Abstract
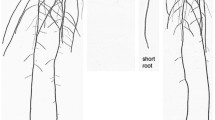
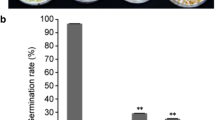
Ribosomal phosphoprotein P1 (RPP1) is an integral component of the P-protein stalk in the 60S subunit of eukaryotic ribosomes and is required for the efficient elongation of translation. Previously, Arabidopsis RPP1A was revealed to be involved in the regulation of seed size and seed storage protein accumulation. In this work, the seedling growth analysis shows that the knockout mutation of Arabidopsis RPP1A significantly promoted seedling growth, particularly in the shoots. The label-free quantitative proteomic analysis demonstrated that a total of 593 proteins were differentially accumulated between the germinating seeds of the wild-type Col-0 and rpp1a mutant. And these proteins were significantly enriched in the intracellular transport, nitrogen compound transport, protein transport, and organophosphate metabolic process. The abundance of proteins involved in the RNA and protein processing processes, including ncRNA processing and protein folding, were significantly increased in the rpp1a mutant. Mutation in RPP1A highlighted the effects on the ribosome, energy metabolism, and nitrogen metabolism. The abundance of enzymes involved in glycolysis and pyruvate mechanism was decreased in the germinating seeds of the rpp1a mutant. Whereas the processes of amino acid biosynthesis, protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum, and biosynthesis of cofactors were enhanced in the germinating seeds of the rpp1a mutant. Taken together, the lack of RPP1A triggered changes in other ribosomal proteins, and the higher amino acid contents in the seedlings of the rpp1a mutant probably contributed to enhanced biosynthesis, processing, and transport of proteins, resulting in accelerated growth. Our results show the novel role of a P-protein and shed new light on the regulatory mechanism of seedling growth.
Key message
Knockout mutation of Arabidopsis RPP1A leads to more amino acid supply to support enhanced seedling growth.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated or analysed during the current study are available in the supplementary information files.
References
Aboulela M, Nakagawa T, Oshima A, Nishimura K, Tanaka Y (2018) The Arabidopsis COPII components, AtSEC23A and AtSEC23D, are essential for pollen wall development and exine patterning. J Exp Bot 69:1615–1633. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.123216
Angelovici R, Fait A, Fernie AR, Galili G (2011) A seed high-lysine trait is negatively associated with the TCA cycle and slows down Arabidopsis seed germination. New Phytol 189:148–159. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03478.x
Asaoka R, Uemura T, Ito J, Fujimoto M, Ito E, Ueda T, Nakano A (2013) Arabidopsis RABA1 GTPases are involved in transport between the trans-Golgi network and the plasma membrane, and are required for salinity stress tolerance. Plant J 73:240–249. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12023
Bailey-Serres J, Vangala S, Szick K, Lee CH (1997) Acidic phosphoprotein complex of the 60S ribosomal subunit of maize seedling roots. components and changes in response to flooding. Plant Physiol 114:1293–1305. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.4.1293
Ballesta JP, Remacha M (1996) The large ribosomal subunit stalk as a regulatory element of the eukaryotic translational machinery. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 55:157–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6603(08)60193-2
Balmer A, Pastor V, Gamir J, Flors V, Mauch-Mani B (2015) The ‘prime-ome’: towards a holistic approach to priming. Trends Plant Sci 20:443–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2015.04.002
Bewley JD (1997) Seed germination and dormancy. Plant Cell 9:1055–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-5266(01)00219-9
Canino G, Bocian E, Barbezier N, Echeverría M, Forner J, Binder S, Marchfelder A (2009) Arabidopsis encodes four tRNase Z enzymes. Plant Physiol 150:1494–1502. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.137950
Che L, Meng H, Ruan J, Peng L, Zhang L (2022) Rubredoxin 1 is required for formation of the functional photosystem II core complex in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 13:824358. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.824358
Chen M, Mooney BP, Hajduch M, Joshi T, Zhou M, Xu D, Thelen JJ (2009) System analysis of an Arabidopsis mutant altered in de novo fatty acid synthesis reveals diverse changes in seed composition and metabolism. Plant Physiol 150:27–41. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.134882
Chen D, Wang Q, Feng J, Ruan Y, Shen WH (2019) Arabidopsis ZUOTIN RELATED FACTOR1 proteins are required for proper embryonic and post-embryonic root development. Front Plant Sci 10:1498. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01498
Cheng CY, Krishnakumar V, Chan AP, Thibaud-Nissen F, Schobel S, Town CD (2017) Araport11: a complete reannotation of the Arabidopsis thaliana reference genome. Plant J 89:789–804. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13415
Diebold R, Schuster J, Däschner K, Binder S (2002) The branched-chain amino acid transaminase gene family in Arabidopsis encodes plastid and mitochondrial proteins. Plant Physiol 129:540–550. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.001602
Du L, Li N, Chen L, Xu Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Li C, Li Y (2014) The ubiquitin receptor DA1 regulates seed and organ size by modulating the stability of the ubiquitin-specific protease UBP15/SOD2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26:665–677. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.122663
Duchêne AM, Giritch A, Hoffmann B, Cognat V, Lancelin D, Peeters NM, Zaepfel M, Marechal-Drouard L, Small ID (2005) Dual targeting is the rule for organellar aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in Arabidopsis thaliana. P Natl Acad Sci USA 102:16484–16489. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504682102
Fakih Z, Plourde MB, Nkouankou CET, Fourcassie V, Bourassa S, Droit A, Germain H (2023) Specific alterations in riboproteomes composition of isonicotinic acid treated arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Mol Biol 111:379–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-022-01332-2
Falcone Ferreyra ML, Pezza A, Biarc J, Burlingame AL, Casati P (2010) Plant L10 ribosomal proteins have different roles during development and translation under ultraviolet-B stress. Plant Physiol 153:1878–1894. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.157057
Feng X, Yang R, Zheng X, Zhang F (2012) Identification of a novel nuclear-localized adenylate kinase 6 from Arabidopsis thaliana as an essential stem growth factor. Plant Physiol Biochem 61:180–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.10.002
Feng J, Gao Y, Wang K, Jiang M (2021) A novel epigenetic regulator ZRF1: insight into its functions in plants. Genes 12:1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081245
Gabruk M, Stecka A, Strzałka W, Kruk J, Strzałka K, Mysliwa-Kurdziel B (2015) Photoactive protochlorophyllide-enzyme complexes reconstituted with PORA, PORB and PORC proteins of A. thaliana: fluorescence and catalytic properties. PLoS ONE 10:e0116990. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116990
Gamir J, Sanchez-Bel P, Flors V (2014) Molecular and physiological stages of priming: how plants prepare for environmental challenges. Plant Cell Rep 33:1935–1949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-014-1665-9
Genisel M, Erdal S, Kizilkaya M (2014) The mitigating effect of cysteine on growth inhibition in salt-stressed barley seeds is related to its own reducing capacity rather than its effects on antioxidant system. Plant Growth Regul 75:187–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9943-7
Gu L, Xu T, Lee K, Lee KH, Kang H (2014) A chloroplast-localized DEAD-box RNA helicaseAtRH3 is essential for intron splicing and plays an important role in the growth and stress response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 82:309–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.07.006
Higashi Y, Hirai MY, Fujiwara T, Naito S, Noji M, Saito K (2006) Proteomic and transcriptomic analysis of Arabidopsis seeds: molecular evidence for successive processing of seed proteins and its implication in the stress response to sulfur nutrition. Plant J 48:557–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02900.x
Hiltunen HM, Illarionov B, Hedtke B, Fischer M, Grimm B (2012) Arabidopsis RIBA proteins: two out of three isoforms have lost their bifunctional activity in riboflavin biosynthesis. Int J Mol Sci 13:14086–14105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131114086
Hou Z, Wang L, Liu J, Hou L, Liu X (2013) Hydrogen sulfide regulates ethylene-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Integr Plant Biol 55:277–289. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12004
Huang J, Xue C, Wang H, Wang L, Schmidt W, Shen R, Lan P (2017) Genes of ACYL CARRIER PROTEIN family show different expression profiles and overexpression of ACYL CARRIER PROTEIN 5 modulates fatty acid composition and enhances salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 8:987. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00987
Hummel M, Dobrenel T, Cordewener JJ, Davanture M, Meyer C, Smeekens SJ, Bailey-Serres J, America TA, Hanson J (2015) Proteomic LC-MS analysis of Arabidopsis cytosolic ribosomes: identification of ribosomal protein paralogs and re-annotation of the ribosomal protein genes. J Proteomics 128:436–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2015.07.004
Ibata H, Nagatani A, Mochizuki N (2016) CHLH/GUN5 function in tetrapyrrole Metabolism is correlated with plastid signaling but not ABA responses in guard cells. Front Plant Sci 7:1650. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01650
Ji CY, Jin R, Xu Z, Kim HS, Lee CJ, Kang L, Kim SE, Lee HU, Lee JS, Kang CH, Chi YH, Lee SY, Xie Y, Li H, Ma D, Kwak SS (2017) Overexpression of Arabidopsis P3B increases heat and low temperature stress tolerance in transgenic sweetpotato. BMC Plant Biol 17:139. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1087-2
Jordan DB, Bacot KO, Carlson TJ, Kessel M, Viitanen PV (1999) Plant riboflavin biosynthesis. Cloning, chloroplast localization, expression, purification, and partial characterization of spinach lumazine synthase. J Biol Chem 274:22114–22121. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.31.22114
Jozwiak M, Bielewicz D, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Jarmolowski A, Bajczyk M (2023) SERRATE: a key factor in coordinated RNA processing in plants. Trends Plant Sci 28:841–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2023.03.009
Kang CH, Lee YM, Park JH, Nawkar GM, Oh HT, Kim MG, Lee SI, Kim WY, Yun DJ, Lee SY (2016) Ribosomal P3 protein AtP3B of Arabidopsis acts as both protein and RNA chaperone to increase tolerance of heat and cold stresses. Plant Cell Environ 39:1631–1642. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12742
Kannan K, Nelson AD, Shippen DE (2008) Dyskerin is a component of the Arabidopsis telomerase RNP required for telomere maintenance. Mol Cell Biol 28:2332–2341. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01490-07
Kaur N, Zhao Q, Xie Q, Hu J (2013) Arabidopsis RING peroxins are E3 ubiquitin ligases that interact with two homologous ubiquitin receptor proteins(F). J Integr Plant Biol 55:108–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12014
Klepikova AV, Kasianov AS, Gerasimov ES, Logacheva MD, Penin AA (2016) A high resolution map of the Arabidopsis thaliana developmental transcriptome based on RNA-seq profiling. Plant J 88:1058–1070. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13312
Lan P, Li W, Schmidt W (2012) Complementary proteome and transcriptome profiling in phosphate-deficient Arabidopsis roots reveals multiple levels of gene regulation. Mol Cell Proteomics 11:1156–1166. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M112.020461
Lee JY, Lee HS, Song JY, Jung YJ, Reinbothe S, Park YI, Lee SY, Pai HS (2013a) Cell growth defect factor1/chaperone-like protein of POR1 plays a role in stabilization of light-dependent protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase in Nicotiana benthamiana and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:3944–3960. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.111096
Lee KH, Park J, Williams DS, Xiong Y, Hwang I, Kang BH (2013b) Defective chloroplast development inhibits maintenance of normal levels of abscisic acid in a mutant of the Arabidopsis RH3 DEAD-box protein during early post-germination growth. Plant J 73:720–732. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12055
Li Y, Zheng L, Corke F, Smith C, Bevan MW (2008) Control of final seed and organ size by the DA1 gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Dev 22:1331–1336. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.463608
Li B, Zheng L, Wang R, Xue C, Shen R, Lan P (2022) A proteomic analysis of Arabidopsis ribosomal phosphoprotein P1A mutant. J Proteomics 262:104594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2022.104594
Liang X, Li SW, Gong LM, Li S, Zhang Y (2020) COPII components Sar1b and Sar1c play distinct yet interchangeable roles in pollen development. Plant Physiol 183:974–985. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.20.00159
Liu T, Arsenault J, Vierling E, Kim M (2021) Mitochondrial ATP synthase subunit d, a component of the peripheral stalk, is essential for growth and heat stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 107:713–726. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15317
Lo KY, Li Z, Wang F, Marcotte EM, Johnson AW (2009) Ribosome stalk assembly requires the dual-specificity phosphatase Yvh1 for the exchange of Mrt4 with P0. J Cell Biol 186:849–862. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200904110
Min MK, Jang M, Lee M, Lee J, Song K, Lee Y, Choi KY, Robinson DG, Hwang I (2013) Recruitment of Arf1-GDP to Golgi by Glo3p-type ArfGAPs is crucial for golgi maintenance and plant growth. Plant Physiol 161:676–691. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.209148
Montoya-García L, Muñoz-Ocotero V, Aguilar R, Sánchez de Jiménez E (2002) Regulation of acidic ribosomal protein expression and phosphorylation in maize. Biochemistry 41:10166–10172. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi020037r
Mou M, Wang Q, Chen Y, Yu D, Chen L (2021) Functional characterization of the Arabidopsis SERRATE under salt stress. Plant Divers 43:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pld.2020.06.010
Mylne JS, Hara-Nishimura I, Rosengren KJ (2014) Seed storage albumins: biosynthesis, trafficking and structures. Funct Plant Biol 41:671–677. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP14035
Nunes-Nesi A, Fernie AR, Stitt M (2010) Metabolic and signaling aspects underpinning the regulation of plant carbon nitrogen interactions. Mol Plant 3:973–996. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssq049
Nusspaumer G, Remacha M, Ballesta JP (2000) Phosphorylation and N-terminal region of yeast ribosomal protein P1 mediate its degradation, which is prevented by protein P2. EMBO J 19:6075–6084. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.22.6075
O’Leary MN, Schreiber KH, Zhang Y, Duc AC, Rao S, Hale JS, Academia EC, Shah SR, Morton JF, Holstein CA, Martin DB, Kaeberlein M, Ladiges WC, Fink PJ, Mackay VL, Wiest DL, Kennedy BK (2013) The ribosomal protein Rpl22 controls ribosome composition by directly repressing expression of its own paralog, Rpl22l1. PLoS Genet 9:e1003708. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003708
Palm D, Simm S, Darm K, Weis BL, Ruprecht M, Schleiff E, Scharf C (2016) Proteome distribution between nucleoplasm and nucleolus and its relation to ribosome biogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA Biol 13:441–454. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1154252
Peng Y, Chen L, Lu Y, Wu Y, Dumenil J, Zhu Z, Bevan MW, Li Y (2015) The ubiquitin receptors DA1, DAR1, and DAR2 redundantly regulate endoreduplication by modulating the stability of TCP14/15 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 27:649–662
Polymenis M, Aramayo R (2015) Translate to divide: control of the cell cycle by protein synthesis. Microb Cell 2:94–104. https://doi.org/10.15698/mic2015.04.198
Ramos RS, Casati P, Spampinato CP, Falcone Ferreyra ML (2020) Ribosomal protein RPL10A contributes to early plant development and abscisic acid-dependent responses in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 11:582353. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.582353
Richter AS, Wang P, Grimm B (2016) Arabidopsis Mg-protoporphyrin IX methyltransferase activity and redox regulation depend on conserved cysteines. Plant Cell Physiol 57:519–527. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcw007
Salih KJ, Duncan O, Li L, Trosch J, Millar AH (2020) The composition and turnover of the Arabidopsis thaliana 80S cytosolic ribosome. Biochem J 477:3019–3032. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20200385
Savada RP, Bonham-Smith PC (2014) Differential transcript accumulation and subcellular localization of Arabidopsis ribosomal proteins. Plant Sci 223:134–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.03.011
Saxena SC, Salvi P, Kaur H, Verma P, Petla BP, Rao V, Kamble N, Majee M (2013) Differentially expressed myo-inositol monophosphatase gene (CaIMP) in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) encodes a lithium-sensitive phosphatase enzyme with broad substrate specificity and improves seed germination and seedling growth under abiotic stresses. J Exp Bot 64:5623–5639. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert336
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Slovak R, Setzer C, Roiuk M, Bertels J, Göschl C, Jandrasits K, Beemster GTS, Busch W (2020) Ribosome assembly factor Adenylate kinase 6 maintains cell proliferation and cell size homeostasis during root growth. New Phytol 225:2064–2076. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16291
Supek F, Bošnjak M, Škunca N, Šmuc T (2011) REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of gene ontology terms. PLoS ONE 6:e21800. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0021800
Szick K, Springer M, Bailey-Serres J (1998) Evolutionary analyses of the 12-kDa acidic ribosomal P-proteins reveal a distinct protein of higher plant ribosomes. P Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2378–2383. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.5.2378
Tabeta H, Higashi Y, Okazaki Y, Toyooka K, Wakazaki M, Sato M, Saito K, Hirai MY, Ferjani A (2022) Skotomorphogenesis exploits threonine to promote hypocotyl elongation. Quant Plant Biol 3:e26. https://doi.org/10.1017/qpb.2022.19
Tang G, Zhu-Shimoni JX, Amir R, Zchori IB, Galili G (1997) Cloning and expression of an Arabidopsis thaliana cDNA encoding a monofunctional aspartate kinase homologous to the lysine-sensitive enzyme of Escherichia coli. Plant Mol Biol 34:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005849228945
Tchórzewski M (2002) The acidic ribosomal P proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 34:911–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1357-2725(02)00012-2
Tchórzewski M, Boldyreff B, Issinger OG, Grankowski N (2000) Analysis of the protein-protein interactions between the human acidic ribosomal P-proteins: evaluation by the two hybrid system. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 32:737–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1357-2725(00)00017-0
Torabinejad J, Donahue JL, Gunesekera BN, Allen-Daniels MJ, Gillaspy GE (2009) VTC4 is a bifunctional enzyme that affects myoinositol and ascorbate biosynthesis in plants. Plant Physiol 150:951–961. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.135129
Vanhaeren H, Chen Y, Vermeersch M, De Milde L, De Vleeschhauwer V, Natran A, Persiau G, Eeckhout D, De Jaeger G, Gevaert K, Inze D (2020) UBP12 and UBP13 negatively regulate the activity of the ubiquitin-dependent peptidases DA1, DAR1 and DAR2. Elife 9:e52276. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.52276.sa2
Wang P, Nolan TM, Clark NM, Jiang H, Montes-Serey C, Guo H, Bassham DC, Walley JW, Yin Y (2021) The F-box E3 ubiquitin ligase BAF1 mediates the degradation of the brassinosteroid-activated transcription factor BES1 through selective autophagy in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 33:3532–3554. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab210
Warner JR, McIntosh KB (2009) How common are extraribosomal functions of ribosomal proteins? Mol Cell 34:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.03.006
Wilson DF (2017) Oxidative phosphorylation: regulation and role in cellular and tissue metabolism. J Physiol 595:7023–7038. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP273839
Wirtz M, Droux M (2005) Synthesis of the sulfur amino acids: cysteine and methionine. Photosynth Res 86:345–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-005-8810-9
Wiśniewski JR, Zougman A, Nagaraj N, Mann M (2009) Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat Methods 6:359–362. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1322
Wiśniewski JR, Hein MY, Cox J, Mann M (2014) A “proteomic ruler” for protein copy number and concentration estimation without spike-in standards. Mol Cell Proteomics 13:3497–3506. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M113.037309
Xia T, Li N, Dumenil J, Li J, Kamenski A, Bevan MW, Gao F, Li Y (2013) The ubiquitin receptor DA1 interacts with the E3 ubiquitin ligase DA2 to regulate seed and organ size in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:3347–3359. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.115063
Xiong W, Lan T, Mo B (2021) Extraribosomal functions of cytosolic ribosomal proteins in plants. Front Plant Sci 12:607157. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.607157
Yan H, Chen D, Wang Y, Sun Y, Zhao J, Sun M, Peng X (2016) Ribosomal protein L18aB is required for both male gametophyte function and embryo development in Arabidopsis. Sci Rep 6:31195. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31195
Yan M, Xue C, Xiong Y, Meng X, Li B, Shen R, Lan P (2020) Proteomic dissection of the similar and different responses of wheat to drought, salinity and submergence during seed germination. J Proteomics 220:103756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2020.103756
Yan M, Zheng L, Li B, Shen R, Lan P (2021) Comparative proteomics reveals new insights into the endosperm responses to drought, salinity and submergence in germinating wheat seeds. Plant Mol Biol 105:287–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-020-01087-8
Zhang C, Zhang W, Ren G, Li D, Cahoon RE, Chen M, Zhou Y, Yu B, Cahoon EB (2015) Chlorophyll synthase under epigenetic surveillance is critical for vitamin E synthesis, and altered expression affects tocopherol levels in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 168:1503–1511. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00594
Zheng L, Karim MR, Hu YG, Shen R, Lan P (2021) Greater morphological and primary metabolic adaptations in roots contribute to phosphate-deficiency tolerance in the bread wheat cultivar Kenong199. BMC Plant Biol 21:381. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03164-6
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M, Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C, Chanda SK (2019) Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun 10:1523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09234-6
Zsigmond L, Tomasskovics B, Deák V, Rigó G, Szabados L, Bánhegyi G, Szarka A (2011) Enhanced activity of galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase and ascorbate-glutathione cycle in mitochondria from complex III deficient Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:809–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2011.04.013
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ruonan Wang, Yuchen Fei, Caiwen Xue, Xin Zhang, Mingke Yan, and Yi Xiong for their help and discussion of the experiments.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070279, 31370280, 41401284), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20221560), and the Project of Priority and Key Areas, Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ISSASIP2206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PL contributed to the conception and design of this study. Material preparation, data collection, and bioinformatics analysis were performed by PL, LZ, PZ, YP, and BL. The first draft of the manuscript was written by LZ. All authors commented and modified the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11103_2023_1378_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file1 Representative images showing the hypocotyl and root phenotypes of the wild-type Col-0, rpp1a-1, and rpp1a-2 mutants grown on ES agar medium. Photographs were taken 4, 6, and 8 days after germination (bar, 1 cm) (PDF 7611 KB)
11103_2023_1378_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
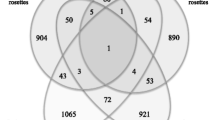
Supplementary file2 Comparison of proteomic profiles between the germinating seeds and young siliques. Venn diagram showing the intersection between total proteins (a), differentially accumulated proteins (DAPs) (b), and DAPs in the ribosome (c) identified between the wild-type Col-0 and rpp1a mutant in the germinating seeds and young siliques (PDF 405 KB)
11103_2023_1378_MOESM3_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary file3 Total high-confidence proteins detected in the germinating seeds of the wild-type Col-0 and rpp1a mutant. (XLSX 2404 KB)
11103_2023_1378_MOESM4_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary file4 Differentially accumulated proteins identified between the germinating seeds of the wild-type Col-0 and rpp1a mutant. (XLSX 32 KB)
11103_2023_1378_MOESM5_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary file5 Gene ontology enrichment results of the differentially accumulated proteins, increased proteins, and decreased proteins identified between the germinating seeds of the wild-type Col-0 and rpp1a mutant (XLSX 26 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Zhou, P., Pan, Y. et al. Proteomic profile of the germinating seeds reveals enhanced seedling growth in Arabidopsis rpp1a mutant. Plant Mol Biol 113, 105–120 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-023-01378-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-023-01378-w