contents), suggesting that net N mineralization during long-term aerobic incubation reflects gross N transformations. Although, gross NO3–N production and gross NO3–N immobilization were observed in all sites, net nitrification in the drier sites was not observed in the first weeks of the study. Our results suggest that, under Mediterranean conditions, mean annual precipitation is the major factor determining the C and N dynamics in soils with Eucalyptus plantations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MA, Attiwill PM (1986) Nutrient cycling and nitrogen mineralization in eucalypt forests of southeastern Australia. II. Indices of nitrogen mineralization. Plant Soil 92:341–362. doi:10.1007/BF02372483
Adams MA, Attiwill PM, Polglase PJ (1989) Availability of nitrogen and phosphorus in forest soils in northeastern Tasmania. Biol Fertil Soils 8:212–218. doi:10.1007/BF00266481
Ahn M-Y, Zimmerman AR, Comerford NB, Sickman JO, Grunwald S (2009) Carbon mineralization and labile organic carbon pools in the sandy soils of a North Florida watershed. Ecosystems 12:672–685. doi:0.1007/s10021-009-9250-8
Attiwill PM, Adams MA (1993) Nutrient cycling in forests. New Phytol 124:561–582
Attiwill PM, Polglase PJ, Weston CJ, Adams MA (1996) Nutrient cycling in forests of south-eastern Australia. In: Attiwill PM, Adams MA (eds) Nutrition of eucalypts. CSIRO, Australia, pp 191–227
Austin AT, Sala OE (2002) Carbon and nitrogen dynamics across a natural precipitation gradient in Patagonia, Argentina. J Veg Sci 13:351–360
Bauhus J, Khanna PK, Raison RJ (1993) The effect of fire on carbon and nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in an Australian forest soil. Aust J Soil Res 31:621–39. doi:10.1071/SR9930621
Berg B, Berg M, Bottner P et al (1993) Litter mass loss in pine forests of Europe and Eastern United States as compared to actual evapotranspiration on a European scale. Biogeochemistry 20:127–153. doi:10.1007/BF00000785
Bernhard-Reversat F (1996) Nitrogen cycling in tree plantations grown on a poor sandy savanna soil in Congo. Appl Soil Ecol 4:161–172. doi:10.1016/0929-1393(96)00096-0
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(85)90144-0
Burton J, Chen Ch XuZ, Ghadiri H (2007) Gross nitrogen transformations in adjacent native and plantation forests of subtropical Australia. Soil Biol Biochem 39:426–433. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.08.011
Couto-Vázquez A, González-Prieto SJ (2006) Short- and medium- term effects of three fire fighting chemicals on the properties of a burnt soil. Sci Total Environ 371:353–361. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.08.016
Davidson EA, Hart SC, Firestone MK (1992) Internal cycling of nitrate in soils of a mature coniferous forest. Ecology 73:1148–1156. doi:10.2307/1940665
DGCN (2000) Tercer Inventario Forestal Nacional 1997–2006. Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Dirección General de Conservación de la Naturaleza. Madrid
Douglas CL, Rasmussen PE, Collins HP, Albrecht SL (1998) Nitrogen mineralization across a climosequence in the pacific northwest. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1765–1772. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(98)00031-5
Egnér H, Riehm H, Domingo WR (1960) Untersuchungen über die chemische Bodenanalyse als Grundlage für die Beurteilung des Nährstoff-zustandes der Böden. II Chemische Extraktionmethod zur Phosphor-und Kaliumbestimmung. Kungl Lantbr Högsk Ann 26:199
Ellis RC, Pennington PI (1989) Nitrification in soils of secondary vegetational successions from Eucalytpus forest and grassland to cool temperate rainforest in Tasmania. Plant Soil 115:59–73. doi:10.1007/BF02220695
Fabião A, Madeira M, Steen E (1987) Root mass in plantations of Eucalyptus globulus in Portugal in relation to soil characteristics. Arid Soil Res Rehab 1:185–194. doi:10.1080/15324988709381143
Falkiner RA, Khanna PK, Raison RJ (1993) Effect of superphosphate addition on N mineralization in some Australian forest soils. Aust J Soil Res 31:285–96. doi:10.1071/SR9930285
Franzluebbers AJ, Haney RL, Honeycutt CW, Arshad MA, Schomberg HH, Hons FM (2001) Climatic influences on active fractions of soil organic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1103–1111. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00016-5
Garcia-Montiel DC, Binkley D (1998) Effect of Eucalytpus saligna and Albizia falcataria on soil processes and nitrogen supply in Hawaii. Oecologia 113:547–556. doi:10.1080/15324988709381143
Garcia-Pausas J, Casals P, Camarero L, Huguet C, Thompson R, Sebastiá MT, Romanyá J (2008) Factors regulating carbon mineralization in the surface and subsurface soils of Pyrenean mountain grasslands. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2803–2810. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.08.001
Gómez-Rey MX, Vasconcelos E, Madeira M (2007) Lysimetric study of eucalypt residue management effects on N leaching and mineralization. Ann For Sci 64:699–706. doi:10.1051/forest:2007050
Gonçalves JLM, Serrano MIP, Mendes KCF, Gava JL (1999) Effects of site management in a Eucalyptus grandis plantation in the humid tropic: São Paulo, Brazil. In: Proceedings of the CIFOR Workshop on Site Management and Productivity in Tropical Plantation Forests, Kerala, India, pp 3–9
Hart SC, Nason GE, Myrold DD, Perry DA (1994) Dynamics of gross nitrogen transformations in an old-growth forest: the carbon connection. Ecology 75:880–891. doi:10.2307/1939413
Hart SC, Binkley D, Perry DA (1997) Influence of red alder on soil nitrogen transformations in two conifer forest of contrasting productivity. Soil Biol Biochem 29:1111–1123. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(97)00004-7
Holtgrieve GW, Jewett PK, Matson PA (2006) Variations in soil N cycling and trace gas emissions in wet tropical forests. Oecologia 146:584–594. doi:10.1007/s00442-005-0222-1
Hontoria C, Rodriguez-Murillo JC, Saa A (1999) Relationships between soil organic carbon and site characteristics in Peninsular Spain. Soil Sci Soc Am J 63:614–621
Houba VJS, Novozamsky I, Termminghoff E (1994) Soil analysis procedures. Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen
IFN (2006) Inventário Florestal Nacional (2005–2006). Divisão de Inventário e Estatísticas Florestais. Direcção Geral das Florestas, Lisboa
Insam H (1990) Are the soil microbial biomass and basal respiration governed by the meteorological regime? Soil Biol Biochem 22:525–532. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(90)90189-7
Jones HE, Madeira M, Herraez L et al (1999) The effect of organic matter management of the productivity of Eucalyptus globulus stands in Spain and Portugal: tree growth and harvest residue decomposition in relation to site and treatment. For Ecol Manage 122:73–86. doi:10.1016/S0378-1127(99)00033-X
Kane ES, Valentine DW, Schuur EAG, Dutta K (2005) Soil carbon stabilization along climate and stand productivity gradients in black spruce forests of interior Alaska. Can J For Res 35:2118–2129. doi:10.1139/x05-093
Keeney D (1982) Nitrogen-availability indices. In: Page A, Miller R, Keeney D (eds) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties. ASA, Madison, WI, pp 711–734
Kent M, Coker P (1992) Vegetation description and analysis: a practical approach. Belhaven Press, London
Khanna PK (1998) Nutrient cycling under mixed-species tree systems in southeast Asia. Agroforest Syst 38:99–120. doi:10.1023/A:1005952410569
Khanna PK, Ludwig B, Bauhus J, O’Hara C (2001) Assessment and significance of labile organic C pools in forest soils. In: Lal R, Kimble JM, Follett R, Stewart BA (eds) Assessment methods for soil carbon. CRC Press, pp 167–182
Kirkham D, Bartholomew WV (1954) Equations for following nutrient transformations in soil, utilizing tracer data. Soil Sci Soc Am J 18:33–34
Li X, Chen Z (2004) Soil microbial biomass C and N along a climatic transect in the Mongolian steppe. Biol Fertil Soils 39:344–351. doi:10.1007/s00374-004-0720-z
Livesley SJ, Adams MA, Grierson PF (2007) Soil water nitrate and ammonium dynamics under a sewage effluent–irrigated eucalypt plantation. J Environ Qual 36:1883–1894. doi:10.2134/jeq2007.0175
Madeira M, Pereira JS (1990–1991) Productivity, nutrient immobilization and soil chemical properties in an Eucalyptus globulus plantation under different water and nutrient regimes. Water Air Soil Poll 54:621–624. doi:10.1007/BF00298698
Madeira M, Andreux F, Portal JM (1989) Changes in soil organic matter characteristics due to reforestation with Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Sci Total Environ 81/82:481–488. doi:10.2134/jeq2007.0175
Madeira M, Fabião A, Pereira JS, Araújo MC, Ribeiro C (2002) Changes in carbon stocks in Eucalyptus globulus Labill. plantations induced by different water and nutrient availability. For Ecol Manag 171:75–85. doi:10.1016/S0378-1127(02)00462-0
Madeira M, Magalhães MC, Azevedo A, Fabião A, Araújo MC, Pina JP (2004) Efeito da gestão dos resíduos de abate nas características do solo e no crescimento de uma plantação de Eucalyptus globulus, em talhadia. Rev Ciências Agrárias 27:414–431
Magalhães MCS (2000) Efeitos de Técnicas de Preparação do Solo e Gestão dos Resíduos Orgânicos em Características Físico-Químicas do Solo de Plantações Florestais, Doctoral Thesis, Universidade Técnica de Lisboa
Martins AA, Madeira M, Réfega AG (1995) Influence of rainfall on properties of soils developed on granite in Portugal. Arid Soil Res Rehabil 9:353–366. doi:10.1080/15324989509385904
Mendham DS, Sankaran KV, O’Connell AM, Grove TS (2002) Eucalyptus globulus harvest residue management effects on soil carbon and microbial biomass at 1 and 5 years after plantation establishment. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1903–1912. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00205-5
Mendham DS, Heagney EC, Corbeels M, O’Connell AM, Grove TS, McMurtrie RE (2004) Soil particulate organic matter effects on nitrogen availability after afforestation with Eucalyptus globulus. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1067–1074. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.02.018
Merino A, Rodríguez-Lopez Á, Brañas J, Rodriguez-Soalleiro R (2003) Nutrition and growth in newly established plantations of Eucalyptus globulus in northwestern Spain. Ann For Sci 60:509–517. doi:10.1051/forest:2003044
Meyer H, Kaiser C, Biasi C, Hämmerle R, Rusalimova O, Lashchinsky N, Baranyi C, Daims H, Barsukov P, Richter A (2006) Soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics along a latitudinal transect in Western Siberia, Russia. Biogeochemistry 81:239–252. doi:10.1007/s10533-006-9039-1
Moroni MT, Smethurst PJ, Holz GK (2002) Nitrogen fluxes in surface soils of young Eucalyptus nitens plantations in Tasmania. Aust J Soil Res 40:543–553. doi:10.1071/SR01024
O’Connell AM, Grove TS, Mendham DS, Rance SJ (2004) Impact of harvest residue management on soil nitrogen dynamics in Eucalyptus globulus plantations in south western Australia. Soil Biol Biochem 36:39–48. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2003.08.017
Oyonarte C, Aranda V, Durante P (2008) Soil surface properties in Mediterranean mountain ecosystems: effects of environmental factors and implications of management. For Ecol Manag 254:156–165. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2007.07.034
Parfitt RL, Salt GJ (2001) Carbon and nitrogen mineralization in sand, silt, and clay fractions of soils under maize and pasture. Aust J of Soil Res 39:361–371. doi:10.1071/SR00028
Pereira JS, Tomé M, Madeira M, Oliveira AC, Tomé J, Almeida MH (1996) Eucalypt plantations in Portugal. In: Attiwill PM, Adams MA (eds) Nutrition of eucalypts. CSIRO, Australia, pp 371–387
Polglase PJ, Attiwill PM, Adams MA (1992) Nitrogen and phosphorus cycling in relation to stand age of Eucalyptus regnans F. Muell. II. N mineralization and nitrification. Plant Soil 142:167–176. doi:10.1007/BF00010964
Reis RM, Gonçalves MZ (1981) Caracterização climática da região agrícola do ribatejo e oeste. O Clima de Portugal. Fasc. XXXII. Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia e Geofísica, Lisboa
Schimel JP, Bennett J (2004) Nitrogen mineralization: challenges of a changing paradigm. Ecology 85:591–602. doi:10.1890/03-8002
Sollins P, Glassman C, Paul EA, Swanston C, Lajtha K, Heil JW, Elliott ET (1999) Soil carbon and nitrogen: pools and fractions. In: Robertson GP (ed) Standard soil methods for long-term ecological research. Oxford Univ. Press, New York, pp 89–105
Sparling GP (1992) Ratio of microbial biomass carbon to soil organic carbon as a sensitive indicator of changes in soil organic matter. Aust J Soil Res 30:195–207. doi:10.1071/SR9920195
Stark JM, Hart SC (1997) High rates of nitrification and nitrite turnover in undisturbed coniferous forests. Nature 385:61–64. doi:10.1038/385061a0
Ste-Marie C, Paré D (1999) Soil, pH and N availability effects on net nitrification in the forest floors of a range of boreal forest stands. Soil Biol Biochem 31:1579–1589. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(99)00086-3
Stevenson FJ (1986) Cycles of soils Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulphur, Macronutrients. Wiley, New York
Vance PC, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(87)90052-6
Verchot LV, Holmes Z, Mulon L, Groffman PM, Lovett GM (2001) Gross vs net rates of N mineralization and nitrification as indicators of functional differences between forest types. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1889–1901. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00095-5
Verhagen FJM, Laanbroek HJ, Woldendorp JW (1995) Competition for ammonium between plant roots and nitrifying and heterotrophic bacteria and the effects of protozoan grazing. Plant Soil 170:241–250. doi:10.1007/BF00010477
WRB (2006) World reference base for soil resources 2006. 2nd edn. World Soil Resources Reports No. 103. FAO, Rome
Zak DR, Pregitzer KS (1990) Spatial and temporal variability of nitrogen cycling in northern Lower Michigan. For Sci 36:367–380
Acknowledgements
The CELBI Pulp Company is acknowledged for allowing the use of its eucalyptus plantations, and Clara Araújo for her assistance in plot selection. Laboratory staff of the Departamento de Ciências do Ambiente (Instituto Superior de Agronomia) is acknowledged for their technical assistance for analytical work and Paulo Marques and Luis Hilário for their help in field work. The authors also thank Marta Carneiro for floristic survey and Prof. Ana Carla Madeira for English style improvement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eric Paterson.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez-Rey, M.X., Madeira, M., Gonzalez-Prieto, S.J. et al. Soil C and N dynamics within a precipitation gradient in Mediterranean eucalypt plantations. Plant Soil 336, 157–171 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0456-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0456-5