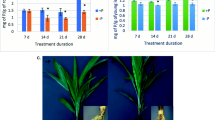
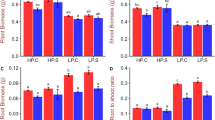
Abstract
Phosphorus (P) is essential for cellular processes like respiration, photosynthesis, biosynthesis of membrane phospholipids, etc. To cope with P deficiency stress, plants adopt reprograming of the expression of genes involved in different metabolic/signaling pathways for survival, growth, and development. Plants use transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and/or post-translational machinery to achieve P homeostasis. Several transcription factors (TFs), miRNAs, and P transporters play important roles in P deficiency tolerance; however, the underlying mechanisms responsible for P deficiency tolerance remain poorly understood. Studies on P starvation/deficiency responses in plants at early (seedling) stage of growth have been reported but only a few of them focused on molecular responses of the plant at advanced (tillering or reproductive) stage of growth. To decipher the strategies adopted by rice at tillering stage under P deficiency stress, a pair of contrasting genotypes [Pusa-44 (a high-yielding, P deficiency sensitive cultivar) and its near-isogenic line (NIL-23, P deficiency tolerant) for Pup1 QTL] was used for morphophysiological, biochemical, and molecular analyses. Comparative analyses of shoot and root tissues from 45-day-old plants grown hydroponically under P sufficient (16 ppm) or P deficient (4 ppm) medium confirmed some of the known morphophysiological responses. Moreover, RNA-seq analysis revealed the important roles of phosphate transporters, TFs, auxin-responsive proteins, modulation in the cell wall, fatty acid metabolism, and chromatin architecture/epigenetic modifications in providing P deficiency tolerance to NIL-23, which were brought in due to the introgression of the Pup1 QTL in Pusa-44. This study provides insights into the molecular functions of Pup1 for P deficiency tolerance, which might be utilized to improve P-use efficiency of rice for better productivity in P deficient soils.
Key message
Introgression of Pup1 QTL in high-yielding rice cultivar modulates mainly phosphate transporters, TFs, auxin-responsive proteins, cell wall structure, fatty acid metabolism, and chromatin architecture/epigenetic modifications at tillering stage of growth under phosphorus deficiency stress.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
RNA-seq raw data are available at NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra) under the BioProject IDs: PRJNA667189 and PRJNA796019.
References
Abel S, Ticconi CA, Delatorre CA (2002) Phosphate sensing in higher plants. Physiol Plant 115:1–8
Ai P, Sun S, Zhao J, Fan X, Xin X, Guo Q et al (2009) Two rice phosphate transporters, OsPht1;2 and OsPht1;6, have different functions and kinetic properties in uptake and translocation. Plant J 57:798–809
Amanullah, (2015) Specific leaf area and specific leaf weight in small grain crops wheat, rye, barley, and oats differ at various growth stages and NPK source. J Plant Nutr 38:1694–1708
Anila M, Mahadevaswamy HK, Bhadana VP, Brajendra Hajira SK, Pranathi K et al (2014) Marker-assisted introgression of Pup1, a major QTL associated with tolerance to low soil phosphorus into the elite rice variety MTU1010. Prog Res 9:735–738
Baldwin JC, Karthikeyan AS, Raghothama KG (2001) LEPS2, a phosphorus starvation-induced novel acid phosphatase from tomato. Plant Physiol 125:728–737
Bariola PA, Howard CJ, Taylor CP, Verburg MT, Jaglan VD, Green PJ (1994) The Arabidopsis ribonuclease gene RNS1 is tightly controlled in response to phosphate limitation. Plant J 6:673–685
Batsale M, Bahammou D, Fouillen L, Mongrand S, Joubès J, Domergue F (2021) Biosynthesis and functions of very-long-chain fatty acids in the responses of plants to abiotic and biotic stresses. Cells 10:1284
Bayle V, Arrighi JF, Creff A, Nespoulous C, Vialaret J, Rossignol M et al (2011) Arabidopsis thaliana high-affinity phosphate transporters exhibit multiple levels of posttranslational regulation. Plant Cell 23:1523–1535
Bournier M, Tissot N, Mari S, Boucherez J, Lacombe E, Briat JF, Gaymard F (2013) Arabidopsis ferritin 1 (AtFer1) gene regulation by the phosphate starvation response 1 (AtPHR1) transcription factor reveals a direct molecular link between iron and phosphate homeostasis. J Biol Chem 288:22670–22680
Bürglin TR, Afolter M (2016) Homeodomain proteins: an update. Chromosoma 125:497
Cai H, Xie W, Lian X (2013) Comparative analysis of differentially expressed genes in rice under nitrogen and phosphorus starvation stress conditions. Plant Mol Biol Report 31:160–173
Carstensen A, Szameitat AE, Frydenvang J, Husted S (2019) Chlorophyll a fluorescence analysis can detect phosphorus deficiency under field conditions and is an effective tool to prevent grain yield reductions in spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Soil 434:79–91
Chacón-López A, Ibarra-Laclette E, Sánchez-Calderón L, Gutiérrez-Alanis D, Herrera-Estrella L (2011) Global expression pattern comparison between low phosphorus insensitive 4 and WT Arabidopsis reveals an important role of reactive oxygen species and jasmonic acid in the root tip response to phosphate starvation. Plant Signal Behav 6:382–392
Chang MX, Gu M, Xia Y, Dai X, Dai C, Zhang J et al (2019) OsPHT1;3 mediates uptake translocation and remobilization of phosphate under extremely low phosphate regimes. Plant Physiol 179:656–670
Chen CY, Wu K, Schmidt W (2015) The histone deacetylase HDA19 controls root cell elongation and modulates a subset of phosphate starvation responses in Arabidopsis. Sci Rep 5:15708
Cheng J, Fang C, Yuan H, Wang S, Wu Y, Liu X, Zhang Y, Luo L (2015) Interaction between carbon metabolism and phosphate accumulation is revealed by a mutation of a cellulose synthase-like protein, CSLF6. J Exp Biol 25:57–67
Chin JH, Gamuyao R, Dalid C, Bustamam M, Prasetiyono J, Moeljopawiro S et al (2011) Developing rice with high yield under phosphorus deficiency: Pup1 sequence to application. Plant Physiol 156:1202–1216
Ciereszko I, Johansson H, Kleczkowski LA (2005) Interactive effects of phosphate deficiency, sucrose and light/dark conditions on gene expression of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 162:343–353
Dai X, Wang Y, Yang A, Zhang WH (2012) OsMYB2P-1, an R2R3 MYB transcription factor, is involved in the regulation of phosphate-starvation responses and root architecture in rice. Plant Physiol 159:169–183
Deng Q-W, Luo X-D, Chen Y-L, Zhou Y, Zhang FT, Hu B-L, Xie J-K (2018) Transcriptome analysis of phosphorus stress responsiveness in the seedlings of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufpogon Grif.). Biol Res 51:7
Devaiah BN, Madhuvanthi R, Karthikeyan AS, Raghothama KG (2009) Phosphate starvation responses and gibberellic acid biosynthesis are regulated by the MYB62 transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 2:43–58
Dia X, Wang Y, Zhang WH (2016) OsWRKY74, a WRKY transcription factor, modulates tolerance to phosphate starvation in rice. J Exp Bot 67:947–960
Dodds PN, Clarke AE, Newbigin E (1996) Molecular characterization of an S-like RNase of Nicotiana alata that is induced by phosphate starvation. Plant Mol Biol 31:227–238
Duff SMG, Moorhead GBG, Lefebvre DD (1989) Phosphate starvation inducible ‘Bypasses’ of adenylate and phosphate dependent glycolytic enzymes in Brassica nigra suspension cells. Plant Physiol 90:1275–1278
El Mazlouzi M, Morel C, Robert T, Yan B, Mollier A (2020) Phosphorus uptake and partitioning in two durum wheat cultivars with contrasting biomass allocation as affected by different P supply during grain filling. Plant Soil 449:179–192
Filstrup CT, Downing JA (2017) Relationship of chlorophyll to phosphorus and nitrogen in nutrient-rich lakes. Inland Waters 7:385–400
Franco-Zorrilla JM, Martín AC, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J (2005) Interaction between phosphate-starvation, sugar, and cytokinin signaling in Arabidopsis and the roles of cytokinin receptors CRE1/AHK4 and AHK3. Plant Physiol 138:847–857
Gamuyao R, Chin HJ, Tanaka JP, Pesaresi P, Catausan S, Dalid C et al (2012) The protein kinase Pstol1 from traditional rice confers tolerance of phosphorous deficiency. Nature 488:535–541
Gho Y-S, Choi H, Moon S, Song MY, Park HE, Kim D-H, Ha S-H, Jung K-H (2020) Phosphate-starvation-inducible S-like RNase genes in rice are involved in phosphate source recycling by RNA decay. Front Plant Sci 11:585561
Grierson PF (1992) Organic acids in the rhizosphere of Banksia integrifolia L.f. Plant Soil 144:259–265
Gu M, Zhang J, Li H, Meng D, Li R, Dai X et al (2017) Maintenance of phosphate homeostasis and root development are coordinately regulated by MYB1, an R2R3-type MYB transcription factor in rice. J Exp Bot 68:3603–3615
Hammond JP, Bennett MJ, Bowen HC, Broadley MR, Eastwood DC et al (2003) Changes in gene expression in Arabidopsis shoots during phosphate starvation and the potential for developing smart plants. Plant Physiol 132:578–596
Hammond JP, White PJ (2008) Sucrose transport in the phloem: integrating root responses to phosphorus starvation. J Exp Bot 59:93–109
Hanson WC (1950) The photometric determination of phosphorus in fertilizers using the phosphovanadomolybdate complex. J Sci Food Agric 1:172–173
Henry JB, Perkins-Veazie P, McCall I, Whipker BE (2019) Restricted phosphorus fertilization increases the betacyanin concentration and red foliage coloration of Alternanthera. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 144:264–273
Heuer S, Lu X, Chin JH, Tanaka JP, Kanamori H, Matsumoto T et al (2009) Comparative sequence analyses of the major quantitative trait locus phosphorus uptake 1 (Pup1) reveal a complex genetic structure. Plant Biotechnol J 7:456–467
Hillwig MS, Lebrasseur ND, Green PJ, Macintosh GC (2008) Impact of transcriptional, ABA-dependent, and ABA-independent pathways on wounding regulation of RNS1 expression. Mol Genet Genomics 280:249–261
Hiscox JD, Israelstam GF (1979) Different methods of chlorophyll extraction. Can J Bot 57:1332–1332
Hufnagel B, de Sousa SM, Assis L et al (2014) Duplicate and conquer: multiple homologs of phosphorus-starvation tolerance1 enhance phosphorus acquisition and sorghum performance on low-phosphorus soils. Plant Physiol 166:659–767
Jiang C, Gao X, Liao L, Harberd NP, Fu X (2007) Phosphate starvation root architecture and anthocyanin accumulation responses are modulated by the gibberellin-DELLA signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 145:1460–1470
Johnson CB, Holloway BR, Smith H, Grierson D (1973) Isoenzymes of acid phosphatase in germinating peas. Planta 115:1–10
Kumar S, Kumar S, Mohapatra T (2021a) Interaction between macro- and micro-nutrients in plants. Front Plant Sci 12:665583
Kumar S (2018) Environmental stress, food safety, and global health: biochemical, genetic and epigenetic perspectives. Med Saf Glob Health 7:145
Kumar S (2019) Genome editing to epigenome editing: towards unraveling the enigmas in developmental biology. Trends Dev Biol 12:1–8
Kumar S (2020) Abiotic stresses and their effects on plant growth, yield and nutritional quality of agricultural produce. Int J Food Sci Agric 4:367–378
Kumar S, Chinnusamy V, Mohapatra T (2018) Epigenetics of modified DNA bases: 5-methylcytosine and beyond. Front Genet 9:640
Kumar S, Pallavi, Chugh C, Seem K, Kumar S, Vinod KK, Mohapatra T (2021b) Characterization of contrasting rice (Oryza sativa L) genotypes reveals the Pi-efficient schema for phosphate starvation tolerance. BMC Plant Biol 21:282
Lauer MJ, Pallardy SG, Belvins DG, Randall DD (1989) Whole leaf carbon exchange characteristics of phosphate deficient soybeans (Glycine max L.). Plant Physiol 91:848–854
Lei M, Liu Y, Zhang B, Zhao Y, Wang X, Zhou Y, Raghothama KG, Liu D (2011) Genetic and genomic evidence that sucrose is a global regulator of plant responses to phosphate starvation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156:1116–1130
Li L, Liu C, Lian X (2010) Gene expression profiles in rice roots under low phosphorus stress. Plant Mol Biol 72:423–432
Liang C, Wang J, Zhao J, Tian J, Liao H (2014) Control of phosphate homeostasis through gene regulation in crops. Curr Opin Plant Biol 21:59–66
Lo SF, Yang SY, Chen KT, Hsing YI, Zeevaart JA, Chen LJ, Yu SM (2008) A novel class of gibberellin 2-oxidases control semidwarfism, tillering, and root development in rice. Plant Cell 20:2603–2618
McNally KL, Childs KL, Bohnert R, Davidson RM, Zhao K, Ulat VJ et al (2009) Genome-wide SNP variation reveals relationships among landraces and modern varieties of rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:12273–12278
Mehra P, Pandey BK, Giri J (2016) Comparative morphophysiological analyses and molecular profiling reveal Pi-efficient strategies of a traditional rice genotype. Front Plant Sci 6:1184
Muchhal US, Raghothama KG (1999) Transcriptional regulation of plant phosphate transporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5868–5872
Mudge SR, Rae AL, Diatlof E, Smith FW (2002) Expression analysis suggests novel roles for members of the PHT1 family of phosphate transporters in Arabidopsis. Plant J 31:341–353
Neelam K, Thakur S, Neha YIS, Kumar K, Dhaliwal SS, Singh K (2017) Novel alleles of phosphorus-starvation tolerance 1 gene (PSTOL1) from Oryza rufpogon confers high phosphorus uptake efficiency. Front Plant Sci 8:509
Nilsson L, Müller R, Nielsen TH (2010) Dissecting the plant transcriptome and the regulatory responses to phosphate deprivation. Physiol Plant 139:129–143
Niu YF, Chai RS, Jin GL, Wang H, Tang CX, Zhang YS (2013) Responses of root architecture development to low phosphorus availability: a review. Ann Bot 112:391–408
Pariasca-Tanaka J, Satoh K, Rose T, Mauleon R, Wissuwa M (2009) Stress response versus stress tolerance: a transcriptome analysis of two rice lines contrasting in tolerance to phosphorus deficiency. Rice 2:167–185
Park MR, Baek SH, de Los Reyes BG, Yun SJ, Hasenstein KH (2012) Transcriptome profiling characterizes phosphate deficiency effects on carbohydrate metabolism in rice leaves. J Plant Physiol 169:193–205
Péret B, Clement M, Nussaume L, Desnos T (2011) Root developmental adaptation to phosphate starvation: better safe than sorry. Trends Plant Sci 16:442–450
Pieters AJ, Paul MJ, Lawlor DW (2001) Low sink demand limits photosynthesis under Pi deficiency. J Exp Bot 52:1083–1091
Plaxton WC (1996) The organization and regulation of plant glycolysis. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:185–214
Poirier Y, Bucher M (2002) Phosphate transport and homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Arabidopsis Book 1:e0024
Reddy YAN, Prasad TG, Udaykumar M (1995) Relationship between leaf area index, specific leaf weight and assimilation rate in rice genotypes. Madras Agric J 82:616–617
Ren P, Meng Y, Li B, Ma X, Si E, Lai Y et al (2018) Molecular mechanisms of acclimatization to phosphorus starvation and recovery underlying full-length transcriptome profiling in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Front Plant Sci 9:500
Ribot C, Wang Y, Poirier Y (2008) Expression analyzes of three members of the AtPHO1 family reveal differential interactions between signaling pathways involved in phosphate deficiency and the responses to auxin, cytokinin, and abscisic acid. Planta 227:1025–1036
Richmond TA, Somerville CR (2000) The cellulose synthase superfamily. Plant Physiol 124:495–498
Rouached H, Arpat AB, Poirier Y (2010) Regulation of phosphate starvation responses in plants: signaling players and cross-talks. Mol Plant 3:288–299
Roveda-Hoyos G, Moreno-Fonseca L (2019) Physiological and antioxidant responses of Cape gooseberry (Physalis peruviana L.) seedlings to phosphorus deficiency. Agron Colomb 37:3–11
Rubio V, Bustos R, Irigoyen ML, Cardona-López X, Rojas-Triana M, Paz-Ares J (2009) Plant hormones and nutrient signaling. Plant Mol Biol 69:361–373
Rubio V, Linhares F, Solano R, Martín AC, Iglesias J, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J (2001) A conserved MYB transcription factor involved in phosphate starvation signaling both in vascular plants and in unicellular algae. Genes Dev 15:2122–2133
Schachtman DP, Reid RJ, Ayling SM (1998) Phosphorus uptake by plants: from soil to cell. Plant Physiol 116:447–453
Secco D, Jabnoune M, Walker H, Shou H, Wu P, Poirier Y et al (2013) Spatio-temporal transcript profiling of rice roots and shoots in response to phosphate starvation and recovery. Plant Cell 25:4285–4304
Sharma S, Borah P, Meena MK, Bindraban P, Pandey R (2018) Evaluation of genotypic variation for growth of rice seedlings under optimized hydroponics medium. Indian J Genet 78:292–301
Shukla T, Kumar S, Khare R, Tripathi RD, Trivedi PK (2015) Natural variations in expression of regulatory and detoxification related genes under limiting phosphate and arsenate stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 6:898
Sun L, Song L, Zhang Y, Zheng Z, Liu D (2016) Arabidopsis PHL2 and PHR1 act redundantly as the key components of the central regulatory system controlling transcriptional responses to phosphate starvation. Plant Physiol 170:499–514
Tewari RK, Kumar P, Tewari N, Srivastava S, Sharma PN (2004) Macronutrient deficiencies and differential antioxidant responses-influence on the activity and expression of superoxide dismutase in maize. Plant Sci 166:687–694
Tian J, Wang C, Zhang Q, He X, Whelan J, Shou H (2012) Overexpression of OsPAP10, a root-associated acid phosphatase, increased extracellular organic phosphorus utilization in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 54:631–639
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. N Phytol 157:423–447
Vasconcelos MJV, Figueiredo JEF, Raghothama KG (2018) Expression analysis of anthocyanin gene induced under phosphorus starvation in maize genotypes with contrasting phosphorus use efficiency. Genet Mol Res 17:GMR18036
Voxeur A, Höfte H (2016) Cell wall integrity signaling in plants: “To grow or not to grow that’s the question.” Glycobiology 26:950–960
Wang J, Qin Q, Pan J, Sun L, Sun Y, Xue Y, Song K (2019) Transcriptome analysis in roots and leaves of wheat seedlings in response to low phosphorus stress. Sci Rep 9:19802
Wang X, Li Q, Yuan W, Cao Z, Qi B, Kumar S et al (2016a) The cytosolic Fe–S cluster assembly component MET18 is required for the full enzymatic activity of ROS1 in active DNA demethylation. Sci Rep 6:26443
Wang YS, Jensen LS, Magid J (2016b) Differential responses of root and root hair traits of spring wheat genotypes to phosphorus deficiency in solution culture. Plant Soil Environ 62:540–546
Wasaki J, Shinano T, Onishi K, Yonetani R, Yazaki J, Fujii F et al (2006) Transcriptomic analysis indicates putative metabolic changes caused by manipulation of phosphorus availability in rice leaves. J Exp Bot 57:2049–2059
Williamson LC, Ribrioux SPCP, Fitter AH, Leyser HMO (2001) Phosphate availability regulates root system architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:875–882
Wissuwa M, Gamat G, Ismail AM (2005) Is root growth under phosphorus deficiency affected by source or sink limitations? J Exp Bot 56:1943–1950
Wissuwa M, Yano M, Ae N (1998) Mapping of QTLs for phosphorus deficiency tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 97:777–783
Yang SY, Grønlund M, Jakobsen I, Grotemeyer MS, Rentsch D, Miyao A et al (2012) Nonredundant regulation of rice arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis by two members of the phosphate transporter1 gene family. Plant Cell 24:4236–4251
Yang T, Li Y, Liu Y, He L, Liu A, Wen J, Mysore KS, Tadege M, Chen J (2021) The 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase WFL is involved in lateral organ development and cuticular wax synthesis in Medicago truncatula. Plant Mol Biol 105:193–204
Yong-Villalobos L, Cervantes-Pérez SA, Gutiérrez-Alanis D, Gonzáles Morales S, Martínez O, Herrera-Estrella L (2016) Phosphate starvation induces DNA methylation in the vicinity of cis-acting elements known to regulate the expression of phosphate-responsive genes. Plant Signal Behav 11:e1173300
Yuan H, Liu D (2008) Signaling components involved in plant responses to phosphate starvation. J Integr Plant Biol 50:849–859
Yugandhar P, Nallamothu V, Panigrahy M, Tipireddy S, Bhadana VP, Voleti SR et al (2018) Nagina 22 mutants tolerant or sensitive to low P in field show contrasting response to double P in hydroponics and pots. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64:1975–1987
Zahraeifard S, Foroozani M, Sepehri A, Oh D-H, Wang G, Mangu V et al (2018) Rice H2A.Z negatively regulates genes responsive to nutrient starvation but promotes expression of key housekeeping genes. J Exp Bot 69:4907–4919
Zhang J, Jiang F, Shen Y, Zhan Q, Bai B, Chen W, Chi Y (2019) Transcriptome analysis reveals candidate genes related to phosphorus starvation tolerance in sorghum. BMC Plant Biol 19:306
Zhu JM, Mickelson SM, Kaeppler SM, Lynch JP (2006) Detection of quantitative trait loci for seminal root traits in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings grown under differential phosphorus levels. Theor Appl Genet 113:1–10
Acknowledgements
SuK acknowledges funding from the Extramural Research Grant of the Division of Crop Sciences, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi, India.
Funding
The research was carried out with financial support from Extramural Research Grant [18(3)/2018-O&P] from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, Government of India, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SuK and TM conceptualize and supervised the experiments. AA and KS carried out the experiments. SaK performed bioinformatic analyses. KKV developed the near isogenic lines, evaluated them and provided the best performers for experimentation. SuK, KS and SaK wrote the manuscript. TM provided ideas for revision; SuK and KS checked the revised manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest. Santosh Kumar is employed at the Decode Genomics Private Limited, New Delhi, and the work was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Agrawal, A., Seem, K. et al. Transcriptome analysis of a near-isogenic line and its recurrent parent reveals the role of Pup1 QTL in phosphorus deficiency tolerance of rice at tillering stage. Plant Mol Biol 109, 29–50 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-022-01254-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-022-01254-z