Abstract
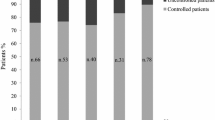
Combination with cabergoline may offer additional benefits to acromegalic patients on pegvisomant monotherapy. We evaluated the safety and efficacy profile of this combination and investigated the determinants of response. An observational, retrospective, cross-sectional study. Fourteen acromegalic patients (9 females), who were partially resistant to somatostatin analogs and on pegvisomant monotherapy. Cabergoline was added because of the presence of persistent mildly increased IGF-I. The mean follow-up time was 18.3 ± 10.4 months. The efficacy and safety profile was assessed. The influence of clinical and biochemical characteristics on treatment efficacy was studied. IGF-I levels returned to normal in 4 patients (28%) at the end of the study. In addition, some decline in IGF-I levels was observed in a further 5 patients. The % IGF-I decreased from 158 ± 64% to 124 ± 44% (p = 0.001). The average change in IGF-I was −18 ± 27% (range −67 to +24%). Lower baseline IGF-I (p = 0.007), female gender (p = 0.013), lower body weight (p = 0.031), and higher prolactin (PRL) levels (p = 0.007) were associated with a better response to combination therapy. There were no significant severe adverse events. Significant tumour shrinkage was observed in 1 patient. Combination therapy with pegvisomant and cabergoline could provide better control of IGF-I in some patients with acromegaly. Baseline IGF-I levels, female gender, body weight, and PRL levels affect the response to this combination therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chanson P, Salenave S, Kamenicky P, Cazabat L, Young J (2009) Pituitary tumours: acromegaly. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 23(5):555–574
Murray RD, Melmed S (2008) A critical analysis of clinically available somatostatin analog formulations for therapy of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(8):2957–2968
Trainer PJ (2009) ACROSTUDY: the first 5 years. Eur J Endocrinol 161(1):S19–S24
Marazuela M, Lucas T, Alvarez-Escola C, Puig-Domingo M, de la Torre NG, de Miguel-Novoa P, Duran-Hervada A, Manzanares R, Luque-Ramirez M, Halperin I, Casanueva FF, Bernabeu I (2009) Long-term treatment of acromegalic patients resistant to somatostatin analogues with the GH receptor antagonist pegvisomant: its efficacy in relation to gender and previous radiotherapy. Eur J Endocrinol 160(4):535–542
Kopchick JJ, Parkinson C, Stevens EC, Trainer PJ (2002) Growth hormone receptor antagonists: discovery, development, and use in patients with acromegaly. Endocr Rev 23(5):623–646
Marazuela M, Paniagua AE, Gahete MD, Lucas T, Alvarez-Escola C, Manzanares R, Cameselle-Teijeiro J, Luque-Ramirez M, Luque RM, Fernandez-Rodriguez E, Castano JP, Bernabeu I (2011) Somatotroph tumor progression during pegvisomant therapy: a clinical and molecular study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(2):E251–E259
Jimenez C, Burman P, Abs R, Clemmons DR, Drake WM, Hutson KR, Messig M, Thorner MO, Trainer PJ, Gagel RF (2008) Follow-up of pituitary tumor volume in patients with acromegaly treated with pegvisomant in clinical trials. Eur J Endocrinol 159(5):517–523
Buchfelder M, Weigel D, Droste M, Mann K, Saller B, Brubach K, Stalla GK, Bidlingmaier M, Strasburger CJ (2009) Pituitary tumor size in acromegaly during pegvisomant treatment: experience from MR re-evaluations of the German Pegvisomant Observational Study. Eur J Endocrinol 161(1):27–35
Hodish I, Barkan A (2008) Long-term effects of pegvisomant in patients with acromegaly. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 4(6):324–332
Moore DJ, Adi Y, Connock MJ, Bayliss S (2009) Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pegvisomant for the treatment of acromegaly: a systematic review and economic evaluation. BMC Endocr Disord 9:20
Neggers SJ, van Aken MO, Janssen JA, Feelders RA, de Herder WW, van der Lely AJ (2007) Long-term efficacy and safety of combined treatment of somatostatin analogs and pegvisomant in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(12):4598–4601
Neggers SJ, de Herder WW, Janssen JA, Feelders RA, van der Lely AJ (2009) Combined treatment for acromegaly with long-acting somatostatin analogs and pegvisomant: long-term safety for up to 4.5 years (median 2.2 years) of follow-up in 86 patients. Eur J Endocrinol 160(4):529–533
Feenstra J, de Herder WW, ten Have SM, van den Beld AW, Feelders RA, Janssen JA, van der Lely AJ (2005) Combined therapy with somatostatin analogues and weekly pegvisomant in active acromegaly. Lancet 365(9471):1644–1646
Trainer PJ, Ezzat S, D’Souza GA, Layton G, Strasburger CJ (2009) A randomized, controlled, multicentre trial comparing pegvisomant alone with combination therapy of pegvisomant and long-acting octreotide in patients with acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 71(4):549–557
Neggers SJ, van Aken MO, de Herder WW, Feelders RA, Janssen JA, Badia X, Webb SM, van der Lely AJ (2008) Quality of life in acromegalic patients during long-term somatostatin analog treatment with and without pegvisomant. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(10):3853–3859
Liuzzi A, Chiodini PG, Botalla L, Cremascoli G, Muller EE, Silvestrini F (1974) Decreased plasma growth hormone (GH) levels in acromegalics following CB 154(2-Br-alpha ergocryptine) administration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 38(5):910–912
An JJ, Cho SR, Jeong DW, Park KW, Ahn YS, Baik JH (2003) Anti-proliferative effects and cell death mediated by two isoforms of dopamine D2 receptors in pituitary tumor cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 206(1–2):49–62
Webster J, Piscitelli G, Polli A, Ferrari CI, Ismail I, Scanlon MF (1994) A comparison of cabergoline and bromocriptine in the treatment of hyperprolactinemic amenorrhea. Cabergoline Comparative Study Group. N Engl J Med 331(14):904–909
Abs R, Verhelst J, Maiter D, Van Acker K, Nobels F, Coolens JL, Mahler C, Beckers A (1998) Cabergoline in the treatment of acromegaly: a study in 64 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83(2):374–378
Sandret L, Maison P, Chanson P (2011) Place of cabergoline in acromegaly: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(5):1327–1335
Roemmler J, Steffin B, Gutt B, Schneider HJ, Sievers C, Bidlingmaier M, Schopohl J (2010) The acute effect of a single application of cabergoline on endogenous GH levels in patients with acromegaly on pegvisomant treatment. Growth Horm IGF Res 20(5):338–344
Colao A, Auriemma RS, Lombardi G, Pivonello R (2011) Resistance to somatostatin analogs in acromegaly. Endocr Rev 32(2):247–271
Castinetti F, Morange I, Dufour H, Regis J, Brue T (2009) Radiotherapy and radiosurgery in acromegaly. Pituitary 12(1):3–10
Freda PU, Reyes CM, Nuruzzaman AT, Sundeen RE, Khandji AG, Post KD (2004) Cabergoline therapy of growth hormone & growth hormone/prolactin secreting pituitary tumors. Pituitary 7(1):21–30
Moyes VJ, Metcalfe KA, Drake WM (2008) Clinical use of cabergoline as primary and adjunctive treatment for acromegaly. Eur J Endocrinol 159(5):541–545
Verhelst JA, Abrams PJ, Abs R (2008) Remission of acromegaly following long-term therapy with cabergoline: report of two cases. Pituitary 11(1):103–107
Higham CE, Atkinson AB, Alywin S, Martin NM, Moyes VJ, Newell-Price J, Trainer PJ (2009) A prospective clinical trial of combined cabergoline and pegvisomant treatment in patients with active acromegaly (Abstract). 91st annual meeting of the endocrine society, 10–13 June 2009, Washington
Cozzi R, Attanasio R, Lodrini S, Lasio G (2004) Cabergoline addition to depot somatostatin analogues in resistant acromegalic patients: efficacy and lack of predictive value of prolactin status. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 61(2):209–215
Cozzi R, Attanasio R, Barausse M, Dallabonzana D, Orlandi P, Da Re N, Branca V, Oppizzi G, Gelli D (1998) Cabergoline in acromegaly: a renewed role for dopamine agonist treatment? Eur J Endocrinol 139(5):516–521
Goldenberg N, Barkan A (2007) Factors regulating growth hormone secretion in humans. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 36(1):37–55
Parkinson C, Burman P, Messig M, Trainer PJ (2007) Gender, body weight, disease activity, and previous radiotherapy influence the response to pegvisomant. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(1):190–195
Lamberts SW, Klijn JG, van Vroonhoven CC, Stefanko SZ, Liuzzi A (1983) The role of prolactin in the inhibitory action of bromocriptine on growth hormone secretion in acromegaly. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 103(4):446–450
Lamberts SW, Liuzzi A, Chiodini PG, Verde S, Klijn JG, Birkenhager JC (1982) The value of plasma prolactin levels in the prediction of the responsiveness of growth hormone secretion to bromocriptine and TRH in acromegaly. Eur J Clin Invest 12(2):151–155
Sherlock M, Fernandez-Rodriguez E, Alonso AA, Reulen RC, Ayuk J, Clayton RN, Holder G, Sheppard MC, Bates A, Stewart PM (2009) Medical therapy in patients with acromegaly: predictors of response and comparison of efficacy of dopamine agonists and somatostatin analogues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(4):1255–1263
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Angel Salgado Barreira, biomedical research technician, for his invaluable assistance with the statistical analysis. This work was supported by Grants FISS 07/1119 (to M.M.) and 11/00161 (to IB).
Conflict of interest
I.B., T.L. and M.M. hold research grants from Pfizer and have received lecture fees from Novartis, Ipsen, and Pfizer. F.F.C. holds research grants from Pfizer and Novartis has and received lecture fees from Pfizer and Novartis. The remaining authors do not have any conflicts of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernabeu, I., Alvarez-Escolá, C., Paniagua, A.E. et al. Pegvisomant and cabergoline combination therapy in acromegaly. Pituitary 16, 101–108 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-012-0382-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-012-0382-z