Abstract
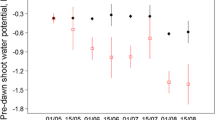
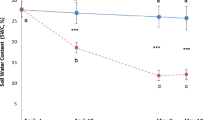
The widespread Mediterranean Pinus pinea showed exceptionally low genetic diversity and low differentiation between traits in the adult phase. We explored the adaptation potential of seedlings from four main Iberian provenances during their regeneration phase. We assessed the variability of shoot growth, allometry, physiological traits, and phenotypic plasticity to the interactive effect of light and water environments during 8-month moderate water-stress cycle and after one-week heat wave. The effect of shade and drought was mainly orthogonal whatever the provenance. The inland La Mancha provenance showed higher shoot growth and biomass compared to the southern coastal Depresión-del-Guadalquivir provenance. Following the heat wave, La Mancha presented higher net photosynthetic rates, a lower decrease in maximal quantum efficiency of PSII, and a higher accumulated relative height growth, thus, showing an adaptive advantage. The observed differences corroborated the ecological grouping of the provenances along latitudinal and inland–coastal gradients. We confirmed the high adaptive plasticity of Pinus pinea to the unpredictable Mediterranean environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- E :
-
transpiration rate
- ETR:
-
apparent phtosynthetic electron transport rate
- Fv/Fm :
-
maximum photochemical efficiency of PSII
- g s :
-
stomatal conductance
- H:
-
soil moisture
- LA:
-
leaf area
- LDM:
-
leaf dry mass
- LMF:
-
leaf mass fraction
- P N :
-
net assimilation rate
- P gmax :
-
maximum rate of gross photosynthesis at saturating irradiance
- R D :
-
dark respiration
- RDM:
-
root dry mass
- RHG:
-
accumulated relative height growth
- RMF:
-
root mass fraction
- SDM:
-
stem dry mass
- ShDM:
-
shoot dry mass
- ShMF:
-
shoot mass fraction
- SLA:
-
specific leaf area
- SMF:
-
stem mass fraction
- S/R:
-
shoot to root ratio
- TDM:
-
total dry mass
- α:
-
quantum yield of assimilation
- ΦPSII :
-
yield of photochemistry in PSII
- ψpd :
-
predawn water potential
References
Awada T., Radoglou K., Fotelli M.A. et al.: Ecophysiology of seedlings of three Mediterranean pine species in contrasting light regimes.–Tree Physiol. 23: 33–41, 2003.
Brouwer R.: Functional equilibrium: sense or nonsense?–Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 31: 335–348, 1983
Calama R., Puértolas J., Madrigal G. et al.: Modeling the environmental response of leaf net photosynthesis in Pinus pinea L. natural regeneration.–Ecol. Model. 251: 9–21, 2013
Chambel M.R., Climent J., Alía R.: Divergence among species and populations of Mediterranean pines in biomass allocation of seedlings grown under two watering regimes.–Ann. For. Sci. 64: 97-97, 2007.
Chuine I., Rehfeldt G.E., Aitken S.N.: Height growth determinants and adaptation to temperature in pines: a case study of Pinus contorta and Pinus monticola.–Can. J. Forest Res. 36: 1059–1066, 2006.
Court-Picon M.C., Gadbin-Henry C., Guibal F. et al.: Dendrometry and morphometry of Pinus pinea L. in Lower Provence (France): adaptability and variability of provenances.–Forest Ecol. Manag. 194: 319–333, 2004.
Cuesta B., Villar-Salvador P., Puértolas J. et al.: Facilitation of Quercus ilex in Mediterranean shrubland is explained by both direct and indirect interactions mediated by herbs.–J. Ecol. 98: 687–696, 2010.
D’Amato A.W., Bradford J., Fraver S., Palik B.: Forest management for mitigation and adaptation to climate change mitigation: insights from long-term silviculture experiments.–Forest Ecol. Manag. 262: 803–816, 2011.
Demmig-Adams B., Adams W.W.: Photoprotection and other responses of plants to high light stress.–Annu. Rev. Plant Phys. 43: 599–626, 1992.
Gardiner E.S., Hodges J.D.: Growth and biomass distribution of cherrybark oak (Quercus pagoda Raf.) seedlings as influenced by light availability.–Forest Ecol. Manag. 108: 127–134, 1998.
Gatti E, Rossi F.: Daily and seasonal trends of gas exchange in Pistacia lentiscus L.–Acta Physiol. Plant. 32: 809–813, 2010.
Gómez-Aparicio L., Valladares F., Zamora R.: Differential light responses of Mediterranean tree samplings: linking ecophysiology with regeneration niche in four co-occurring species.–Tree Physiol. 26: 947–958, 2006.
Gordo F.J., Rojo L.I., Calama R. et al.: Silviculture of Pinus pinea L. natural regeneration in public forests in Valladolid province.–In: Gordo J., Calama R., M. Pardos et al. (ed.): [Natural Regeneration of Pine Stands in the Sandy Lands of the Spanish Northern Plateau.] Pp 145–160. Universidad de Valladolid-INIA, Valladolid 2012. [In Spanish]
Kaelke C.M., Kruger E.L., Reich P.B.: Trade-offs in seedling survival, growth, and physiology among hardwood species of contrasting successional status along a light-availability gradient.–Can. J. Forest Res. 31: 1602–1616, 2001.
Keeley J.E., Zedler P.H.: Evolution of life histories in Pinus.–In: Richardson D.M. (ed.): Ecology and Biogeography of Pinus. Pp. 219–249. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1998.
Lindner M, Calama R.: Climate change and the need for adaptation in Mediterranean forests.–In: Lucas-Borja N.E. (ed.): Forest Management of Mediterranean Forests under the new Context of Climate Change. Building Alternatives for the Coming Future. Pp. 13–30. Nova Science Publ., New York 2013.
Lindner M., García J., Kolström M. et al.: Impacts of climate change on European forests and options for adaptation.–Report to the EC Directorate-General for Agriculture and Rural Development, AGRI-2007-G4-06. Pp. 173. European Commission Directorate General for Agriculture and Rural Development, Brussels 2008.
Lindner M., Maroschek M., Netherer S. et al.: Climate change impacts, adaptive capacity, and vulnerability of European forest ecosystems.–Forest Ecol. Manag. 259: 698–709, 2010.
Linhart Y.C., Grant M.B.: Evolutionary significance of local genetic differentiation in plants.–Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 27: 237–277, 1996.
Loewe-Muñoz V., Delard-Rodríguez C., Balzarini M. et al.: Impact of climate and management variables on stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) growing in Chile.–Agr. Forest Meteorol. 214-215: 106–116, 2015.
López R., Zehavi A., Climent J. et al.: Contrasting ecotypic differentiation for growth and survival in Pinus canariensis.–Aust. J. Bot. 55: 759–769, 2007.
Manes F., Seufert G., Vitale M., Ecophysiological studies of Mediterranean plant species at the Castelporziano estate.–Atmos. Environ. 31: 51–60, 1997.
Manso R., Pukkala T., Pardos M. et al.: Modelling Pinus pinea forest management to attain natural regeneration under present and future climatic scenarios.–Can. J. Forest Res. 44: 250–262, 2014.
Mayoral C., Calama R., Sanchez-Gonzalez M. et al.: Modelling the influence of light, water and temperature on photosynthesis in young trees of mixed Mediterranean Forests.–New Forest. 46: 485–506, 2015.
Mutke S., Gordo J., Chambel M.R. et al.: Phenotypic plasticity is stronger than adaptative differentiation among Mediterranean Stone pine provenances.–For. Syst. 19: 356–366, 2010.
Pardos M., Climent J., Almeida H. et al.: The role of developmental stage in frost tolerance of Pinus pinea L. seedlings and saplings.–Ann. Forest Sci. 71: 551–562, 2014.
Pardos M., Puértolas J., Madrigal G. et al.: Seasonal changes in the physiological activity of regeneration under a natural light gradient in a Pinus pinea regular stand.–For. Syst. 19: 367–380, 2010.
Pons T.L., Poorter H.: The effect of irradiance on the carbon balance and tissue characteristics of five herbaceous species differing in shade-tolerance.–Front. Plant Sci. 5: 1–14, 2014.
Poorter H., Nagel O.: The role of biomass allocation in the growth response of plants to different levels of light, CO2, nutrients and water: a quantitative review.–Aust. J. Plant Phys. 2: 595–607, 2000.
Poorter H., Niklas K.J., Reich P.B. et al.: Biomass allocation to leaves, stems and roots: meta-analyses of interspecific variation and environmental control.–New Phytol. 193: 30–50, 2012.
Poorter L.: Growth responses of 15 rain-forest tree species to a light gradient: the relative importance of morphological and physiological traits.–Funct. Ecol. 13: 396–410, 1999.
Puértolas J., Oliet J.A., Jacobs D.F. et al.: Is light the key factor for success of tube shelters in forest restoration planting under Mediterranean climates.–Forest Ecol. Manag. 260: 610–617, 2010.
Reich P.B., Luo Y., Bradford J.B. et al.: Temperature drives global patterns in forest biomass distribution in leaves, stems, and roots.–P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111: 13721–13726, 2014.
Reich P.B.: Root-shoot relations: optimality in acclimation and 13 adaptation or the “Emperor’s New Clothes”.–In: Elshe A.K. (ed.): Plant Roots: the Hidden Half. Pp. 205–220. Wailey, New York 2002.
Robson T.M., Rodríguez-Calcerrada J., Sánchez-Gómez D. et al.: Summer drought impedes beech seedling performance more in a sub-Mediterranean forest understory than in small gaps.–Tree Physiol. 29: 249–259, 2009.
Rubio-Casal A.E., Leira-Doce P., Figueroa M.E. et al.: Contrasted tolerance to low and high temperatures of three tree taxa co-occurring on coastal dune forests under Mediterranean climate.–J. Arid Environ. 74: 429–439, 2010.
Sabaté S., Gracia C.A., Sánchez C.A.: Likely effects of climate change on growth of Quercus ilex, Pinus halepensis, Pinus pinaster, Pinus sylvestris and Fagus sylvatica forests in the Mediterranean region.–Forest Ecol. Manag. 162: 23–37, 2002.
Sack L., Grubb P.J.: The combined impacts of deep shade and drought on the growth and biomass allocation of shade-tolerant woody seedlings.–Oecologia 131: 175–185, 2002.
Sack L.: Responses of temperate woody seedlings to shade and drought: do trade-offs limit potential niche differentiation?–Oikos 107: 107–127, 2004.
Sánchez-Gómez D., Valladares F., Zavala M.A., Performance of seedlings of Mediterranean woody species under experimental gradients of irradiance and water availability: trade-offs and evidence for niche differentiation.–New Phytol. 170: 795–806, 2006.
Sánchez-Gómez D., Velasco-Conde T., Cano-Martín F.J. et al.: Inter-clonal variation in functional traits in response to drought for a genetically homogeneous Mediterranean conifer.–Environ. Exp. Bot. 70: 104–109, 2011.
Sims D.A., Gebauer R.L.E., Pearcy R.W.: Scaling sun and shade photosynthetic acclimation of Alocasia macrorrhiza to wholeplant performance.–Plant Cell. Environ. 17: 889–900, 1994.
Spathelf P., van der Maaten E. van der Maaten-Theunissen et al.: Climate change impacts in European forests: The expert views of local observers.–Ann. Forest Sci. 71: 131–137, 2014.
Thornley J.H.M., Johnson I.R.: Plant and Crop Modeling: a Mathematical Approach to Plant and Crop Physiology. Pp. 73. The Blackburn Press, Caldwell 1990.
Valladares F., Dobarro I., Sánchez-Gómez D. et al.: Photoinhibition and drought in Mediterranean woody saplings: scaling effects and interaction in sun and shade phenotypes.–J. Exp. Bot. 56: 483–494, 2005.
Valladares F., Matesanz S., Guilhaumon F. et al.: The effects of phenotypic plasticity and local adaptation on forecasts of species range shifts under climate change.–Ecol. Lett. 17: 1351–1364, 2014.
Valladares F., Pearcy R.W.: Drought can be more critical in the shade than in the sun: a field study of carbon gain and photoinhibition in a Californian shrub during a dry El Niño year.–Plant Cell. Environ. 25: 749–759, 2002.
Valladares F., Wright J., Lasso E. et al.: Plastic phenotypic response to light of 16 congeneric shrubs from a Panamanian rainforest.–Ecology 81: 1925–1936, 2000.
Vendramin G.G., Fady B., González-Martínez S.C. et al.: Genetically depauperate but widespread: the case of an emblematic Mediterranean pine.–Evolution 62: 680–688, 2008.
Wolf A., Field C.B., Berry J.A.: Allometric growth and allocation in forests: a perspective from FLUXNET.–Ecol. Appl. 21: 1546–1556, 2011.
Yamamoto Y.: Quality control of photosystem II: the mechanisms for avoidance and tolerance of light and heat stresses are closely linked to membrane fluidity of the thylakoids.–Front. Plant Sci. 7: 1136, 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: This study was supported by the Spanish National Programme for Fundamental Research Projects (Projects no. AGL2010-15521 and RTA2013-00011-C02-01). We are especially grateful to M. Conde, G. Madrigal, and E. Garriga for technical support in the greenhouse.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pardos, M., Calama, R. Responses of Pinus pinea seedlings to moderate drought and shade: is the provenance a differential factor?. Photosynthetica 56, 786–798 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-017-0732-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-017-0732-1