Abstract
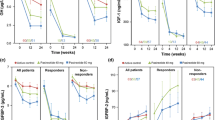
To describe glucose status changes in patients with acromegaly receiving somatostatin analog lanreotide as primary treatment. This retrospective, single-center study conducted during 1996–2008, included acromegalic patients receiving primary lanreotide treatment. Baseline and last follow-up visit assessments included glucose status (according to American Diabetes Association criteria), growth hormone (GH), and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) levels. Glucose control was considered improved when fasting plasma glucose or antidiabetic treatments were reduced, and deteriorated if fasting glucose was the same/higher but with increased antidiabetic treatments. 42 patients (median age 50 years; range 29–75 years) were included. At baseline, 26 (62%) were normoglycemic, eight (19%) had impaired glucose tolerance/fasting glycemia, and eight (19%) had diabetes mellitus; family history of diabetes mellitus was significantly associated with abnormal glucose status. At final visit, the mean (SE) lanreotide dose was 108 (21) mg/month. Median treatment duration was 23 months, range 3–138 months, and 74% of patients received the 120-mg dose. Median GH levels decreased significantly (baseline, 12 [5–20] μg/l; final visit, 2.1 [1.0–4.7] μg/l; P < 0.0001); IGF-1 levels were age- and sex-normalized in 33% of patients. Glucose control deteriorated in seven patients (17%) and improved from abnormal levels in 10 (24%). Deterioration was associated with smaller GH decreases (median change, −3.4 μg/l vs. −10.7 μg/l, P = 0.014) and improvement with trend to lower BMI and younger age. During primary lanreotide treated acromegalic patients 60% had no change, 24% had an improvement and 17% had a worsening of glucose status. Deterioration was significantly associated with smaller GH decreases during primary lanreotide treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melmed S (2009) Acromegaly pathogenesis and treatment. J Clin Invest 119:3189–3202
Holdaway IM, Rajasoorya CR, Gamble GD (2004) Factors influencing mortality in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:667–674
Moller N, Jorgensen JO, Abildgard N, Orskov L, Schmitz O, Christiansen JS (1991) Effects of growth hormone on glucose metabolism. Horm Res 36:32–35
Mauras N, Haymond MW (2005) Are the metabolic effects of GH and IGF-1 separable? Growth Horm IGF Res 15:19–27
Clemmons DR (2004) The relative roles of growth hormone and IGF-1 in controlling insulin sensitivity. J Clin Invest 113:25–27
Melmed S, Colao A, Barkan A, Molitch M, Grossman AB, Kleinberg D, Clemmonds D, Chanson P, Laws E, Schlechte J, Vance ML, Ho K, Giustina A (2009) Guidelines for acromegaly management: an update. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:1509–1517
Strowski MZ, Blake AD (2008) Function and expression of somatostatin receptors of the endocrine pancreas. Mol Cell Endocrinol 286:169–179
Caron P, Beckers A, Cullen DR, Goth MI, Gutt B, Laurberg P, Pico A, Valimaki M, Zgliczynski W (2002) Efficacy of the new long-acting formulation of lanreotide (lanreotide Autogel) in the management of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:99–104
Giustina A, Chanson P, Bronstein MD, Klibanski A, Lamberts S, Casanueva F, Trainer P, Ghigo E, Ho K, Melmed S (2010) A consensus on criteria for cure of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:3141–3148
AACE Diabetes Mellitus Clinical Practice Guidelines Task Force (2010) American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists medical guidelines for clinical practice for the management of diabetes mellitus. Endocr Pract 13(Suppl. 1):1–68
Angeletti G (2003) The metabolic complications of acromegaly. J Endocrinol Invest 26(8 supp):18–19
Colao A, Pivonello R, Auriemma RS, Galdiero M, Savastano S, Lombardi G (2007) Beneficial effect on dose escalation of octreotide LAR as first-line therapy in patients with acromegaly. Eur J Endocrinol 157:579–587
Atttanasio R, Baldelli R, Pivonello R, Grottoli S, Bocca L, Gasco V, Giusti M, Tamburrano G, Colao A, Cozzi R (2003) Lanreotide 60 mg, a new long-acting formulation: effectiveness in the chronic treatment of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:5258–5265
Colao A, Auriemma RS, Savastano S, Galdiero M, Grasso L, Lombardi G, Pivonello R (2009) Glucose tolerance and somatostatin analogue treatment in acromegaly: a 12-month study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:2907–2914
Colao A, Auriemma RS, Galdiero M, Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Esposito F, Grasso L, Lombardi G, Pivonello R (2009) Impact of somatostatin analogs versus surgery on glucose metabolism in acromegaly: results of a 5-year observational, open, prospective study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:528–537
Fieffe S, Morange I, Petrossians P, Chanson P, Rohmer V, Cortet C, Borson Chazot F, Brue T, Delemer B (2011) Diabetes in acromegaly, prevalence, risk factors and evolution; data from the French acromegaly register. Eur J Endocrinol 164:877–884
DECODE Study Group (2003) Age-and-sex–specific prevalences of diabetes and impaired glucose regulation in 13 European cohorts. Diabetes Care 26:61–69
Kusnik-Joinville O, Weill A, Salanave B, Ricordeau P, Allemand H (2008) Prevalence and treatment of diabetes in France. Diabetes Metab 34:266–272
Abdelmalak B, Abdelmalak JB, Knittel J, Christiansen E, Mascha E, Zimmerman R, Argalius M, Foss J (2010) The prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes in non cardiac surgery patients, an observational study. Can J Anesth 57:1058–1064
Kreze A, Kreze-Spirova E, Mikulecky M (2001) Risk factors for glucose intolerance in active acromegaly. Braz J Med Biol Res 34:1429–1433
Balkau B, Lange C, Fezeu L, Tichet J, Lauzon-Guillain B, Czernichow S, Fumeron F, Froguel P, Vaxillaire M, Cauchi S, Ducimetière P, Eschwege E (2008) Predicting diabetes: clinical, biological, and genetic approaches: data from the epidemiological study on the insulin resistance syndrome (DESIR). Diabetes Care 31:2056–2061
Stelmachowska-Banas M, Zdunowski P, Zgliczynski W (2009) Abnormalities in glucose homeostasis in acromegaly. Does the prevalence of glucose intolerance depend on the level of activity of the disease and the duration of the symptoms? Endokrynol Pol 60:20–24
Biering H, Knappe G, Gerl H, Lochs H (2000) Prevalence of diabetes in acromegaly and cushing syndrome. Acta Med Austriaca 27:27–31
Nabarro JD (1987) Acromegay. Clin Endocrinol 26:481–512
Holt R, Simpson H, Sönksen P (2003) The role of the growth hormone—insulin—like factor axis in glucose homeostasis. Diabet Med 20:3–15
Mazziotti G, Floriani I, Bonadonna S, Torri V, Chanson P, Giustina A (2009) Effects of somatostatin analogs on glucose homeostasis: a meta-analysis of acromegaly studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:1500–1508
Mazziotti G, Porcelli T, Bogazzi F, Bugari G, Cannavò S, Colao A, Cozzi R, De Marinis L, degli Uberti E, Grottoli S, Minuto F, Montini M, Spinello M, Giustina A (2011) Effects of high-dose octreotide LAR on glucose metabolism in patients with acromegaly inadequately controlled by conventional somatostatin analog therapy. Eur J Endocrinol 164:341–347
Baldelli R, Battista C, Leonetti F, Ghiggi MR, Ribaudo MC, Paoloni A, D’Amico E, Ferretti E, Baratta R, Liuzzi A, Trischitta V, Tamburrano G (2003) Glucose homeostasis in acromegaly: effects of long-acting somatostatin analogue treatment. Clin Endocrinol 59:492–499
Ronchi C, Epaminonda P, Cappiello V, Beck-Peccoz P, Arosio M (2002) Effects of two different somatostatin analogs on glucose tolerance in acromegaly. J Endocrinol Invest 25:502–507
Webb S, Ortega E, Rodriguez-Espinosa J, Mato ME, Corcoy R (2001) Decreased insulin requirements after LAR-octreotide but not after lanreotide in an acromegalic patient. Pituitary 4:275–278
Gutt B, Bidlingmaier M, Kretschmar K, Dieterle C, Steffin B, Schopohl J (2005) Four-year follow-up of acromegalic patients treated with the new long acting formulation of lanreotide (lanreotide Autogel). Exp Clin Endo Diabetes 113:139–144
Steffin B, Gutt B, Bidlingmaier M, Dieterle C, Oltmann F, Schopohl J (2006) Effects of the long-acting somatostatin analogue lanreotide Autogel on glucose tolerance and insulin resistance in acromegaly. Eur J Endocrinol 155:73–78
Ayuk J, Stewart SE, Stewart PM, Sheppard MC (2002) Long-term safety and efficacy of depot long-acting somatostatin analogs for the treatment of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:4142–4146
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge editorial assistance from Watermeadow Medical for clarity of language and formatting to journal requirements, funded by Ipsen. This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Couture, E., Bongard, V., Maiza, JC. et al. Glucose status in patients with acromegaly receiving primary treatment with the somatostatin analog lanreotide. Pituitary 15, 518–525 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-011-0361-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-011-0361-9