Abstract
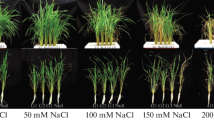
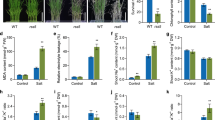
Glutathione reductase (GR) is one of important antioxidant enzymes in plants. This enzyme catalyzes the reduction of glutathione disulfide (GSSG) to reduced glutathione (GSH) with the accompanying oxidation of NADPH. Previously, we showed that salt-stress-responsive GR3 is a functional protein localized in chloroplasts and mitochondria in rice. To learn more about the role of GR3 in salt-stress tolerance, we investigated the response to 100 mM NaCl treatment in wild-type rice (WT); GR3 knockout mutant of rice (gr3); and the functional gr3-complementation line (C1). Rice GR3 was primarily expressed in roots at the seedling stage and ubiquitously expressed in all tissues except the sheath at heading stage. GR3 promoter-GUS was expressed in the vascular cylinder and cortex of root tissues in rice seedlings, vascular tissue of nodes, embryo and aleurone layer of seeds, and young flowers. Under both normal and salt-stress conditions, total GR activity was decreased by 20 % in gr3. Oxidative stress, indicated by malondialdehyde content, was greater in gr3 than the WT under salt stress. As compared with the WT, gr3 was sensitive to salt and methyl viologen; it showed inhibited growth, decreased maximal efficiency of photosystem II, decreased GSH and GSSG contents, and the ratio of GSH to GSSG. Conversely, the gr3-complementation line C1 rescued the tolerance to methyl viologen and salinity and recovered the growth and physiological damage caused by salinity. These results reveal that GR3 plays an important role in salt stress tolerance by regulating the GSH redox state in rice.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aono M, Saji H, Fujiyama K, Sugita M, Kondo N, Tanaka K (1995) Decrease in activity of glutathione reductase enhances paraquat sensitivity in transgenic Nicotina tabacum. Plant Physiol 107:645–648
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Asada K (1999) The water-water cycle in chloroplasts: scavenging of active oxygen and dissipation of excess photons. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:601–639
Beauchamp CO, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase. Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gel. Anal Biochem 44:276–287
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Broadbent P, Creissen GP, Kular B, Wellburn AR, Mullineaux PM (1995) Oxidative stress responses in transgenic tobacco containing altered levels of glutathione reductase activity. Plant J 8:247–255
Chen YP, Xing LP, Wu GJ, Wang HZ, Wang XE, Cao AZ, Chen PD (2007) Plastidial glutathione reductase from Haynaldia villosa is an enhancer of powdery mildew resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Plant Cell Physiol 48:1702–1712
Christensen AH, Quail PH (1996) Ubiquitin promoter-based vectors for high-level expression of selectable and/or screenable marker genes in monocotyledonous plants. Transgenic Res 5:213–218
Diaz-Vivancos P, Faize M, Barba-Espin G, Faize L, Petri C, Hernández JA, Burgos L (2013) Ectopic expression of cytosolic superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase leads to salt stress tolerance in transgenic plums. Plant Biotechnol J 11:976–985
Ding MQ, Hou PC, Shen X, Wang M, Deng S, Sun J, Xiao F, Wang R, Ding S, Lu Q, Zhang Y, Yang Z, Wen X, Zhang L, Lu C (2009) Enhanced sensitivity to oxidative stress in transgenic tobacco plants with decreased glutathione reductase activity leads to a decrease in ascorbate pool and ascorbate redox state. Plant Mol Biol 69:577–592
Ding S, Lei M, Lu Q, Zhang A, Yin Y, Wen X, Zhang L, Lu C (2012) Enhanced sensitivity and characterization of photosystem II in transgenic tobacco plants with decreased chloroplast glutathione reductase under chilling stress. Biochim Biophys Acta 1817:1979–1991
Edwards EA, Rawsthorne S, Mullineaux PM (1990) Subcellular distribution of multiple forms of glutathione reductase in leaves of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Planta 180:278–284
Foster JG, Hess JL (1980) Superoxide dismutase and glutathione reductase activities in cotton leaf tissue exposed to an atmosphere enriched in oxygen. Plant Physiol 66:482–487
Foyer CH, Souriau N, Perret S, Lelandais M, Kunert KJ, Pruvost C, Jouanin L (1995) Overexpression of glutathione reductase but not glutathione synthetase leads to increases in antioxidant capacity and resistance to photoinhibition in poplar trees. Plant Physiol 109:1047–1057
Foyer CH, Theodoulou FL, Delrot S (2001) The functions of intercellular and intracellular glutathione transport systems in plants. Trends Plant Sci 6:486–492
Grattan SR, Grieve CM (1999) Mineral nutrient acquisition and response by plants grown in saline environment. In: Pessarakli M (ed) Handbook of plant and crop stress. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 203–229
Griffiths OW (1980) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem 106:207–212
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hong CY, Cheng KJ, Tseng TH, Wang CS, Liu LF, Yu SM (2004) Production of two highly active bacterial phytases with broad pH optima in germinated transgenic rice seeds. Transgenic Res 13:29–33
Hong CY, Chao YY, Yang MY, Cheng SY, Cho SC, Kao CH (2009a) NaCl-induced expression of glutathione reductase in roots of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings is mediated through hydrogen peroxide but not abscisic acid. Plant Soil 320:103–115
Hong CY, Chao YY, Yang MY, Cho SC, Kao CH (2009b) Na+ but not Cl− or osmotic stress is involved in NaCl-induced expression of glutathione reductase in roots of rice seedlings. J Plant Physiol 166:1598–1606
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Kato M, Shimizu S (1987) Chlorophyll metabolism in higher plant. VII. Chlorophyll degradation in senescing tobacco leaves; phenolic-dependent peroxidative degradation. Can J Bot 65:729–735
Law MY, Charles SA, Halliwell B (1983) Glutathione and ascorbic acid in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) chloroplasts. The effect of hydrogen peroxide and paraquat. Biochem J 210:899–903
Le Martret B, Poage M, Shiel K, Nugent GD, Dixm PJ (2011) Tobacco chloroplast transformants expressing genes encoding dehydroascorbate reductase, glutathione reductase, and glutathione-S-transferase, exhibit altered anti-oxidant metabolism and improved abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Biotechnol J 9:661–673
Maughan SC, Pasternak M, Cairns N, Kiddle G, Brach T, Jarvis R, Haas F, Nieuwland J, Lim B, Müller C, Salcedo-Sora E, Kruse C, Orsel M, Hell R, Miller AJ, Bray P, Foyer CH, Murray JA, Meyer AJ, Cobbett CS (2010) Plant homologs of the Plasmodium falciparum chloroquinone-resistance transporter, PfCRT, are required for glutathione homeostasis and stress responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:2331–2336
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Munns R (1993) Physiological processes limiting plant growth in saline soil: some dogmas and hypotheses. Plant Cell Environ 16:15–24
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:239–250
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Ann Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Noctor G, Foyer CH (1998) Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:249–279
Noctor G, Arisi A, Jouanin L, Kunert K, Rennenberg H, Foyer C (1998) Glutathione: biosynthesis, metabolism and relationship to stress tolerance explored in transformed plants. J Exp Bot 49:623–647
Noctor G, Gomez L, Vanacker H, Foyer CH (2002) Interactions between biosynthesis, compartmentation, and transport in the control of glutathione homeostasis and signalling. J Exp Bot 53:1280–1304
Noctor G, Mhamdi A, Chaouch S, Han Y, Neukermans J, Marquez-Garcia B, Queval G, Foyer CH (2012) Glutathione in plants: an integrated overview. Plant Cell Environ 35:454–484
Plett D, Berger B, Tester M (2010) Genetic determinants of salinity tolerance in crop plants. In: Jenks MA, Wood AJ (eds) Genes for plant abiotic stress. Blackwell Publishing, Iowa, pp 83–111
Rengasamy P (2006) World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J Exp Bot 57:1017–1023
Roxas VP, Smith RK, Allen ER, Allen RD (1997) Overexpression of glutathione S-transferase/glutathione peroxidase enhances the growth of transgenic tobacco during stress. Nat Biotechnol 15:988–991
Scandalios JG (2002) The rise of ROS. Trends Biochem Sci 27:483–486
Shavrukov Y (2013) Salt stress or salt shock: which genes are we studying? J Exp Bot 64:119–127
Sheu JJ, Yu TS, Tong WF, Yu SM (1996) Carbohydrate starvation stimulates differential expression of rice alpha-amylase genes that is modulated through complicated transcriptional and posttranscriptional processes. J Biol Chem 271:26998–27004
Shu DF, Wang LY, Duan M, Deng YS, Meng QW (2011) Antisense-mediated depletion of tomato chloroplast glutathione reductase enhances susceptibility to chilling stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:1228–1237
Tzafrir I, Pena-Muralla R, Dickerman A, Berg M, Rogers R, Hutchens S, Sweeney TC, McElver J, Aux G, Patton D, Meinke D (2004) Identification of genes required for embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 135:1206–1220
Van Kooten O, Snel JFH (1990) The use of chlorophyll fluorescence nomenclature in plant stress physiology. Photosynth Res 25:147–150
Wu TM, Lin WR, Kao YT, Hsu YT, Yeh CH, Hong CY, Kao CH (2013) Identification and characterization of a novel chloroplast/mitochondria co-localized glutathione reductase 3 involved in salt stress response in rice. Plant Mol Biol 8:379–390
Yamane K, Taniguchi M, Miyake H (2012) Salinity-induced subcellular accumulation of H2O2 in leaves of rice. Protoplasma 249:301–308
Acknowledgments
We thank Laura Smales for English editing. This work was supported by research grants NSC 101-2313-B-002-008-MY3 and NSC 101-2324-B-002-020 from the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of the Republic of China to C.-Y. Hong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, TM., Lin, WR., Kao, C.H. et al. Gene knockout of glutathione reductase 3 results in increased sensitivity to salt stress in rice. Plant Mol Biol 87, 555–564 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0290-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0290-5