Abstract
Key message
Construction of ML-hGRN for the salt pathway in Populus davidiana × P. bolleana. Construction of ML-hGRN for the lignocellulosic pathway in Populus davidiana × P. bolleana under salt stress.
Abstract
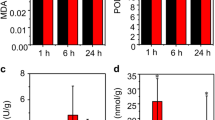
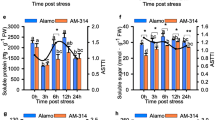
Many woody plants, including Populus davidiana × P. bolleana, have made great contributions to human production and life. High salt is one of the main environmental factors that restricts the growth of poplar. This study found that high salt could induce strong biochemical changes in poplar. To detect the effect of salt treatment on gene expression, 18 libraries were sequenced on the Illumina sequencing platform. The results identified a large number of early differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and a small number of late DEGs, which indicated that most of the salt response genes of poplar were early response genes. In addition, 197 TFs, including NAC, ERF, and other TFs related to salt stress, were differentially expressed during salt treatment, which indicated that these TFs may play an important role in the salt stress response of poplar. Based on the RNA-seq analysis results, multilayered hierarchical gene regulatory networks (ML-hGRNs) of salt stress- and lignocellulosic synthesis-related DEGs were constructed using the GGM algorithm. The lignocellulosic synthesis regulatory network under salt stress revealed that lignocellulosic synthesis might play an important role in the process of salt stress resistance. Furthermore, the NAC family transcription factor PdbNAC83, which was found in the upper layer in both pathways, was selected to verify the accuracy of the ML-hGRNs. DAP-seq showed that the binding site of PdbNAC83 included a “TT(G/A)C(G/T)T” motif, and ChIP-PCR further verified that PdbNAC83 can regulate the promoters of at least six predicted downstream genes (PdbNLP2-2, PdbZFP6, PdbMYB73, PdbC2H2-like, PdbMYB93-1, PdbbHLH094) by binding to the “TT(G/A)C(G/T)T” motif, which indicates that the predicted regulatory network diagram obtained in this study is relatively accurate. In conclusion, a species-specific salt response pathway might exist in poplar, and this finding lays a foundation for further study of the regulatory mechanism of the salt stress response and provides new clues for the use of genetic engineering methods to create high-quality and highly resistant forest germplasms.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
Abbreviations
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- TFs:
-
Transcription factors
- ML-hGRNs:
-
Multilayered hierarchical gene regulatory networks
- GGM:
-
Graphic Gaussian model
- DAP-seq:
-
DNA affinity purification sequencing
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
References
Boutet E, Lieberherr D, Tognolli M, Schneider M, Bansal P, Bridge AJ, Poux S, Bougueleret L, Xenarios I (2016) UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot, the manually annotated section of the UniProt KnowledgeBase: how to use the entry view. Methods Mol Biol 1374:23–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3167-5_2
Chabannes M, Ruel K, Yoshinaga A, Chabbert B, Jauneau A, Joseleau JP, Boudet AM (2001) In situ analysis of lignins in transgenic tobacco reveals a differential impact of individual transformations on the spatial patterns of lignin deposition at the cellular and subcellular levels. Plant J 28:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2001.01159.x
Chen S, Jiang J, Li H, Liu G (2012) The salt-responsive transcriptome of Populus simonii × Populus nigra via DGE. Gene 504:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.05.023
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Gu J (2018) fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34:i884–i890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Chen K, Song M, Guo Y, Liu L, Xue H, Dai H, Zhang Z (2019) MdMYB46 could enhance salt and osmotic stress tolerance in apple by directly activating stress-responsive signals. Plant Biotechnol J 17:2341–2355. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13151
Cheng Z, Zhang X, Zhao K, Yao W, Li R, Zhou B, Jiang T (2019) Over-expression of ERF38 gene enhances salt and osmotic tolerance in transgenic poplar. Front Plant Sci 10:1375. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01375
Dixon RA, Paiva NL (1995) Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 7:1085. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.7.7.1085
Donaldson LA (2001) Lignification and lignin topochemistry—an ultrastructural view. Phytochemistry 57:859–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(01)00049-8
El-Gebali S, Mistry J, Bateman A, Eddy SR, Luciani A, Potter SC, Qureshi M, Richardson LJ, Salazar GA, Smart A, Sonnhammer ELL, Hirsh L, Paladin L, Piovesan D, Tosatto SCE, Finn RD (2019) The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D427–D432. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky995
Fasani E, DalCorso G, Costa A, Zenoni S, Furini A (2019) The Arabidopsis thaliana transcription factor MYB59 regulates calcium signalling during plant growth and stress response. Plant Mol Biol 99:517–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-019-00833-x
Gong Q, Li S, Zheng Y, Duan H, Xiao F, Zhuang Y, He J, Wu G, Zhao S, Zhou H, Lin H (2020) SUMOylation of MYB30 enhances salt tolerance by elevating alternative respiration via transcriptionally upregulating AOX1a in Arabidopsis. Plant J 102:1157–1171. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14689
Guo LM, Li J, He J, Liu H, Zhang HM (2020) A class I cytosolic HSP20 of rice enhances heat and salt tolerance in different organisms. Sci Rep 10:1383. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58395-8
He F, Niu MX, Feng CH, Li HG, Su Y, Su WL, Pang H, Yang Y, Yu X, Wang HL, Wang J, Liu C, Yin W, Xia X (2020) PeSTZ1 confers salt stress tolerance by scavenging the accumulation of ROS through regulating the expression of PeZAT12 and PeAPX2 in populus. Tree Physiol 40:1292–1311. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpaa050
Hu P, Zhang K, Yang C (2019) BpNAC012 positively regulates abiotic stress responses and secondary wall biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 179:700–717. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.01167
Jensen MK, Kjaersgaard T, Nielsen MM, Galberg P, Petersen K, O’Shea C, Skriver K (2010) The Arabidopsis thaliana NAC transcription factor family: structure-function relationships and determinants of ANAC019 stress signalling. Biochem J 426:183–196. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20091234
Ju YL, Yue XF, Min Z, Wang XH, Fang YL, Zhang JX (2020) VvNAC17, a novel stress-responsive grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) NAC transcription factor, increases sensitivity to abscisic acid and enhances salinity, freezing, and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 146:98–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.11.002
Kim JH, Nguyen NH, Jeong CY, Nguyen NT, Hong SW, Lee H (2013) Loss of the R2R3 MYB, AtMyb73, causes hyper-induction of the SOS1 and SOS3 genes in response to high salinity in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 170:1461–1465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2013.05.011
Kucukoglu M, Nilsson J, Zheng B, Chaabouni S, Nilsson O (2017) WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX4 (WOX4)-like genes regulate cambial cell division activity and secondary growth in populus trees. New Phytol 215:642–657. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14631
Kumari S, Deng W, Gunasekara C, Chiang V, Chen HS, Ma H, Davis X, Wei H (2016) Bottom-up GGM algorithm for constructing multilayered hierarchical gene regulatory networks that govern biological pathways or processes. BMC Bioinform 17:132. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-016-0981-1
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Leshem Y, Melamed-Book N, Cagnac O, Ronen G, Nishri Y, Solomon M, Cohen G, Levine A (2006) Suppression of Arabidopsis vesicle-SNARE expression inhibited fusion of H2O2-containing vesicles with tonoplast and increased salt tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18008–18013. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0604421103
Li Q, Brown J, Huang H, Bickel P (2011) Measuring reproducibility of high-throughput experiments. Ann Appl Stat 5:1752–1779
Liu J, Rice JH, Chen N, Baum TJ, Hewezi T (2014) Synchronization of developmental processes and defense signaling by growth regulating transcription factors. PLoS ONE 9(5):e98477. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0098477
Liu Z, Lei X, Wang P, Wang Y, Lv J, Li X, Gao C (2020) Overexpression of ThSAP30BP from Tamarix hispida improves salt tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 146:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.11.020
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Lu Q, Shao F, Macmillan C, Wilson IW, van der Merwe K, Hussey SG, Myburg AA, Dong X, Qiu D (2018) Genomewide analysis of the lateral organ boundaries domain gene family in Eucalyptus grandis reveals members that differentially impact secondary growth. Plant Biotechnol J 16:124–136. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12754
Machanick P, Bailey T (2011) MEME-ChIP: motif analysis of large DNA datasets. Bioinformatics 27:1696–1697. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr189
Miller G, Shulaev V, Mittler R (2008) Reactive oxygen signaling and abiotic stress. Physiol Plant 133:481–489. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2008.01090.x
Min JH, Chung JS, Lee KH, Kim CS (2015) The CONSTANS-like 4 transcription factor, AtCOL4, positively regulates abiotic stress tolerance through an abscisic acid-dependent manner in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 57:313–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12246
Minoru K, Michihiro A, Susumu G, Masahiro H, Mika H, Masumi I, Toshiaki K, Shuichi K, Shujiro O, Toshiaki T (2008) KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D480–D484. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm882
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT, Salzberg SL (2016) Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat Protoc 11:1650–1667. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2016.095
Piao W, Sakuraba Y, Paek NC (2019) Transgenic expression of rice MYB102 (OsMYB102) delays leaf senescence and decreases abiotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMB Rep 52:653–658. https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.11.071
Pruthvi V, Narasimhan R, Nataraja KN (2014) Simultaneous expression of abiotic stress responsive transcription factors, AtDREB2A, AtHB7 and AtABF3 improves salinity and drought tolerance in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). PLoS ONE 9:e111152. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111152
Qiu Q, Ma T, Hu Q, Liu B, Wu Y, Zhou H, Wang Q, Wang J, Liu J (2011) Genome-scale transcriptome analysis of the desert poplar, Populus euphratica. Tree Physiol 31:452–461. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpr015
Quan M, Du Q, Xiao L, Lu W, Wang L, Xie J, Song Y, Xu B, Zhang D (2019) Genetic architecture underlying the lignin biosynthesis pathway involves noncoding RNAs and transcription factors for growth and wood properties in populus. Plant Biotechnol J 17:302–315. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12978
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ (2009) The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci 14:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.10.007
Shi YN, Liu XF, Li X, Dong WC, Donald G, Yin XR, Chen KS (2017) SIMYB1 and SIMYB2, two new MYB genes from tomato, transcriptionally regulate cellulose biosynthesis in tobacco. J Integr Agric 2017(16):65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61389-8
Wang PL, Wang LQ, Liu ZY, Zhang TQ, Wang YY, Li YB, Gao CQ (2019) Molecular characterization and expression profiles of GRAS genes in response to abiotic stress and hormone treatment in Tamarix hispida. Trees 33:213–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-018-1771-3
Wei XA, Yao WJ, Jiang TB, Zhou BR (2016) Identification of WRKY gene in response to abiotic stress from WRKY transcription factor gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Northeast for Univ 44(45–48):55
Wu Z, Liang J, Wang C, Zhao X, Zhong X, Cao X, Li G, He J, Yi M (2018) Overexpression of lily HsfA3s in Arabidopsis confers increased thermotolerance and salt sensitivity via alterations in proline catabolism. J Exp Bot 69:2005–2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery035
Xiong JL, Wang HC, Tan XY, Zhang CL, Naeem MS (2018) 5-Aminolevulinic acid improves salt tolerance mediated by regulation of tetrapyrrole and proline metabolism in Brassica napus L. seedlings under NaCl stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 124:88–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.01.001
Yan Y, Wang P, Lu Y, Bai Y, Wei Y, Liu G, Shi H (2021) MeRAV5 promotes drought stress resistance in cassava by modulating hydrogen peroxide and lignin accumulation. Plant J 107:847–860. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15350
Yang Y, Yu TF, Ma J, Chen J, Zhou YB, Chen M, Ma YZ, Wei WL, Xu ZS (2020) The Soybean bZIP transcription factor gene GmbZIP2 confers drought and salt resistances in transgenic plants. Int J Mol Sci 21:670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020670
Yao W, Wang S, Zhou B, Jiang T (2016) Transgenic poplar overexpressing the endogenous transcription factor ERF76 gene improves salinity tolerance. Tree Physiol 36:896–908. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpw004
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY (2012) clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 16:284–287. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2011.0118
Yu YT, Wu Z, Lu K, Bi C, Liang S, Wang XF, Zhang DP (2016) Overexpression of the MYB37 transcription factor enhances abscisic acid sensitivity, and improves both drought tolerance and seed productivity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 90:267–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0411-1
Zang D, Wang C, Ji X, Wang Y (2015) Tamarix hispida zinc finger protein ThZFP1 participates in salt and osmotic stress tolerance by increasing proline content and SOD and POD activities. Plant Sci 235:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.02.016
Zhang Y, Liu T, Meyer CA, Eeckhoute J, Johnson DS, Bernstein BE, Nusbaum C, Myers RM, Brown M, Li W, Liu XS (2008) Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol 9:R137. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2008-9-9-r137
Zhang SH, Shi YH, Du CNN, HQ, Fan WN, Wang CZ, (2015) EuKaryotic Orthologous Groups (KOG) classifications of alfalfa transcripts. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122170.g006
Zhang AD, Liu DD, Hua CM, Yan A, Liu BH, Wu MJ, Liu YH, Huang LL, Ali I, Gan YB (2016) The Arabidopsis gene zinc finger protein 3(ZFP3) is involved in salt stress and osmotic stress response. PLoS ONE 11:e0168367. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0168367
Zhang TQ, Zhao YL, Wang YC, Liu ZY, Gao CQ (2018) Comprehensive analysis of MYB gene family and their expressions under abiotic stresses and hormone treatments in Tamarix hispida. Front Plant Sci 9:1303. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01303
Zhang X, Cheng Z, Zhao K, Yao W, Sun X, Jiang T, Zhou B (2019) Functional characterization of poplar NAC13 gene in salt tolerance. Plant Sci 281:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.01.003
Zhao H, Jiang J, Li K, Liu G (2017) Populus simonii × Populus nigra WRKY70 is involved in salt stress and leaf blight disease responses. Tree Physiol 37:827–844. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpx020
Zhao K, Zhang D, Lv K, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Li R, Zhou B, Jiang T (2019a) Functional characterization of poplar WRKY75 in salt and osmotic tolerance. Plant Sci 289:110259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110259
Zhao YY, Yang ZE, Ding YP, Liu LS, Han X, Zhan JJ, Wei X, Diao YY, Qin WQ, Wang P, Liu PP, Sajjad M, Zhang XL, Ge XY (2019b) Over-expression of an R2R3 MYB Gene, GhMYB73, increases tolerance to salt stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 286:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.05.021
Zhao HM, Li HY, Jia YQ, Wen XJ, Guo HY, Xu HY, Wang YC (2020) Building a robust chromatin immunoprecipitation method with substantially improved efficiency. Plant Physiol 183:1026–1034. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.20.00392
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0600106) and the Heilongjiang Touyan Innovation Team Program (Tree Genetics and Breeding Innovation Team).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XJL and ZYL wrote the manuscript and performed the experiments. QJX and JRF performed the assays. CYW and JHL performed the data analysis. CQG and CW designed the study. CQG provided funds for the current study and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11103_2022_1267_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 (TIF 56902 kb) Fig. S1 The phenotypes of poplar plants used for the construction of the networks. A–F showed the phenotypes of poplar plants with 200 mM NaCl stress for 0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h and 48 h, respectively. Bars = 1 cm
11103_2022_1267_MOESM2_ESM.png
Supplementary file2 (PNG 42 kb) Fig. S2 Sample PCA assay. Each sample group included three biological replicates (rep-1, 2, and 3)
11103_2022_1267_MOESM3_ESM.png
Supplementary file3 (PNG 218 kb) Fig. S3 Verification of transcriptome data by qRT-PCR. The bar chart shows the qRT-PCR results for 15 selected genes in Populus davidiana × P. bolleana. All relative transcription levels were log2-transformed. The line chart shows the gene expression data obtained by RNA-Seq
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, X., Liu, Z., Xie, Q. et al. Construction of two regulatory networks related to salt stress and lignocellulosic synthesis under salt stress based on a Populus davidiana × P. bolleana transcriptome analysis. Plant Mol Biol 109, 689–702 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-022-01267-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-022-01267-8