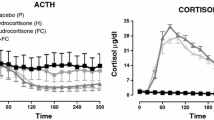
Abstract
A large body of in vitro evidence shows that cytokines influence the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis both in physiological conditions and in Cushing’s disease (CD). In order to study in vivo the role of intrapituitary cytokines in CD, we assayed two cytokines known for their action on the pituitary, i.e. interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), and also soluble interleukin-6 receptor (sIL-6R), important for the neural activities of IL-6, in a carefully selected sample of subjects affected by CD undergoing bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling. Similarly to ACTH, all cytokines basally showed a higher concentration in the ipsilateral sinus compared to the controlateral one and to that of peripheral blood; after CRH infusion, both ipsilaterally and controlaterally, IL-6 and sIL-6R values increased compared to basal ones, while IL-1β increased significantly up to 5 min after CRH and then decreased significantly compared to basal values in subsequent measurements; peripherically no significant variations in the cytokines were observed after CRH. Again similarly to ACTH, the three cytokines presented a higher increase ipsilaterally than controlaterally; moreover all three interleukins in the ipsilateral sinuses showed positive and significant correlations between their basal value and that of basal ACTH. These findings allow us to hypothesize that the central production of IL-1β and IL-6 could be involved in ACTH hypersecretion which occurs in CD: more specifically, we hypothesize that these cytokines are produced directly by the corticotroph adenoma and have the task of enhancing tumoral secretion of ACTH with an autocrine-paracrine mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vilcek J, Feldmann M (2004) Historical review: cytokines as therapeutics and targets of therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:201–209. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2004.02.011
Oppenheim JJ (2001) Cytokines: past, present, and future. Int J Hematol 74:3–8. doi:10.1007/BF02982543
Haedo MR, Gerez J, Fuertes M, Giacomini D, Páez-Pereda M, Labeur M, Renner U, Stalla GK, Arzt E (2009) Regulation of pituitary function by cytokines. Horm Res 72:266–274. doi:10.1159/000245928
Cambronero JC, Rivas FJ, Borrell J, Guaza C (1992) Interleukin-1-beta induces pituitary adrenocorticotropin secretion: evidence for glucocorticoid modulation. Neuroendocrinology 55:648–654. doi:10.1159/000126184
Swolin-Eide D, Ohlsson C (1998) Effects of cortisol on the expression of interleukin-6 and interleukin-1 beta in human osteoblast-like cells. J Endocrinol 156:107–114. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1560107
Goujon E, Parnet P, Laye S, Combe C, Kelley KW, Dantzer R (1995) Stress downregulates lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of proinflammatory cytokines in the spleen, pituitary, and brain of mice. Brain Behav Immun 9:292–303. doi:10.1006/brbi.1995.1028
Del Rey A, Besedovsky H, Sorkin E, Dinarello CA (1987) Interleukin-1 and glucocorticoid hormones integrate an immunoregulatory feedback circuit. Ann N Y Acad Sci 496:85–90. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb35749.x
Besedovsky H, del Rey A, Sorkin E, Dinarello CA (1986) Immunoregulatory feedback between interleukin-1 and glucocorticoid hormones. Science 233:652–654. doi:10.1126/science.3014662
Renner U, De Santana EC, Gerez J, Fröhlich B, Haedo M, Pereda MP, Onofri C, Stalla GK, Arzt E (2009) Intrapituitary expression and regulation of the gp130 cytokine interleukin-6 and its implication in pituitary physiology and pathophysiology. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1153:89–97. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03970.x
Renner U, Gloddek J, Pereda MP, Arzt E, Stalla GK (1998) Regulation and role of intrapituitary IL-6 production by folliculostellate cells. Domest Anim Endocrinol 15:353–362. doi:10.1016/S0739-7240(98)00027-7
Hanisch A, Dieterich KD, Dietzmann K, Lüdecke K, Buchfelder M, Fahlbusch R, Lehnert H (2000) Expression of members of the interleukin-6 family of cytokines and their receptors in human pituitary and pituitary adenomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:4411–4414. doi:10.1210/jc.85.11.4411
McCann SM, Kimura M, Karanth S, Yu WH, Mastronardi CA, Rettori V (2000) The mechanism of action of cytokines to control the release of hypothalamic and pituitary hormones in infection. Ann NY Acad Sci 917:4–18. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb05368.x
Brown SL, Smith LR, Blalock JE (1987) Interleukin 1 and interleukin 2 enhance proopiomelanocortin gene expression in pituitary cells. J Immunol 139:3181–3183
De Souza EB (1993) Corticotropin-releasing factor and interleukin-1 receptors in the brain-endocrine-immune axis. Role in stress response and infection. Ann NY Acad Sci 697:9–27. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb49919.x
Gloddek J, Pagotto U, Paez Pereda M, Arzt E, Stalla GK, Renner U (1999) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide, interleukin-6 and glucocorticoids regulate the release of vascular endothelial growth factor in pituitary folliculostellate cells. J Endocrinol 160:483–490. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1600483
Pereda MP, Lohrer P, Kovalovsky D, Perez Castro C, Goldberg V, Losa M, Chervín A, Berner S, Molina H, Stalla GK, Renner U, Arzt E (2000) Interleukin-6 is inhibited by glucocorticoids and stimulates ACTH secretion and POMC expression in human corticotroph pituitary adenomas. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 108:202–207. doi:10.1055/s-2000-7887
Malarkey WB, Zvara BJ (1989) Interleukin-1 beta and other cytokines stimulate adrenocorticotropin release from cultured pituitary cells of patients with Cushing’s disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 69:196–199. doi:10.1210/jcem-69-1-196
Watanobe H, Tamura T, Habu S, Kakizaki Y, Kohsaka A, Suda T (1998) Measurement of cytokines in the cavernous sinus plasma from patients with Cushing’s disease. Neuropeptides 32:119–123. doi:10.1016/S0143-4179(98)90026-9
Merola B, Longobardi S, Colao A, Di Somma C, Ferone D, Di Rella F, Pivonello R, Covelli V, Annunziato L, Lombardi G (1996) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases after corticotropin-releasing hormone administration in Cushing’s disease. In vivo and in vitro studies. Neuroendocrinology 64:393–397. doi:10.1159/000127142
Kurotani R, Yasuda M, Oyama K, Egashira N, Sugaya M, Teramoto A, Osamura RY (2001) Expression of interleukin-6, interleukin-6 receptor (gp80), and the receptor’s signal-transducing subunit (gp130) in human normal pituitary glands and pituitary adenomas. Mod Pathol 14:791–797
März P, Otten U, Rose-John S (1999) Neural activities of IL-6-type cytokines often depend on soluble cytokine receptors. J Neurosci 11:2995–3004. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00755.x
Arnaldi G, Angeli A, Atkinson AB, Bertagna X, Cavagnini F, Chrousos GP, Fava GA, Findling JW, Gaillard RC, Grossman AB, Kola B, Lacroix A, Mancini T, Mantero F, Newell-Price J, Nieman LK, Sonino N, Vance ML, Giustina A, Boscaro M (2003) Diagnosis and complications of Cushing’s syndrome: a consensus statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:5593–5602. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-030871
Oldfield EH, Doppman JL, Nieman LK, Chrousos GP, Miller DL, Katz DA, Cutler GB Jr, Loriaux DL (1991) Petrosal sinus sampling with and without corticotropin-releasing hormone for the differential diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. N Engl J Med 325:897–905
Oldfield EH, Chrousos GP, Schulte HM, Schaaf M, McKeever PE, Krudy AG, Cutler GB Jr, Loriaux DL, Doppman JL (1985) Preoperative lateralization of ACTH-secreting pituitary microadenomas by bilateral and simultaneous inferior petrosal venous sinus sampling. N Engl J Med 312:100–103
Bonelli FS, Huston J 3rd, Carpenter PC, Erickson D, Young WF Jr, Meyer FB (2000) Adrenocorticotropic hormone-dependent Cushing’s syndrome: sensitivity and specificity of inferior petrosal sinus sampling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:690–696
Holm S (1979) A Simple Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test Procedure. Scand J Stat 6:65–70
Courtois-Cox S, Jones SL, Cichowski K (2008) Many roads lead to oncogene-induced senescence. Oncogene 27:2801–2809. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210950
Leu SJ, Singh VK (1992) Stimulation of interleukin-6 production by corticotropin-releasing factor. Cell Immunol 143:220–227. doi:10.1016/0008-8749(92)90018-K
Singh VK, Leu SJ (1990) Enhancing effect of corticotropin-releasing neurohormone on the production of interleukin-1 and interleukin-2. Neurosci Lett 120:151–154. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(90)90025-5
Reyes TM, Coe CL (1998) Resistance of central nervous system interleukin-6 to glucocorticoid inhibition in monkeys. Am J Physiol 275:R612–R618
DeRijk R, Michelson D, Karp B, Petrides J, Galliven E, Deuster P, Paciotti G, Gold PW, Sternberg EM (1997) Exercise and circadian rhythm-induced variations in plasma cortisol differentially regulate interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) production in humans: high sensitivity of TNF alpha and resistance of IL-6. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:2182–2191. doi:10.1210/jc.82.7.2182
Feldmann M (2008) Many cytokines are very useful therapeutic targets in disease. J Clin Invest 118:3533–3536. doi:10.1172/JCI37346
Acknowledgments
No external funding, apart from the support of the authors’ institutions, was available for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paoletta, A., Arnaldi, G., Papa, R. et al. Intrapituitary cytokines in Cushing’s disease: do they play a role?. Pituitary 14, 236–241 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-010-0285-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-010-0285-9