Abstract
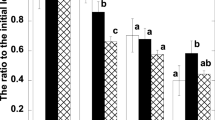
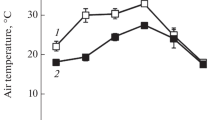
The partial shading effect on the photosynthetic apparatus of the sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) was examined by monitoring oxygen evolution, maximum quantum yield of PSII photochemistry in dark-adapted leaves (Fv/Fm), the chlorophyll (Chl) concentrations and the Rubisco contents, and leaf mass per area (LMA) at the leaf level and by determining the concentrations of cytochrome (Cyt) f and the reaction centres of photosystem (PS) I and PSII at the thylakoid level. In this experiment, partial shading was defined as the shading of 2nd leaves with shade cloths, and the whole treatment was defined as the covering of the whole individuals with shade cloths. In the leaf level responses, oxygen evolution, LMA, Chl concentrations and Rubisco contents decreased in all shade treatments administered for six days. Fv/Fm remained constant irrespective of the shade treatments. On the other hand, in the thylakoid-level responses, the concentrations of the thylakoid components per unit Chl and the stoichiometry of the two photosystems showed no statistical difference among the shade treatments. The data obtained from the present study indicate that the partial shading affected the leaf-level responses rather than the thylakoid-level responses. The light received at the lower leaves might serve as a factor in the regulation of the leaf properties of the upper leaves due to the whole plant photosynthesis, while this factor did not have an effect at the thylakoid level.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C550 :
-
electrochromic band shift of pheophytin in the PSII reaction centre complex
- Chl:
-
chlorophyll
- Cyt:
-
cytochrome
- DCIP:
-
2,6-dichlorophenol indophenol
- DCMU:
-
3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea
- Fm :
-
maximum fluorescence yield in the dark-adapted leaves
- Fℴ :
-
minimal Chl fluorescence yield in the dark adapted leaves
- Fv :
-
variable fluorescence yield in the dark-adapted leaves
- Fv/Fm :
-
maximum quantum yield of PSII photochemistry in dark-adapted leaves
- LMA:
-
leaf mass per area
- P700 :
-
the reaction center complex in photosystem I
- PART:
-
partial shading treatment
- PPFD:
-
photosynthetic photon flux density
- PS:
-
photosystem
- QA :
-
primary quinone acceptor of PSII
- WHOLE:
-
whole shading treatment
References
Burkey, K.O., Wells, R.: Effects of natural shade on soybean thylakoid membrane composition. — Photosynth. Res. 50: 149–158, 1996.
Chow, W.S., Anderson, J.M.: Photosynthetic responses of Pisum sativum to an increase in irradiance during growth 1. Photosynthetic activities. — Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 14: 1–8, 1987.
Crafts-Brandner, S.J., Egli, D.B.: Sink removal and leaf senescence in soybean. Cultivar effects. — Plant Physiol. 85: 662–666, 1987.
De la Torre, W.R., Burkey, K.O.: Acclimation of barley to changes in light intensity: photosynthetic electron transport activity and components. — Photosynth. Res. 24: 127–136, 1990.
Hikosaka, K.: Effects of leaf age, nitrogen nutrition and photon flux density on the organization of the photosynthetic apparatus in leaves of a vine (Ipomoea tricolor Cav.) grown horizontally to avoid mutual shading of leaves. — Planta 198: 144–150, 1996.
Hirose, T., Werger, M.J.A.: Maximizing daily canopy photosynthesis with respect to the leaf nitrogen allocation pattern in the canopy. — Oecologia 72: 520–526, 1987.
Kura-Hotta, M., Satoh, K., Katoh, S.: Relationship between photosynthesis and chlorophyll content during leaf senescence of rice seedlings. — Plant Cell Physiol. 28: 1321–1329, 1987.
Laemmli, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. — Nature 227: 680–685, 1970.
Layne, D.R., Flore, J.A.: End-product inhibition of photosynthesis in Prunus cerasus L. in response to whole-plant source-sink manipulation. — J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 120: 583–599, 1995.
Lazár, D.: Chlorophyll a fluorescence induction. — Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1412: 1–28, 1998.
Lee, W.-J., Whitmarsh, J.: Photosynthetic apparatus of pea thylakoid membranes. Response to growth light intensity. — Plant Physiol. 89: 932–940, 1988.
Leong, T.-Y., Anderson, J.M.: Adaptation of the thylakoid membranes of pea chloroplasts to light intensities. 2. Regulation of electron transport capacities, electron carriers, coupling factor (CF1) activity and rates of photosynthesis. — Photosynth. Res. 5: 117–128, 1984.
Mae, T., Ohira, K.: The remobilization of nitrogen related to leaf growth and senescence in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). — Plant Cell Physiol. 22: 1067–1074, 1981.
McCauley, S.W., Melis, A.: Quantitation of photosystem II in spinach chloroplasts. — Biochim. Biophys. Acta 849: 175–182, 1986.
Melis, A.: Dynamics of photosynthetic membrane composition and function. — Biochim. Biophys Acta 1058: 87–106, 1991.
Melis, A., Harvey, G.W.: Regulation of photosystem stoichiometry, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b content and relation to chloroplast ultrastructure. — Biochim. Biophys. Acta 637: 138–145, 1981.
Melis, A., Homann, P.H.: Kinetic analysis of the fluorescence induction in 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea poisoned chloroplasts. — Photochem. Photobiol. 21: 431–437, 1975.
Mondal, M.H., Brun, W.A., Brenner, M.L.: Effects of sink removal on photosynthesis and senescence in leaves of soybean (Glycine max L.) plants. — Plant Physiol. 61: 394–397, 1978.
Monsi, M., Saeki, T.: [On the factor light in plant communities and its importance for matter production.] — Jap. J. Bot. 14: 22–52, 1953. [In German.]
Murchie, E.H., Horton, P.: Contrasting patterns of photo-synthetic acclimation to the light environment are dependent on the differential expression of the responses to altered irradiance and spectral quality. — Plant Cell Environ. 21: 139–148, 1998.
Okada, K., Inoue, Y., Satoh, K., Katoh, S.: Effects of light on degradation of chlorophyll and proteins during senescence of detached rice leaves. — Plant Cell Physiol. 33: 1183–1191, 1992.
Okada, K., Katoh, S.: Two long-term effects of light that control the stability of proteins related to photosynthesis during senescence of rice leaves. — Plant Cell Physiol. 39: 393–404, 1998.
Pons, T.L., Pearcy, R.W.: Nitrogen reallocation and photosynthetic acclimation in response to partial shading in soybean plants. — Physiol. Plant. 92: 636–644, 1994.
Porra, R.J., Thompson, W.A., Kriedemann, P.E.: Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophyll a and b extracted with four different solvents: verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. — Biochim. Biophys. Acta 975: 384–394, 1988.
Sawada, S., Kuninaka, M., Watanabe, K. et al.: The mechanism to suppress photosynthesis through end-product inhibition in single-rooted soybean leaves during acclimation to CO2 enrichment. Plant Cell Physiol. 42: 1093–1102, 2001.
Thimann, K.V., Tetley, R.M., Krivak, B.M.: Metabolism of oat leaves during senescence. V. Senescence in light. — Plant Physiol. 59: 448–454, 1977.
van Kooten, O., Snel, J.F.H.: The use of chlorophyll fluorescence nomenclature in plant stress physiology. — Photosynth. Res. 25: 147–150, 1990.
Yamazaki, J.: Is light quality involved in the regulation of the photosynthetic apparatus in attached rice leaves? — Photosynth. Res. 105: 63–71, 2010a.
Yamazaki, J.: Changes in the photosynthetic characteristics and photosystem stoichiometries in wild-type and Chl b-deficient mutant rice seedlings under various irradiances. — Photosynthetica 48: 521–529, 2010b.
Yamazaki, J., Kamimura, Y., Okada, M., Sugimura, Y.: Changes in photosynthetic characteristics and photosystem stoichiometries in the lower leaves in rice seedlings. — Plant Sci. 148: 155–163, 1998.
Yano, S., Terashima, I.: Separate localization of light signal perception for sun or shade type chloroplast and palisade tissue differentiation in Chenopodium album. — Plant Cell Physiol. 42: 1303–1310, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: We express our gratitude to the mentor, Professor Yasumaro Kamimura, for his fruitful discussions and continuous encouragement throughout this work and we dedicate this paper for his 70th birthday. We thank Professor Emiko Maruta for her helpful suggestions. We also thank our collaborators for their excellent technical assistance and many suggestions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamazaki, J., Shinomiya, Y. Effect of partial shading on the photosynthetic apparatus and photosystem stoichiometry in sunflower leaves. Photosynthetica 51, 3–12 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-012-0073-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-012-0073-z