Abstract
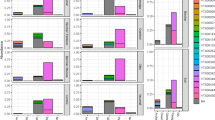
Competition plays an important role in the replacement of native species by alien plants. A greenhouse experiment was conducted to investigate whether the competition pattern of alien Robinia pseudoacacia L. and native Quercus acutissima Carr. is affected by soil sterilization. Physiological traits, such as gas-exchange parameters and chlorophyll (Chl) content, and growth traits, such as the biomass accumulation of the two species, were examined in natural soil or in soil sterilized with benomyl. The results show that native Q. acutissima inhibits the growth of R. pseudoacacia in natural soil. When the two plants coexisted and competed under sterilization treatment, R. pseudoacacia was less inhibited by Q. acutissima and the competition of R. pseudoacacia decreased the growth of Q. acutissima in terms of biomass, Chl a, Chl b, total Chl, and Chl a/b. These results suggest that soil sterilization benefits the growth of R. pseudoacacia and changes the competition pattern by the changed soil biota. Soil sterilization increased the biomass of root nodules, which ultimately benefits the growth of R. pseudoacacia and root nodule bacteria may be important in the dispersal and invasion process of nitrogen-fixing alien plants such as R. pseudoacacia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C a :
-
ambient CO2 concentration
- C i :
-
intercellular CO2 concentration
- Chl:
-
chlorophyll
- E :
-
transpiration rate
- g s :
-
stomatal conductance
- L s :
-
stomatal limitation
- NST:
-
nonsterilization treatment
- P N :
-
net photosynthetic rate
- ST:
-
sterilization treatment
- WUE:
-
instantaneous water-use efficiency
References
Amaya-Carpio, L., Davies, F.T., Fox, T., He, C.: Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic fertilizer influence photosynthesis, root phosphatase activity, nutrition, and growth of Ipomoea carnea ssp. fistulosa. — Photosynthetica 47: 1–10, 2009.
Beckstead, J., Parker, I.M.: Invasiveness of Ammophila arenaria: Release from soil-borne pathogens? — Ecology 84: 2824–2831, 2003.
Callaway, R.M., Mahall, B.E., Wicks, C., Pankey, J., Zabinski, C.: Soil fungi and the effects of an invasive forb on grasses: Neighbor identity matters. — Ecology 84: 129–135, 2003.
Callaway, R.M., Newingham, B., Zabinski, C.A., Mahall, B.E.: Compensatory growth and competitive ability of an invasive weed are enhanced by soil fungi and native neighbours. — Ecol. Lett. 4: 429–433, 2001.
Callaway, R.M., Thelen, G.C., Barth, S., Ramsey, P.W., Gannon, J.E.: Soil fungi alter interactions between the invader Centaurea maculosa and North American natives. — Ecology 85: 1062–1071, 2004.
Chen, H., Liu, J., Zhang, Y.L., Wang, Q., Ge, X.L., Wei, Y.H., Wang, R.Q.: Influence of invasive plant Coreopsis grandiflora on the functional diversity of soil microbial communities. — J. Environ. Biol. 32: 567–572, 2011.
Chittka, L., Schurkens, S.: Successful invasion of a floral market — An exotic Asian plant has moved in on Europe’s river-banks by bribing pollinators. — Nature 411: 653–653, 2001.
Corbin, J.D., D’Antonio, C.M.: Competition between native perennial and exotic annual grasses: Implications for an historical invasion. — Ecology 85: 1273–1283, 2004.
Cronk, Q.C.B., Fuller, J.L.: Plant Invaders: The Threat to Natural Ecosystems. Chapman & Hall, London. 1995.
Cui, Q.G., He, W.M.: Soil biota, but not soil nutrients, facilitate the invasion of Bidens pilosa relative to a native species Saussurea deltoidea. — Weed Res. 49: 201–206, 2009.
Dakora, F.D., Keya, S.O.: Contribution of legume nitrogen fixation to sustainable agriculture in Sub-Saharan Africa. — Soil Biol. Biochem. 29: 809–817, 1997.
de Boer, W., Folman, L.B., Gunnewiek, P.J.A.K., Svensson, T., Bastviken, D., Oberg, G., del Rio, J.C., Boddy, L.: Mechanism of antibacterial activity of the white-rot fungus Hypholoma fasciculare colonizing wood. — Can. J. Microbiol. 56: 380–388, 2010.
Dutta, R.K., Agrawal, M.: Effect of tree plantations on the soil characteristics and microbial activity of coal mine spoil land. — Tropical Ecol. 43: 315–324, 2002.
Gupta, K., Bishop, J., Peck, A., Brown, J., Wilson, L., Panda, D.: Antimitotic antifungal compound benomyl inhibits brain microtubule polymerization and dynamics and cancer cell proliferation at mitosis, by binding to a novel site in tubulin. — Biochemistry 43: 6645–6655, 2004.
He, W.M., Dong, M.: Plasticity in physiology and growth of Salix matsudana in response to simulated atmospheric temperature rise in the Mu Us Sandland. — Photosynthetica 41: 297–300, 2003.
Hetrick, B.A.D., Wilson, G.W.T., Hartnett, D.C.: Relationship between mycorrhizal dependence and competitive ability of two tallgrass prairie grasses. — Can. J. Bot. 67: 2608–2615, 1989.
Johnson, N.C., Graham, J.H., Smith, F.A.: Functioning of mycorrhizal associations along the mutualism-parasitism continuum. — New Phytol. 135: 575–586, 1997.
Jung, S.C., Matsushita, N., Wu, B.Y., Kondo, N., Shiraishi, A., Hogetsu, T.: Reproduction of a Robinia pseudoacacia population in a coastal Pinus thunbergii windbreak along the Kujukurihama Coast, Japan. — J. Forest Res.-JPN 14: 101–110, 2009.
Karaman, M., Jovin, E., Malbasa, R., Matavuly, M., Popovic, M.: Medicinal and edible lignicolous fungi as natural sources of antioxidative and antibacterial agents. — Phytother Res. 24: 1473–1481, 2010.
Killingbeck, K.T.: Nutrients in senesced leaves: Keys to the search for potential resorption and resorption proficiency. — Ecology 77: 1716–1727, 1996.
Knevel, I.C., Lans, T., Menting, F.B.J., Hertling, U.M., van der Putten, W.H.: Release from native root herbivores and biotic resistance by soil pathogens in a new habitat both affect the alien Ammophila arenaria in South Africa. — Oecologia 141: 502–510, 2004.
Kuhn, I., Durka, W., Klotz, S.: BiolFlor — a new plant-trait database as a tool for plant invasion ecology. — Diversity Distributions 10: 363–365, 2004.
Kuster, E.C., Kuhn, I., Bruelheide, H., Klotz, S.: Trait interactions help explain plant invasion success in the German flora. — J. Ecol. 96: 860–868, 2008.
Kyle, G., Leishman, M.R.: Functional trait differences between extant exotic, native and extinct native plants in the hunter river, NSW: a potential tool in riparian rehabilitation. — River Res. Appl. 25: 892–903, 2009.
Landgraf, D., Wedig, S., Klose, S.: Medium- and short-term available organic matter, microbial biomass, and enzyme activities in soils under Pinus sylvestris L. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. in a sandy soil in NE Saxony, Germany. — J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sc. 168: 193–201, 2005.
Leishman, M.R., Haslehurst, T., Ares, A., Baruch, Z.: Leaf trait relationships of native and invasive plants: community- and global-scale comparisons. — New Phytol. 176: 635–643, 2007.
Levine, J.M., Adler, P.B., Yelenik, S.G.: A meta-analysis of biotic resistance to exotic plant invasions. — Ecol. Lett. 7: 975–989, 2004.
Liancourt, P., Callaway, R.M., Michalet, R.: Stress tolerance and competitive-response ability determine the outcome of biotic interactions. — Ecology 86: 1611–1618, 2005.
Lichtenthaler, H.K., Wellburn, A.R.: Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. — Biochem. Soc. Trans. 11: 591–592, 1983.
Littschwager, J., Lauerer, M., Blagodatskaya, E., Kuzyakov, Y.: Nitrogen uptake and utilisation as a competition factor between invasive Duchesnea indica and native Fragaria vesca. — Plant Soil 331: 105–114, 2010.
Niu, H.B., Liu, W.X., Wan, F.H., Liu, B.: An invasive aster (Ageratina adenophora) invades and dominates forest understories in China: altered soil microbial communities facilitate the invader and inhibit natives. — Plant Soil 294: 73–85, 2007.
Noh, N.J., Son, Y., Kim, R.H., Seo, K.W., Koo, J.W., Park, I.H., Lee, Y.J., Lee, K.H., Son, Y.M.: Biomass accumulations and the distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus within three Quercus acutissima stands in Central Korea. — J. Plant Biol. 50: 461–466, 2007.
Pattison, R.R., Goldstein, G., Ares, A.: Growth, biomass allocation and photosynthesis of invasive and native Hawaiian rainforest species. — Oecologia 117: 449–459, 1998.
Paul, A.L., Semer, C., Kucharek, T., Ferl, R.J.: The fungicidal and phytotoxic properties of benomyl and PPM in supplemented agar media supporting transgenic arabidopsis plants for a Space Shuttle flight experiment. — Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 55: 480–485, 2001.
Paul, N.D., Ayres, P.G., Wyness, L.E.: On the use of fungicides for experimentation in natural vegetation. — Funct. Ecol. 3: 759–769, 1989.
Popova, M., Trusheva, B., Gyosheva, M., Tsvetkova, I., Bankova, V.: Antibacterial triterpenes from the threatened wood-decay fungus Fomitopsis rosea. — Fitoterapia 80: 263–266, 2009.
Qi, S.H., Xu, Y., Xiong, H.R., Qian, P.Y., Zhang, S.: Antifouling and antibacterial compounds from a marine fungus Cladosporium sp F14. — World J. Microb. Biot. 25: 399–406, 2009.
Reinhart, KO, Callaway, RM: Soil biota and invasive plants. — New Phytol. 170: 445–457, 2006.
Reinhart, K.O., Packer, A., Van der Putten, W.H., Clay, K.: Plant-soil biota interactions and spatial distribution of black cherry in its native and invasive ranges. — Ecol. Lett. 6: 1046–1050, 2003.
Rice, S.K., Westerman, B., Federici, R.: Impacts of the exotic, nitrogen-fixing black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) on nitrogen-cycling in a pine-oak ecosystem. — Plant Ecol. 174: 97–107, 2004.
Shochat, E., Lerman, S.B., Anderies, J.M., Warren, P.S., Faeth, S.H., Nilon, C.H.: Invasion, competition, and biodiversity loss in urban ecosystems. — Bioscience 60: 199–208, 2010.
Simard, S.W., Perry, D.A., Jones, M.D., Myrold, D.D., Durall, D.M., Molina, R.: Net transfer of carbon between ectomycorrhizal tree species in the field. — Nature 388: 579–582, 1997.
Smith, M.D., Hartnett, D.C., Rice, C.W.: Effects of long-term fungicide applications on microbial properties in tallgrass prairie soil. — Soil Biol. Biochem. 32: 935–946, 2000.
Šraj-KrŽič, N., Pongrac, P., Regvar, M., Gaberscik, A.: Photonharvesting efficiency and arbuscular mycorrhiza in amphibious plants. — Photosynthetica 47: 61–67, 2009.
Taniguchi, T., Tanaka, C., Tamai, S., Yamanaka, N., Futai, K.: Identification of Cylindrocladium sp causing damping-off disease of Japanese black pine (Pinus thunbergii) and factors affecting the disease severity in a black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia)-dominated area. — J. Forest Res.-JPN 13: 233–240, 2008.
Van der Putten, W.H., Peters, B.A.M.: How soil-borne pathogens may affect plant competition. — Ecology 78: 1785–1795, 1997.
Von Holle, B., Joseph, K.A., Largay, E.F., Lohnes, R.G.: Facilitations between the introduced nitrogen-fixing tree, Robinia pseudoacacia, and nonnative plant species in the glacial outwash upland ecosystem of cape cod, MA. — Biodivers. Conserv. 15: 2197–2215, 2006.
Wang, N., Yu, F.H., Li, P.X., He, W.M., Liu, F.H., Liu, J.M., Dong, M.: Clonal integration affects growth, photosynthetic efficiency and biomass allocation, but not the competitive ability, of the alien invasive Alternanthera philoxeroides under severe stress. — Ann. Bot. 101: 671–678, 2008.
Wang, R.Q., Zhou, G.Y.: [The Vegetation of Shandong Province.] — Shandong Science Technology Publisher, Jinan 2000. [In Chin.]
Wei, G.H., Chen, W.M., Zhu, W.F., Chen, C., Young, J.P.W., Bontemps, C.: Invasive Robinia pseudoacacia in China is nodulated by Mesorhizobium and Sinorhizobium species that share similar nodulation genes with native American symbionts. — FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 68: 320–328, 2009.
Woo, S.Y., Kwon, K.W., Lee, J.C., Choi, J.H., Kang, B.S.: Recovery of net photosynthetic rate after SO2 fumigation in Quercus acutissima, Pinus densiflora, Populus alba × glandulosa, and Acanthopanax sessiliflorus. — Photosynthetica 41: 319–320, 2003.
Xu, C.Y., Griffin, K.L., Schuster, W.S.F.: Leaf phenology and seasonal variation of photosynthesis of invasive Berberis thunbergii (Japanese barberry) and two co-occurring native understory shrubs in a northeastern United States deciduous forest. — Oecologia 154: 11–21, 2007.
Yu, H., He, W.M., Liu, J., Miao, S.L., Dong, M.: Native Cuscuta campestris restrains exotic Mikania micrantha and enhances soil resources beneficial to natives in the invaded communities. — Biol. Invasions 11: 835–844, 2009.
Zhang, D., Yang, X., Kang, J.S., Choi, H.D., Son, B.W.: Chlorohydroaspyrones A and B, antibacterial aspyrone derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Exophiala sp. — J. Nat. Prod. 71: 1458–1460, 2008a.
Zhang, H.Y., Xie, H.H., Qiu, S.X., Xue, J.H., Wei, X.Y.: Heteroatom-containing antibacterial phenolic metabolites from a terrestrial Ampelomyces fungus. — Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 72: 1746–1749, 2008b.
Zhang, X.Q., Liu, J., Welham C.V.J., Liu, C.C., Li, D.N., Chen, L., W, R.Q.: The effects of clonal integration on morphological plasticity and placement of daughter ramets in black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia). — Flora 201: 547–554, 2006.
Zhao, J., Zhou, L. Antibacterial activity of endophytic fungi from rhizomes of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. — Phytopathology 98: S180–S180, 2008.
Zheng, Y.L., Feng, Y.L., Liu, W.X., Liao, Z.Y.: Growth, biomass allocation, morphology, and photosynthesis of invasive Eupatorium adenophorum and its native congeners grown at four irradiances. — Plant Ecol. 203: 263–271, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: This research was financially supported by the “Major National Science and Technology Project” (Grant no. 2009ZX07210-009), the “National Natural Science Fund of China” (Grant no. 30970166), and the “Research Award for Outstanding Young Scientist in Shandong Province” (Grant no. 2006BS08008). The authors thank Enpapers Company for improving the quality of English used in the manuscript and to Dr. Edward C. Mignot of Shandong University for the linguistic advice on earlier versions of the paper. We are also grateful to the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their very helpful comments.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Wang, R.Q., Ge, X.L. et al. Competition and soil fungi affect the physiological and growth traits of an alien and a native tree species. Photosynthetica 50, 77–85 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-012-0013-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-012-0013-y