Abstract
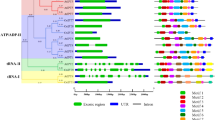
Gulf annual ryegrass has been identified as potential Pi hyperaccumulator, however the molecular mechanism remains largely unknown. A suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) analysis was used to evaluate the phosphate (Pi) responsive genome expression pattern changes in Gulf annual ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum L.). Differential screening identified 384 putative Pi-starvation induced cDNAs. Bioinformatic analysis revealed that 116 cDNAs are nonredundant unigenes of which 108 exhibited high similarities with Genbank entries. The differential expression patterns of 13 cDNAs, representing diverse functional categories, were confirmed by RNA gel blot analysis. Further, detailed molecular analysis of three genes (LmPAP1, LmIPS1 and LmIDS1) was carried out by cloning and characterization of full-length cDNAs. LmPAP1 is 1,414 bp in length with an open reading frame (ORF) of 1,188 bp capable of encoding an N-terminal signal peptide of 26 amino acids. LmIPS1 gene is a member of TPSI1/Mt4 family that contains 3 short ORFs. The cDNA of LmIDS1 is 346 bp in size including a single ORF of 222 nucleotides that encodes 74 amino acid proteins, exhibiting homology with IDS1 with similarity to type 2 metallothionein like protein. In our preliminary screening of different genotypes of annual ryegrass for hyperaccumulation of Pi in their shoots, Gulf and Urugrary showed significant differences with values of 1.0% and 0.7%, respectively. Since it is logical to assume a plausible correlation that may exist between Pi-accumulation in the shoots and the expression of Pi-responsive genes, the expression of LmPAP1, LmIPS1 and LmIDS1 was evaluated in these two genotypes grown under different Pi regimes. Although there was a significant induction of these genes in both the genotypes grown under Pi-deprived condition, the abundance of LmPAP1 transcripts was relatively higher in the Gulf genotype as compared to that in the Urugrary genotype. A similar trend was observed in qRT-PCR data of other tested genotypes of annual ryegrasses. This suggests the potential role of LmPAP1 in accumulation of Pi in Gulf grass. In addition, Gulf grass genotype revealed higher levels of total P, 33Pi uptake, and APase activity as compared to Urugrary. Together, these results suggest that the Gulf ryegrass has evolved mechanisms to acquire and hyperaccumulate more Pi under different Pi regimes by activating multiple Pi acquisition and mobilization mechanisms.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LmPAP1:
-
Lolium multiflorum purple acid phosphatase 1
- LmIPS1:
-
Loliummultiflorum induced by phosphate starvation 1
- LmIDS1:
-
Lolium multiflorum iron deficiency specific 1
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tags
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- UBCE2:
-
Ubiquitin conjugating enzyme
References
Aarts JMMJG, Hontelez JGJ, Fischer P, Verkerk R, Kammen AV, Zabel P (1991) Acid phosphatase-1, a tightly linked marker for root-knot nematode resistance in tomato: from protein to gene, using PCR and degenerate primers containing deoxyinosine. Plant Mol Biol 16:647–661. doi:10.1007/BF00023429
Abe K, Ozaki Y (1998) Comparison of useful terrestrial and aquatic plant species for removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from domestic wastewater. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 44:599–607
Abe K, Ozaki Y, Mizuta K (1999) Evaluation of useful plants for the treatment of polluted pond water and low N and P concentrations. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 45:409–417
Bozzo GG, Dunn EL, Plaxton WC (2006) Differential synthesis of phosphate-starvation inducible purple acid phosphatase isozymes in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) suspension cells and seedlings. Plant Cell Environ 29:303–313. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01422.x
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Burkholder JM, Mallin MA, Glasgow HB, Larsen LM, McIver MR, Shank GC et al (1997) Impacts to a coastal river and estuary from rupture of a large swine waste holding lagoon. J Environ Qual 26:1451–1466
Delorme TA, Angle JS, Coale FJ, Chaney RL (2000) Phytoremediation of phosphorus-enriched soils. Int J Phytoremed 2:173–181. doi:10.1080/15226510008500038
Diatchenko L, Lukyanov S, Lau YF, Siebert PD (1999) Suppression subtractive hybridization: a versatile method for identifying differentially expressed genes. Methods Enzymol 303:349–380. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(99)03022-0
Duff SMG, Moorhead GBG, Lefebvre DD, Plaxton WC (1989) Phosphate starvation inducible: bypasses of adenylate and phosphate dependent glycolytic enzymes in Brassica nigra suspension cells. Plant Physiol 90:1275–1278
Franco-Zorrilla JM, Valli A, Todesco M, Mateos I, Puga MI, Rubio-Somoza I et al (2007) Target mimicry provides a new mechanism for regulation of microRNA activity. Nat Genet 39:1033–1037. doi:10.1038/ng2079
Frossard E, Condron LM, Oberson A, Sinaj S, Fardeau JC (2000) Processes governing phosphorus availability in temperate soils. J Environ Qual 29:15–23
Graciet E, Lebreton S, Gontero B (2004) Emergence of new regulatory mechanisms in the Benson-Calvin pathway via protein-protein interactions: a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase/CP12/phosphoribulokinase complex. J Exp Bot 55:1245–1254. doi:10.1093/jxb/erh107
Hayes JE, Richardson AE, Simpson RJ (1999) Phytase and acid phosphatase activities in extracts from roots of temperate pasture grass and legume seedlings. Aust J Plant Physiol 26:801–809
Hou XL, Wu P, Jiao FC, Jia QJ, Chen HM, Yu J et al (2005) Regulation of the expression of OsIPS1 and OsIPS2 in rice via systemic and local Pi signaling and hormones. Plant Cell Environ 28:353–364. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01272.x
Jain A, Vasconcelos MJ, Sahi SV, Raghothama KG (2007a) Molecular mechanisms of plant adaptation to phosphate deficiency. Plant Breed Rev 29:359–419. doi:10.1002/9780470168035.ch7
Jain A, Poling MD, Karthikeyan AS, Blakeslee JJ, Peer WA, Titapiwatanakun MurphyAS, Raghothama KG (2007b) Differential effects of sucrose and auxin on localized phosphate deficiency-induced modulation of different traits of root system architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 144:232–247. doi:10.1104/pp.106.092130
Kavanova M, Lattanzi FA, Grimoldi AA, Schnyder H (2006) Phosphorus deficiency decreases cell division and elongation in grass leaves. Plant Physiol 141:766–775. doi:10.1104/pp.106.079699
Kolari KK, Sarjala T (1995) Acid phosphatase activity and phosphorus nutrition in scots pine needles. Tree Physiol 15:747–752
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685. doi:10.1038/227680a0
Lee TM, Tsai PF, Shyu YT, Sheu F (2005) The effects of phosphite on phosphate starvation responses of Ulva lactuca (Ulvales, Chlorophyta). J Phycol 41:975–982. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2005.00119.x
Li M, Osaki M, Rao LM, Tadano T (1997) Secretion of phytase from the roots of several plant species under phosphorus deficient conditions. Plant Soil 195:161–169. doi:10.1023/A:1004264002524
Li D, Zhu H, Liu K, Liu X, Leggewie G, Udvardi M et al (2002) Purple acid phosphatases of Arabidopsis thaliana. Comparative analysis and differential regulation by phosphate deprivation. J Biol Chem 277:27772–27781. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204183200
Lin SI, Chiang SF, Lin WY, Chen JW, Tseng CY, Wu PC et al (2008) Regulatory network of microRNA A399 and PHO2 by systemic signaling. Plant Physiol 147:732–746. doi:10.1104/pp.108.116269
Liu C, Muchhal US, Raghothama KG (1997) Differential expression of TPS11, a phosphate starvation-induced gene in tomato. Plant Mol Biol 33:867–874. doi:10.1023/A:1005729309569
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Misson J, Raghothama KG, Jain A, Jouhet J, Block MA, Bligny R et al (2005) A genome-wide transcriptional analysis using Arabidopsis thaliana Affymetrix gene chips determined plant responses to phosphate deprivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11934–11939. doi:10.1073/pnas.0505266102
Morcuende R, Bari R, Gibon Y, Zheng W, Pant BD, Blasing O et al (2007) Genome-wide reprogramming of metabolism and regulatory networks of Arabidopsis in response to phosphorus. Plant Cell Environ 30:85–112. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.01608.x
Muchhal US, Pardo JM, Raghothama KG (1996) Phosphate transporters from the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10519–10523. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.19.10519
Müller R, Morant M, Jarmer H, Nilsson L, Nielsen TH (2007) Genome-wide analysis of the Arabidopsis leaf transcriptome reveals interaction of phosphate and sugar metabolism. Plant Physiol 143:156–171. doi:10.1104/pp.106.090167
Novak JM, Chan ASK (2002) Development of P hyperaccumulator plant strategies to remediate soils with excess P concentrations. Crit Rev Plant Sci 21:493–509. doi:10.1080/0735-260291044331
Peterson AE, Speth PE, Corey RB, Wright TW, Schlecht PL (1994) Effects of twelve years of liquid sludge application on soil phosphorus levels. In: Clapp CE (ed) Sewage sludge: land utilization, the environment. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 1–20
Pfannschmidt T (2003) Chloroplast redox signals: how photosynthesis controls its own genes. Trends Plant Sci 8:33–41. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(02)00005-5
Pilon-Smits E, Pilon M (2002) Phytoremediation of metals using transgenic plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 21:439–459. doi:10.1080/0735-260291044313
Raghothama KG, Karthikeyan AS (2005) Phosphate acquisition. Plant Soil 274:37–49. doi:10.1007/s11104-004-2005-6
Rao IM, Borrero V, Ricaurte J, Garcia R (1999) Adaptive attributes of tropical forage species to acid soils. V. Differences in phosphorus acquisition form less available inorganic and organic sources of phosphate. J Plant Nutr 22:1175–1196
Richardson AE, Hadobas PA, Hayes JE (2001) Extracellular secretion of Aspergillus phytase from Arabidopsis roots enables plants to obtain phosphorus from phytate. Plant J 25:641–649. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00998.x
Rubio V, Linhares F, Solano R, Mart’ın AC, Iglesias J, Leyva A et al (2001) A conserved MYB transcription factor involved in phosphate starvation signaling both in vascular plants and in unicellular algae. Genes Dev 15:2122–2133. doi:10.1101/gad.204401
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Schachtman DP, Shin R (2007) Nutrient sensing and signaling: NPKS. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:47–69. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103750
Schenk G, Guddat LW, Ge Y, Carrington LE, Hume DA, Hamilton S et al (2000) Identification of mammalian-like purple acid phosphatases in a wide range of plants. Gene 250:117–125. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00186-4
Sharma NC, Sahi SV (2005) Characterization of phosphate accumulation in Lolium multiflorum for remediation of phosphorus-enriched soils. Environ Sci Technol 39:5475–5440. doi:10.1021/es050198t
Sharma NC, Sahi SV, Jain JC, Raghothama KG (2004) Enhanced accumulation of phosphate by Lolium multiflorum cultivars grown in phosphate-enriched medium. Environ Sci Technol 38:2443–2448. doi:10.1021/es030466s
Sharma NC, Starnes DL, Sahi SV (2007) Phytoextraction of excess soil phosphorus. Environ Pollut 146:120–127. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.06.006
Sharpley AN, Foy RH, Withers PJA (2000) Practical and innovative measures for the control of agricultural phosphorus losses to water: an overview. J Environ Qual 29:1–9
Shin H, Shin HS, Chen RJ, Harrison MJ (2006) Loss of At4 function impacts phosphate distribution between the roots and the shoots during phosphate starvation. Plant J 45:712–726. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02629.x
Sims JT, Edwards AC, Schoumans OF, Simard RR (2000) Integrating soil phosphorus testing into environmentally based agricultural management practice. J Environ Qual 29:60–71
Sistani KR, Pederson GA, Brink GE, Rowe DE (2003) Nutrient uptake by ryegrass cultivars and crabgrass from a highly phosphorus-enriched soil. J Plant Nutr 26:2521–2535. doi:10.1081/PLN-120025476
Tian J, Venkatachalam P, Liao H, Yan X, Raghothama K (2007) Molecular cloning and characterization of phosphorus starvation responsive genes in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Planta 227:151. doi:10.1007/s00425-007-0603-2
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allen DL (2003) P acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157:423–447. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00695.x
Venkatachalam P, Thulaseedharan A, Raghothama KG (2007) Identification of expression profiles of tapping panel dryness (TPD) associated genes from the latex of rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.). Planta 226:499–515. doi:10.1007/s00425-007-0500-8
Wang Y-H, Garvin DF, Kochian LV (2002) Rapid induction of regulatory and transporter genes in response to phosphorus, potassium, and iron deficiencies in tomato. Evidence for cross talk and root/rhizosphere mediated signals. Plant Physiol 130:1361–1370. doi:10.1104/pp.008854
Wang Y, Ribot C, Rezzonico E, Poirier Y (2004) Structure and expression profile of the Arabidopsis PHO1 gene family indicates a broad role in inorganic phosphate homeostasis. Plant Physiol 135:200–411
Ward JT, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Salt DE, Raghothama KG (2008) The role of iron on the primary root elongation of Arabidopsis during phosphate deficiency. Plant Physiol 147:1181–1191. doi:10.1104/pp.108.118562
Wasaki J, Yonetani R, Kuroda S, Shinano T, Yazaki J, Fujii F et al (2003) Transcriptomic analysis of metabolic changes by phosphorus stress in rice plant roots. Plant Cell Environ 26:1515–1523. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3040.2003.01074.x
Wasaki J, Shinano T, Onishi K, Yonetani R, Yazaki J, Fujii F et al (2006) Transcriptomic analysis indicates putative metabolic changes caused by manipulation of phosphorus availability in rice leaves. J Exp Bot 57:2049–2059. doi:10.1093/jxb/erj158
Wawrzynska A, Lewandowska M, Hawkesford MJ, Sirko A (2005) Using a suppression subtractive library-based approach to identify genes regulated in response to short-term sulphur deficit. J Exp Bot 56:1575–1590. doi:10.1093/jxb/eri152
Withers PJA, Edwards AC, Foy RH (2001) Phosphorus cycling in UK agriculture and implications for phosphorus loss from soil. Soil Use Manage 17:139–149. doi:10.1079/SUM200181
Wu P, Ma LG, Hou XL, Wang MY, Wu YR, Liu FY et al (2003) Phosphate starvation triggers distinct alterations of genome expression in Arabidopsis roots and leaves. Plant Physiol 132:1260–1271. doi:10.1104/pp.103.021022
Xiao K, Harrison M, Wang ZY (2006) Cloning and characterization of a novel purple acid phosphatase gene (MtPAP1) from Medicago truncatula Barrel Medic. J Integr Plant Biol 48:204–211. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7909.2006.00204.x
Yang T, Poovaiah BW (2002) Hydrogen peroxide homeostasis: activation of plant catalase by calcium/calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4097–4102. doi:10.1073/pnas.052564899
Zhang Y, Mian MAR, Chekhovskiy K, So S, Kupfer D, Lai HS et al (2005) Differential gene expression in Festuca under heat stress conditions. J Exp Bot 56:897–907. doi:10.1093/jxb/eri082
Acknowledgments
This research was carried out with the support from the US Department of Agriculture (Grant 58-6406-1-017) awarded to S. Sahi. Authors duly acknowledge the support and encouragement from the Applied Research and Technology Program, Western Kentucky University, in carrying out this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venkatachalam, P., Jain, A., Sahi, S. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of phosphate (Pi) responsive genes in Gulf ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum L.): a Pi hyperaccumulator. Plant Mol Biol 69, 1–21 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9401-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9401-x