Abstract
Key message
Moderate overexpression of CYP734A4 improves grain number per main panicle and seed setting rate.
Abstract
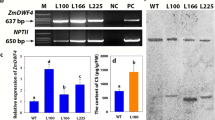
Brassinosteroid (BR) homeostasis and signaling are crucial for plant growth and development. CYP734A genes encode cytochrome P450 monooxygenases that control the level of bioactive BRs by degrading BRs. However, fertile plants overexpressing CYP734As have not been reported in rice. Here, we isolated a novel semi-dominant mutant brd3-D, in which T-DNA was inserted approximately 4 kb upstream of the CYP734A4 gene (GenBank Accession AB488667), causing its overexpression. The mutant is characterized by dwarfism, small grains, and erect leaves and is less sensitive to brassinolide-induced lamina joint inclination and primary root elongation. However, increased grain number per main panicle and improved seed setting rate were also found in heterozygous brd3-D. To our knowledge, these traits have not been reported in other BR deficient mutants. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis indicated that phenotypic severity of the brd3-D mutant is positively correlated with the CYP734A4 transcription level. In accordance with the increased expression of CYP734A4, a lower castasterone (a rice BR) content was detected in the brd3-D mutants. Knockout of brd3-D by using the CRISPR/Cas9 system rescued the mutation. In addition, transgenic plants overexpressing CYP734A4 with the 35S enhancer mimicked the brd3-D phenotypes, confirming that moderate overexpression of the CYP734A4 gene can improve grain number per main panicle and the seed setting rate in rice. Further studies showed that overexpression of CYP734A4 influences the expressions of multiple genes involved in the BR pathway, and the expression of CYP734A4 is induced by exogenous brassinolide, confirming the negative regulatory role of CYP734A4 in the BR pathway. CYP734A4 might provide a useful gene resource for developing new high-yielding rice varieties.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai MY, Zhang LY, Gampala SS, Zhu SW, Song WY, Chong K, Wang ZY (2007) Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13839–13844
Bajguz A (2011) Brassinosteroids-occurrence and chemical structures in plants. In: Brassinosteroids: a class of plant hormone, 1st edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–28
Duan K, Li L, Hu P, Xu SP, Xu ZH, Xue HW (2006) A brassinolide-suppressed rice MADS-box transcription factor, OsMDP1, has a negative regulatory role in BR signaling. Plant J 47:519–531
Gudesblat GE, Russinova E (2011) Plants grow on brassinosteroids. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14(5):530–537
Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Shimizu-Sato S, Inukai Y, Fujioka S, Shimada Y, Takatsuto S, Agetsuma M, Yoshida S, Watanabe Y, Uozu S, Kitano H, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M (2002) Loss-of-function of a rice brassinosteroid biosynthetic enzyme, C-6 oxidase, prevents the organized arrangement and polar elongation of cells in the leaves and stem. Plant J 32:495–508
Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Umemura K, Uozu S, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2003) A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450. Plant Cell 15:2900–2910
Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Hasegawa Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2005) The Rice brassinosteroid-deficient dwarf2 mutant, defective in the rice homolog of Arabidopsis DIMINUTO/DWARF1, is rescued by the endogenously accumulated alternative bioactive brassinosteroid, dolichosterone. Plant Cell 17:2243–2254
Hu X, Qian Q, Xu T, Zhang Y, Dong G, Gao T, Xie Q, Xue Y (2013) The U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase TUD1 functions with a heterotrimeric G alpha subunit to regulate Brassinosteroid-mediated growth in rice. PLoS Genet 9:e1003391
Husar S, Berthiller F, Fujioka S, Rozhon W, Khan M, Kalaivanan F, Elias L, Higgins GS, Li Y, Schuhmacher R et al (2011) Overexpression of the UGT73C6 alters brassinosteroid glucoside formation in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 11:51
Je BI, Piao HL, Park SJ, Park SH, Kim CM, Xuan YH, Huang J, Do Choi Y, An G, Wong HL, Fujioka S, Kim MC, Shimamoto K, Han CD (2010) RAV-Like1 maintains brassinosteroid homeostasis via the coordinated activation of BRI1 and biosynthetic genes in rice. Plant Cell 22:1777–1791
Koh S, Lee SC, Kim MK, Koh JH, Lee S, An G, Choe S, Kim SR (2007) T-DNA tagged knockout mutation of rice OsGSK1, an orthologue of Arabidopsis BIN2, with enhanced tolerance to various abiotic stresses. Plant mol Biol 65:453–466
Li D, Wang L, Wang M, Xu YY, Luo W, Liu YJ, Xu ZH, Li J, Chong K (2009) Engineering OsBAK1 gene as a molecular tool to improve rice architecture for high yield. Plant Biotechnol J 7:791–806
Liu YG, Mitsukawa N, Oosumi T, Whittier RF (1995) Efficient isolation and mapping of Arabidopsis thaliana T-DNA insert junctions by thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR. Plant J 8:457–463
Lu YJ, Zhen KL (1992) A simple method for DNA extraction of rice. Chin J Rice Sci 6:47–48 (in Chinese)
Mori M, Nomura T, Ooka H, Ishizaka M, Yokota T, Sugimoto K, Okabe K, Kajiwara H, Satoh K, Yamamoto K, Hirochika H, Kikuchi S (2002) Isolation and characterization of a rice dwarf mutant with a defect in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 130:1152–1161
Morinaka Y, Sakamoto T, Inukai Y, Agetsuma M, Kitano H, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M (2006) Morphological alteration caused by brassinosteroid insensitivity increases the biomass and grain production of rice. Plant Physiol 3:924–931
Nakamura M, Satoh T, Tanaka S, Mochizuki N, Yokota T, Nagatani A (2005) Activation of the cytochrome P450 gene, CYP72C1, reduces the levels of active brassinosteroids in vivo. J Exp Bot 56:833–840
Nakamura A, Fujioka S, Sunohara H, Kamiya N, Hong Z, Inukai Y, Miura K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Hasegawa Y, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2006) The role of OsBRI1 and its homologous genes, OsBRL1 and OsBRL3, in rice. Plant Physiol 140:580–590
Neff MM, Nguyen SM, Malancharuvil EJ, Fujioka S, Noguchi T, Seto H, Tsubuki M, Honda T, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Chory J (1999) BAS1: a gene regulating brassinosteroid levels and light responsiveness in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:15316–15323
Park W, Kim HB, Kim WT, Park PB, An G, Choe S (2006) Rice bending lamina 2 (bin2) mutants are defective in a Cytochrome P450 (CYP734A6) gene predicted to mediate brassinesteroid catabolism. J Plant Biol 49(6):469–476
Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ohnishi T, Sunohara H, Fujioka S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Mizutani M, Sakata K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Tanaka H, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2006) Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency increase biomass production and grain yield in rice. Nat Biotechnol 24:105–109
Sakamoto T, Kawabe A, Tokida-Segawa A, Shimizu B, Takatsuto S, Shimada Y, Fujioka S, Mizutani M (2011) Rice CYP734As function as multisubstrate and multifunctional enzymes in brassinosteroid catabolism. Plant J 67:1–12
Shimada A, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Sakamoto T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Sazuka T, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M (2006) The rice SPINDLY gene functions as a negative regulator of gibberellin signaling by controlling the suppressive function of the DELLA protein, SLR1, and modulating brassinosteroid synthesis. Plant J 48:390–402
Takahashi N, Nakazawa M, Shibata K, Yokota T, Ishikawa A, Suzuki K, Kawashima M, Ichikawa T, Shimada H, Matsui M (2005) shk1-D, a dwarf Arabidopsis mutant caused by activation of the CYP72C1 gene, has altered brassinosteroid levels. Plant J 42:13–22
Tanabe S, Ashikari M, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Kitano H, Matsuoka M, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Iwasaki Y (2005) A novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant, dwarf11, with reduced seed length. Plant Cell 17:776–790
Tanaka A, Nakagawa H, Tomita C, Shimatani Z, Ohtake M, Nomura T, Jiang CJ, Dubouzet JG, Kikuchi S, Sekimoto H, Yokota T, Asami T, Kamakura T, Mori M (2009) BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice. Plant Physiol 151:669–680
Thornton L, Peng H, Neff M (2011) Rice CYP734A cytochrome P450s inactivate brassinosteroids in Arabidopsis. Planta 234(6):1151–1162
Tong H, Jin Y, Liu W, Li F, Fang J, Yin Y, Qian Q, Zhu L, Chu C (2009) DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING, a new member of the GRAS family, plays positive roles in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Plant J 58:803–816
Tong H, Liu L, Jin Y, Du L, Yin Y, Qian Q, Zhu L, Chu C (2012) DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell 24:2562–2577
Turk EM, Fujioka S, Seto H, Shimada Y, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Wang H, Torres QI, Ward JM, Murthy G, Zhang J, Walker JC, Neff MM (2005) BAS1 and SOB7 act redundantly to modulate Arabidopsis photomorphogenesis via unique brassinosteroid inactivation mechanisms. Plant J 42(1):23–34
Vragović K, Sela A, Friedlander-Shani L, Fridman Y, Hacham Y, Holland N, Bartom E, Mockler TC, Savaldi-Goldstein S (2015) Translatome analyses capture of opposing tissue-specific brassinosteroid signals orchestrating root meristem differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(3):923–928
Wang MB, Waterhouse PM (1997) A rapid and simple method of assaying plants transformed with hygromycin or PPT resistance gene. Plant Mol Biol Rep 15:209–215
Wang L, Xu YY, Ma QB, Li D, Xu ZH, Chong K (2006) Heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunit is involved in rice brassinosteroid response. Cell Res 16:916–922
Wang L, Xu Y, Zhang C, Ma Q, Joo SH, Kim SK, Xu Z, Chong K (2008) OsLIC, a novel CCCH-type zinc finger protein with transcription activation, mediates rice architecture via brassinosteroids signaling. PLoS One 3:1–12
Wang L, Wang Z, Xu Y, Joo SH, Kim SK, Xue Z, Xu Z, Chong K (2009) OsGSR1 is involved in crosstalk between gibberellins and brassinosteroids in rice. Plant J 57:498–510
Wang C, Shen L, Fu YP, Yan CJ, Wang KJ (2015) A simple CRISPR/Cas9 system for multiplex genome editing in rice. J Genet Genomics 42(12):703–706
Wu CY, Trieu A, Radhakrishnan P, Kwok SF, Harris S, Zhang K, Wang J, Wan J, Zhai H, Takatsuto S, Matsumoto S, Fujioka S, Feldmann KA, Pennell RI (2008) Brassinosteroids regulate grain filling in rice. Plant Cell 20:2130–2145
Wu C, Fu YP, Hu GC, Si HM, Cheng SH, Liu WZ (2010) Isolation and characterization of a rice mutant with narrow and rolled leaves. Planta 232:313–324
Yamamuro C, Ihara Y, Wu X, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2000) Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell 12:1591–1606
Zhang LY, Bai MY, Wu J, Zhu JY, Wang H, Zhang Z, Wang W, Sun Y, Zhao J, Sun X, Yang H, Xu Y, Kim SH, Fujioka S, Lin WH, Chong K, Lu TG, Wang ZY (2009) Antagonistic HLH/bHLH transcription factors mediate brassinosteroid regulation of cell elongation and plant development in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:3767–3780
Zhang C, Xu Y, Guo S, Zhu J, Huan Q, Liu H, Wang L, Luo G, Wang X, Chong K (2012) Dynamics of brassinosteroid response modulated by negative regulator LIC in rice. PLoS Genet 8:e1002686
Zhang C, Bai MY, Chong K (2014) Brassinosteroid-mediated regulation of agronomic traits in rice. Plant cell rep 33:683–696
Zhu ZG, Xiao H, Fu YP, Hu GC, Yu YH, Si HM, Zhang JL, Sun ZX (2001) Construction of transgenic rice populations by inserting the maize transponson Ac/Ds and genetic analysis for several mutants. Chinese J Biotech 17:288–292 [In Chinese with English abstract]
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31271686), the Important National Science & Technology Specific Projects for Breeding New Transgenic Varieties in China (2014ZX08001-004 and 2014ZX08010-004) and the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (2012RG002-6).
Author contributions
WL and ZH conceived the project and designed the experiments. WQ, CW, GH, YF and WL performed experiments; WQ and WL analyzed data and wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Wenjing Qian and Chao Wu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, W., Wu, C., Fu, Y. et al. Novel rice mutants overexpressing the brassinosteroid catabolic gene CYP734A4 . Plant Mol Biol 93, 197–208 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-016-0558-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-016-0558-4