Abstract
Key message
CmHKT1;1 selectively exports Na+ from plant cells. Upon NaCl stress, its expression increased in a salt-tolerant melon cultivar. Overexpression of CmHKT1;1 increased transgenic Arabidopsis salt tolerance through improved K+/Na+ balance.
Abstract
High-affinity K+ transporters (HKTs) are thought to be involved in reducing Na+ in plant shoots under salt stress and modulating salt tolerance, but their function in a moderately salt-tolerant species of melon (Cucumis melo L.) remains unclear. In this study, a Na+ transporter gene, CmHKT1;1 (GenBank accession number: MK986658), was isolated from melons based on genome data. The transcript of CmHKT1;1 was relatively more abundant in roots than in stems or leaves from melon seedlings. The tobacco transient expression system showed that CmHKT1;1 was plasma-membrane localized. Upon salt stress, CmHKT1;1 expression was more strongly upregulated in a salt-tolerant melon cultivar, ‘Bingxuecui’ (BXC) compared with a salt-sensitive cultivar, ‘Yulu’ (YL). Electrophysiological evidence demonstrated that CmHKT1;1 only transported Na+, rather than K+, when expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Overexpression of CmHKT1;1 increased salt sensitivity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Under NaCl treatments, transgenic Arabidopsis plants accumulated significantly lower concentrations of Na+ in shoots than wild type plants and showed a better K+/Na+ balance, leading to better Fv/Fm, root length, biomass, and enhanced plant growth. The CmHKT1;1 gene may serve as a useful candidate for improving crop salt tolerance.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams E, Shin R (2014) Transport, signaling, and homeostasis of potassium and sodium in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 56:231–249. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12159
Ali A, Maggio A, Bressan RA, Yun DJ (2019) Role and functional differences of HKT1-type transporters in plants under salt stress. Int J Mol Sci 20(5):1059
Ali A, Khan IU, Jan M, Khan HA, Hussain S, Nisar M, Chung WS, Yun DJ (2018) The high-affinity potassium transporter EpHKT1;2 from the extremophile Eutrema parvula mediates salt tolerance. Front Plant Sci 9:1108
Ali Z, Park HC, Ali A, Oh DH, Aman R, Kropornicka A et al (2012) TsHKT1;2, a HKT1 homolog from the extremophile Arabidopsis relative Thellungiella salsuginea, shows K+ specificity in the presence of NaCl. Plant Physiol 158:1463–1474
Almeida DM, Oliveira MM, Saibo NJ (2017) Regulation of Na+ and K+ homeostasis in plants: towards improved salt stress tolerance in crop plants. Genet Mol Biol 40(1):326–345
Ben Amar S, Brini F, Sentenac H, Masmoudi K, Very AA (2014) Functional characterization in Xenopus oocytes of Na+ transport systems from durum wheat reveals diversity among two HKT1;4 transporters. J Exp Bot 65:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert361
Berthomieu P, Conejero G, Nublat A, Brackenbury WJ, Lambert C, Savio C, Uozumi N, Oiki S, Yamada K, Cellier F, Gosti F, Simonneau T, Essah PA, Tester M, Very AA, Sentenac H, Casse F (2003) Functional analysis of AtHKT1 in Arabidopsis shows that Na+ recirculation by the phloem is crucial for salt tolerance. EMBO J 22:2004–2014. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg207
Botía P, Navarro JM, Cerdá A, Martínez V (2005) Yield and fruit quality of two melon cultivars irrigated with saline water at different stages of development. Eur J Agron 23:243–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2004.11.003
Byrt CS, Platten JD, Spielmeyer W, James RA, Lagudah ES, Dennis ES, Tester M, Munns R (2007) HKT1;5-like cation transporters linked to Na+ exclusion loci in wheat, Nax2 and Kna1. Plant Physiol 143:1918–1928. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.093476
Byrt CS, Xu B, Krishnan M, Lightfoot DJ, Athman A, Jacobs AK, Watson-Haigh NS, Plett D, Munns R, Tester M et al (2014) The Na+ transporter, TaHKT1;5-D, limits shoot Na+ accumulation in bread wheat. Plant J 80:516–526
Chen H, Chen X, Gu H, Wu B, Zhang H, Yuan X, Cui X (2014) GmHKT1;4, a novel soybean gene regulating Na+/K+ ratio in roots enhances salt tolerance in transgenic plants. Plant Growth Regul 73:299–308
Corratge-Faillie C, Jabnoune M, Zimmermann S, Very AA, Fizames C, Sentenac H (2010) Potassium and sodium transport in non-animal cells: the Trk/Ktr/HKT transporter family. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:2511–2532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0317-7
Cotsaftis O, Plett D, Shirley N, Tester M, Hrmova M (2012) A two-staged model of Na+ exclusion in rice explained by 3D modeling of HKT transporters and alternative splicing. PLOS ONE 7:e39865
Davenport RJ, Munoz-Mayor A, Jha D, Essah PA, Rus A, Tester M (2007) The Na+ transporter AtHKT1;1 controls retrieval of Na+ from the xylem in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 30:497–507. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01637.x
Deinlein U, Stephan AB, Horie T, Luo W, Xu G, Schroeder JI (2014) Plant salt-tolerance mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci 19:371–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.02.001
Gao JP, Chao DY, Lin HX (2007) Understanding abiotic stress tolerance mechanisms: recent studies on stress response in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 49:742–750. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2007.00495.x
Garciadeblas B, Senn ME, Banuelos MA, Rodriguez-Navarro A (2003) Sodium transport and HKT transporters: the rice model. Plant J 34:788–801
Hamamoto S, Horie T, Hauser F, Deinlein U, Schroeder JI, Uozumi N (2015) HKT transporters mediate salt stress resistance in plants: from structure and function to the field. Curr Opin Biotechnol 32:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.11.025
Han Y, Yin S, Huang L, Wu X, Zeng J, Liu X, Qiu L, Munns R, Chen Z, Zhang G (2018) A sodium transporter HvHKT1; 1 confers salt tolerance in barley via regulating tissue and cell ion homeostasis. Plant Cell Physiol 59(10):1976–1989
Hassani D, Khalid M, Huang D, Zhang Y-D (2019) Morphophysiological and molecular evidence supporting the augmentative role of in mitigation of salinity in Cucumis melo L. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica 51(3):301–312
Hauser F, Horie TA (2010) conserved primary salt tolerance mechanism mediated by HKT transporters: a mechanism for sodium exclusion and maintenance of high K+/Na+ ratio in leaves during salinity stress. Plant Cell Environ. 33(4):552–565. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02056.x
Horie T, Hauser F, Schroeder JI (2009) HKT transporter-mediated salinity resistance mechanisms in Arabidopsis and monocot crop plants. Trends Plant Sci 14:660–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.08.009
Huang LT, Zhao LN, Gao LW, Véry Anne-Aliénor, Sentenac Hervé, Zhang YD (2018) Constitutive expression of CmSKOR, an outward K+ channel gene from melon, in Arabidopsis thaliana involved in saline tolerance. Plant Sci 274:492–502
Huang S, Spielmeyer W, Lagudah ES, Munns R (2008) Comparative mapping of HKT genes in wheat, barley, and rice, key determinants of Na+ transport, and salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 59:927–937. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ern033
James RA, Davenport RJ, Munns R (2006) Physiological characterization of two genes for Na+ exclusion in durum wheat, Nax1 and Nax2. Plant Physiol 142:1537–1547. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.086538
Julkowska MM, Testerink C (2015) Tuning plant signaling and growth to survive salt. Trends Plant Sci 20:586–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2015.06.008
Kobayashi NI, Yamaji N, Yamamoto H, Okubo K, Ueno H, Costa A, Tanoi K, Matsumura H, Fujii-Kashino M, Horiuchi T, Nayef MA, Shabala S, An G, Ma JF, Horie T (2017) OsHKT1;5 mediates Na+ exclusion in the vasculature to protect leaf blades and reproductive tissues from salt toxicity in rice. Plant J 91:657–670. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13595
Kronzucker HJ, Britto DT (2011) Sodium transport in plants: a critical review. New Phytol 189:54–81
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Liu W, Fairbairn DJ, Schachtman RDP (2001) Characterization of two hkt1 homologues from eucalyptus camaldulensis that display intrinsic osmosensing capability. Plant Physiol 127(1):283–294
Mäser P, Eckelman B, Vaidyanathan R, Horie T, Fairbairn DJ, Kubo M, Yamagami M, Yamaguchi K, Nishimura M, Uozumi N (2002a) Altered shoot/root Na+ distribution and bifurcating salt sensitivity in Arabidopsis by genetic disruption of the Na+ transporter AtHKT1. FEBS Lett 531:157–161
Mäser P, Hosoo Y, Goshima S, Horie T, Eckelman B, Yamada K, Yoshida K, Bakker EP, Shinmyo A, Oiki S (2002b) Glycine residues in potassium channel-like selectivity filters determine potassium selectivity in four-loop-per-subunit HKT transporters from plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:6428–6433
Mendlinger S, Pasternak D (1992) Effect of time of salinization on flowering, yield and fruit quality factors in melon, Cucumis melo L. J Hortic Sci 67:529–534
Moller IS, Gilliham M, Jha D, Mayo GM, Roy SJ, Coates JC, Haseloff J, Tester M (2009) Shoot Na+ exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na+ transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 7:2163–2178
Munns R, James RA, Xu B, Athman A, Conn SJ, Jordans C, Byrt CS, Hare RA, Tyerman SD, Tester M, Plett D, Gilliham M (2012) Wheat grain yield on saline soils is improved by an ancestral Na+ transporter gene. Nat Biotechnol 30:360–364. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2120
Nishijima T, Furuhashi M, Sakaoka S, Morikami A, Tsukagoshi H (2017) Ectopic expression of Mesembryanthemum crystallinum sodium transporter McHKT2 provides salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 81:2139–2144
Platten JD, Cotsaftis O, Berthomieu P, Bohnert H, Davenport RJ, Fairbairn DJ, Horie T, Leigh RA, Lin HX, Luan S, Maser P, Pantoja O, Rodriguez-Navarro A, Schachtman DP, Schroeder JI, Sentenac H, Uozumi N, Very AA, Zhu JK, Dennis ES, Tester M (2006) Nomenclature for HKT transporters, key determinants of plant salinity tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 11:372–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2006.06.001
Ren ZH, Gao JP, Li LG, Cai XL, Huang W, Chao DY, Zhu MZ, Wang ZY, Luan S, Lin HX (2005) A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat Genet 37:1141–1146. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1643
Ren ZJ, Liu Y, Kang D, Fan KJ, Wang CY, Wang GY, Liu YJ (2015) Two alternative splicing variants of maize HKT1;1 confer salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 123:569–578
Ruan CJ, da Silva JAT, Mopper S, Pei Q, Lutts S (2010) Halophyte improvement for a salinized world. Crit Rev Plant Sci 29:329–359. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2010.524517
Rus A, Lee BH, Munoz-Mayor A, Sharkhuu A, Miura K, Zhu JK, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2004) AtHKT1 facilitates Na+ homeostasis and K+ nutrition in planta. Plant Physiol 136:2500–2511. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.042234
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sarabi B, Bolandnazar S, Ghaderi N, Ghashghaie J (2017) Genotypic differences in physiological and biochemical responses to salinity stress in melon (Cucumis melo. L) plants: prospects for selection of salt tolerant landraces. Plant Physiol Biochem 119:294–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.09.006
Schachtman DP, Schroeder JI (1994) Structure and transport mechanism of a high-affinity potassium uptake transporter from higher plants. Nature 370:655–658. https://doi.org/10.1038/370655a0
Shabala S (2013) Learning from halophytes: physiological basis and strategies to improve abiotic stress tolerance in crops. Ann Bot 112:1209–1221. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mct205
Su Y, Luo W, Lin W, Ma L, Kabir M (2015) Model of cation transportation mediated by high-affinity potassium transporters (hkts) in higher plants. Biological Procedures Online 17(1):1–13
Sun J, Cao H, Cheng J, He X, Sohail H, Niu M, Huang Y, Bie Z (2018) Pumpkin CmHKT1;1 controls shoot Na+ accumulation via limiting Na+ transport from rootstock to scion in grafted cucumber. Int J Mol Sci 19(9):2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092648
Sunarpi Horie T, Motoda J, Kubo M, Yang H, Yoda K, Horie R, Chan WY, Leung HY, Hattori K, Konomi M, Osumi M, Yamagami M, Schroeder JI, Uozumi N (2005) Enhanced salt tolerance mediated by AtHKT1 transporter-induced Na unloading from xylem vessels to xylem parenchyma cells. Plant J 44:928–938. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02595.x
Tedeschi A, Lavini A, Riccardi M, Pulvento C, d’Andria R (2011) Melon crops (Cucumis melo L., cv. Tendral) grown in a mediterranean environment under saline-sodic conditions: Part I. Yield and quality. Agric Water Manage 98(9):1329–1338
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Thomson MJ, de Ocampo M, Egdane J, Rahman MA, Sajise AG, Adorada DL, Tumimbang-Raiz E, Blumwald E, Seraj ZI, Singh RK, Gregorio GB, Ismail AM (2010) Characterizing the saltol quantitative trait locus for salinity tolerance in rice. Rice 3:148–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12284-010-9053-8
Tilman D, Balzer C, Hill J, Befort BL (2011) Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:20260–20264. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1116437108
Uozumi N, Kim EJ, Rubio F, Yamaguchi T, Muto S, Tsuboi A, Bakker EP, Nakamura T, Schroeder JI (2000) The Arabidopsis HKT1 gene homolog mediates inward Na+ currents in Xenopus laevis oocytes and Na+ uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plant Physiol 122(4):1249–1260
Véry AA, Gaymard F, Bosseux C, Sentenac H, Thibaud JB (1995) Expression of a cloned plant K+ channel in Xenopus oocytes: analysis of macroscopic currents. Plant J 7:321–332
Wang LM, Zhang LD, Chen JB, Huang DF, Zhang YD (2016) Physiological analysis and transcriptome comparison of two muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.) cultivars in response to salt stress. Genet Mol Res 15(3):1–18. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15038738
Wang L, Wei S, Chen J, Zhang Y, Huang D (2013) Regulation of the inward rectifying K+ channel MIRK and ion distribution in two melon cultivars (Cucumis melo L.) under NaCl salinity stress. Acta Physiol Plant 35:2789–2800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1311-0
Wang R, Jing W, Xiao L (2015) The rice high-affinity potassium transporter1;1 is involved in salt tolerance and regulated by an MYB-type transcription factor. Plant Physiol 168(3):1076–1090. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00298
Wang T, Gassmann W, Rubio F, Schroeder JI, Glass ADM (1998) Rapid up-regulation of HKT1, a high-affinity potassium transporter gene, in roots of barley and wheat following withdrawal of potassium. Plant Physiol 118:651–659
Wang TT, Ren ZJ, Liu ZQ, Feng X, Guo RQ, Li BG, Li LG, Jing HC (2014) SbHKT1;4, a member of the high-affinity potassium transporter gene family from Sorghum bicolor, functions to maintain optimal Na+ /K+ balance under Na+ stress. J Integr Plant Biol 56:315–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12144
Yasar F, Kusvuran S, Ellialtioglu S (2006) Determination of anti-oxidant activities in some melon (Cucumis melo L.) varieties and cultivars under salt stress. J Hortic Sci Biotech 81:627–630. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2006.11512115
Zhang YD, Very AA, Wang LM, Deng YW, Sentenac H, Huang DF (2011) A K+ channel from salt-tolerant melon inhibited by Na+. New Phytol 189:856–868. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03526.x
Zhao LN, Zhang FR, Liu B, Yang SL, Xiong X, Hassani D, Zhang YD (2019) CmRAV1 shows differential expression in two melon (Cucumis melo L.) cultivars and enhanced salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 51(11):1123–1133. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmz107
Zhu M, Shabala L, Cuin TA, Huang X, Zhou M, Munns R, Shabala S (2016) Nax loci affect SOS1-like Na+/H+ exchanger expression and activity in wheat. J Exp Bot 67:835–844. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv493
Acknowledgements
We thanked Dr. Limin Wang help doing the voltage-clamp experiments in B&PMP (Biochimie et Physiologie Moléculaires des Plantes) in France. This work was sponsored by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 31372079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L-W G conducted the experiments and wrote the draft manuscript. S-L Y participated in the experiment of subcellular localization and yeast test. S-W W participated in the preparation of the plant material and wrote the part of the discussion. Y-D Z designed the research plan together with D-F H, revised the paper, analyzed the electrophysiological experiments and part of the data. All of authors in this study read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
No competing interests declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11103_2020_1011_MOESM3_ESM.tif
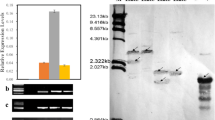
Independent candidates from the 35 overexpression lines were choosed for detection. OE1 and OE6 were selected for the following experiments. Supplementary material 3 (TIFF 134 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, LW., Yang, SL., Wei, SW. et al. Supportive role of the Na+ transporter CmHKT1;1 from Cucumis melo in transgenic Arabidopsis salt tolerance through improved K+/Na+ balance. Plant Mol Biol 103, 561–580 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-020-01011-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-020-01011-0