Abstract
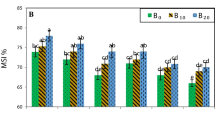
Salinization and alkalization of soil are widespread environmental problem and the alkali stress is more destructive than the effects caused by salt stress. To compare the mechanism of salt and alkali stresses, a sunflower variety (Helianthus annuus L. cv. Baikuiza 6) was tested under saline or alkaline conditions by mixing two neutral salts (NaCl and Na2SO4) or two alkaline salts (NaHCO3 and Na2CO3). The results showed that saline conditions differed greatly from alkaline conditions in their threshold intensities where sunflower can germinate, survive and grow. Under saline conditions, the emergence time was delayed, and the emergence rate and seedling survival rate also decreased with increasing salinity. However, under alkaline conditions, the rate of seedling survival decreased sharply but the emergence time and emergence rate did not change. In addition, the damaging effects of alkali stress on growth and photosynthesis were more severe than those of saline. In shoots, the main inorganic osmolyte and cation was K+ rather than Na+; the primary organic osmolytes were organic acid and soluble sugar rather than proline. Organic acid, NO3 −, and Cl− (only under saline condition) were the main source of anion. In addition, the osmotic adjustment and ion balance differed among sunflower roots, stems, and leaves. In conclusion, saline and alkaline conditions are two different stress conditions and there are special responses to two stress conditions for sunflower.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C i :
-
intercellular CO2 concentration
- E :
-
transpiration rate
- g s :
-
stomatal conductance
- P N :
-
net photosynthetic rate
References
Backhausen, J.E., Kitzmahn, C., Scheibe, R.: Competition between electron acceptors in photosynthesis: Regulation of the malate valve during CO2 fixation and nitrate reduction. — Photosynth. Res. 42: 75–86, 1994.
Bao, S.D.: Analysis Methods for Soil and Agriculture Chemistry.: China Agr. Press, Beijing 1981.
Bethke, P.C., Drew, M.C.: Stomatal and non-stomatal components to inhibition of photosynthesis in leaves of Capsicum annuum during progressive exposure to NaCl salinity. — Plant Physiol. 99: 219–226, 1992.
Campbell, S.A., Nishio, J.N.: Iron deficiency studies of sugar beet using an improved sodium bicarbonate-buffered hydroponic growth system. — J. Plant Nutr. 23: 741–757, 2000.
Demir, I., Mavi, K., Ozcoban, M., Okcu, G.: Effect of salt stress on germination and seedling growth in serially harvested aubergine (Solanum melongena L.) seeds during development. — Israel J. Plant Sci. 51: 125–131, 2003.
El-Samad, H.M.A., Shaddad, M.A.K.: Comparative effect of sodium carbonate, sodium sulphate, and sodium chloride on the growth and related metabolic activities of pea plants. — J. Plant Nutr. 19: 717–728, 1996.
Fidalgo, F., Santos, A., Santos, I., Salema, R.: Effects of long-term salt stress on antioxidant defence systems, leaf water relations and chloroplast ultrastructure of potato plants. Assoc. — Appl. Biol. 145: 185–192, 2004.
Ge, Y., Li, J.D.: A preliminary study on the effects of halophytes on salt accumulation and desalination in the soil of Songnen Plain, northeast China. — Acta Pratacu. Sin. 1: 70–76, 1990.
Ghoulam, C., Foursy, A., Fares, K.: Effects of salt stress on growth, inorganic ions and proline accumulation in relation to osmotic adjustment in five sugar beet cultivars. — Environ. Exp. Bot. 47: 39–50, 2002.
James, R.A., Munns., R., von Cammerer, S., Trejo, C., Miller, C., Condon, T. (A.G.): Photosynthetic capacity is related to the cellular and subbcelluar partitioning of Na+, K+ and Cl− in salt-affected barley and durum wheat. — Plant Cell Environ. 29: 2185–2197, 2006.
Jing, J.H., Ding, Z.R. (Trans): Determine S content. — In: Boqinnoke, X. H.: Analysis Method of Plant Biochemistry. Pp. 264–267. Science Press, Beijing 1981.
Katerji, N., van Hoorn, J.W., Hamdy, A., Mastrorilli, M.: Salt tolerance classification of crops according to soil salinity and to water stress day index. — Agric. Water Manage. 43: 99–109, 2000.
Katerji, N., van Hoorn, J.W., Hamdy, A., Mastrorilli, M.: Salt tolerance of crops according to three classification methods and examination of some hypothesis about salt tolerance. — Agric. Water Manag. 47: 1–8, 2001.
Khan, M., Ungar, I.A., Showalter, A.M.: The effect of salinity on the growth, water status, and ion content of a leaf succulent perennial halophyte, Suaeda fruticosa (L.) Forssk. — J. Arid. Environ. 45: 73–84, 2000.
Koyro, H.W.: Effect of salinity on growth, photosynthesis, water relations and solute composition of the potential cash crop halophyte Plantago coronopus (L.). — Environ. Exp. Bot. 56: 136–146, 2006.
Li, C.Y., Fang, B., Yang, C.W., Shi, D.C., Wang D.L.: Effects of various salt-alkaline mixed stresses on the state of mineral elements in nutrient solutions and the growth of alkali resistant halophyte Chloris virgata. — J. Plant Nutr. 32: 1137–1147, 2009.
Liu, J., Zhang, M.L., Zhang, Y., Shi, D.C.: Effects of simulated salt and alkali conditions on seed germination and seedling growth of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). — Acta Agron. Sin. 34: 1818–1825, 2008.
Ma, J.F., Zheng, S.J., Matsumoto, H., Hiradate, S.: Detoxifying aluminum with buckweat. — Nature 390: 569–570, 1997.
Ma, Y., Qu, B.B., Guo, L.Q., Shi, D.C., Wang, D.L.: A characteristic of the growth and solute accumulation in shoots of an alkali-tolerant Kochia Sieversiana under salt-alkaline mixed stress. — Acta Pratacu. Sin. 16: 25–33, 2007.
Munns, R.: Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. — Plant Cell Environ. 25: 239–250, 2002.
Parida, A.K., Das, A.B.: Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: A review. — Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 60: 324–349, 2005.
Qiu, N.W., Lu, Q.T., Lu, C.M.: Photosynthesis, photosystem II efficiency and the xanthophyll cycle in the salt-adapted halophyte Atriplex centralasiatica. — New Phytol. 159: 479–486, 2003.
Sagi, M., Dovrat, A., Kipnis, T., Lips, H.: Ionic balance, biomass production, and organic nitrogen as affected by salinity and nitrogen source in annual ryegrass. — J. Plant Nutr. 20: 1291–1316, 1997.
Santa-Cruz, A., Martinez-Rodriguez, M.M., Perez-Alfocea, F., Romero-Aranda, R., Bolarin, M.C.: The rootstock effect on the tomato salinity response depends on the shoot genotype. — Plant Sci. 162: 825–831, 2002.
Scheible, W.R., González-Fontes, A., Marianne, L., Müller-Röber, B., Caboche, M., Stitt, M.: Nitrate acts as a signal to induce organic acid metabolism and repress starch metabolism in tobacco. — Plant Cell 9: 783–798, 1997.
Sheng, Y.M., Shi, D.C., Xiao, H.X., Xu, Y.: The effect on growth of sunflower to mixed salts with various natural and alkaline. — J. Northeast Normal Univ. 4: 65–69, 1999.
Shi, D.C., Yin, L.J.: Strain responses in Na2CO3-stressed Leymus chinensis seedlings and their mathematical analysis. — Acta Bot. Sin. 34: 386–393, 1992.
Shi, D.C., Yin, L.J.: Difference between salt (NaCl) and alkaline (Na2CO3) stresses on Puccinellia tenuiflora (Griseb.) Scribn. et Merr. plants. — Acta Bot. Sin. 35: 144–149, 1993.
Shi, D.C., Zhao, K.F.: Effects of NaCl and Na2CO3 on growth of Puccinellia tenuiflora and on present state of mineral elements in nutrient solution. — Acta Pratacu. Sin. 6: 51–61, 1997.
Shi, D.C., Yin, S.J, Yang, G.H., Zhao, K.F.: Citric acid accumulation in an alkali-tolerant plant Puccinellia tenuiflora under alkaline stress. — Acta Bot. Sin. 44: 537–540, 2002.
Shi, D.C., Sheng, Y.M.: Effect of various salt-alkaline mixed stress conditions on sunflower seedlings and analysis of their stress factors. — Environ. Exp. Bot. 54: 8–21, 2005.
Shi, D.C., Wang, D.L.: Effects of various salt-alkali mixed stresses on Aneurolepidium chinense (Trin.) Kitag. — Plant Soil. 271: 15–26, 2005.
Sultana, N., Ikeda, T., Itoh R.: Effect of NaCl salinity on photosynthesis and dry matter accumulation in developing rice grains. — Environ. Exp. Bot. 42: 211–220, 1999.
Tian, J.C., Wang X.C., Liu G.T.: The coupling and regulation between photosynthesis and nitrogen, carbon metabolism in plant. — Chin. Bull. Life Sci. 13: 145–147, 2001.
Thompson, D.I., Edwards, T.J., Van Staden, J.: A novel dual-phase culture medium promotes germination and seedling establishment from immature embryos in South African Disa (Orchidaceae) Species. — Plant Growth Regul. 53: 163–171, 2007.
Wang, B.S., Zhao, K.F.: Comparison of extractive methods of Na+ and K+ in wheat leaves. — Plant Physiol. Commun. 31: 50–52, 1995.
Wei, Y., Xu, X.., Tao, H., Wang, P.: Growth performance and physiological response in the halophyte Lycium barbarum grown at salt-affected soil. — Ann. Appl. Biol. 149: 263–269, 2006.
Xie, D.Y., Wang, H.P., Wang, F.X., Feng, F.Q.: Effects of cotton seeds germaination and seedling growth under salt stress. — Chin. Cotton 27: 12–13, 2000.
Yang, C.W., Li, C.Y., Zhang, M.L., Liu, J., Ju, M., Shi, D.C., Wang, D.L.: pH and ion balance in wheat-wheatgrass under salt- or alkali stress. — Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 19: 1000–1005, 2007a.
Yang, C.W., Chong, J.N., Li, C.Y., Kim, C.M., Shi, D.C., Wang, D.L.: Osmotic adjustment and ion balance traits of an alkali resistant halophyte Kochia sieversiana during adaptation to salt and alkali conditions. — Plant Soil 294: 263–276, 2007b.
Yang, C.W., Wang, P., Li, C.Y., Shi, D.C., Wang, D.L.: Comparison of effects of salt and alkali stresses on the growth and photosynthesis of wheat. — Photosynthetica 46: 107–114, 2008a.
Yang, C.W., Jianaer., A., Li, C.Y., Shi, D.C., Wang, D.L.: Comparison of the effects of salt-stress and alkali-stress on photosynthesis and energy storage of an alkali-resistant halophyte Chloris virgata. — Photosynthetica. 46: 273–278, 2008b.
Yang, C.W., Shi, D.C., Wang, D.L.: Comparative effects of salt and alkali stresses on growth, osmotic adjustment and ionic balance of an alkali-resistant halophyte suaeda glauca (Bge.). — Plant Growth Regul. 56: 179–190, 2008c.
Yang, C.-W., Zhang, M.-L., Liu, J., Shi, D.-C., Wang, D.-L.: Effects of buffer capacity on growth, photosynthesis, and solute accumulation of a glycophyte (wheat) and a halophyte (Chloris virgata). — Photosynthetica 47: 55–60, 2009.
Ye, W.W., Liu, J.D.: Effects of NaCl and food grade salt on germination of seed of cotton. — Chin. Cotton 21: 14–15, 1994.
Zhang, J.L., Cheng, Y.S., Wu, J.L., Wang, D., Quan, D.L., Zhang, G.B.: Physiological responses and salt-tolerance of sunflower (Helianthus annus) under salt stress injury. — Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 25: 45–49, 2003.
Zhu, G. L., Deng, X.W., Zuo, W.N.: Determination of free proline in plants. Plant — Physiol. Commun. 1: 35–37, 1983.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30671491). We thank International Science Editing (ISE) from Ireland for language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Guo, W.Q. & Shi, D.C. Seed germination, seedling survival, and physiological response of sunflowers under saline and alkaline conditions. Photosynthetica 48, 278–286 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-010-0034-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-010-0034-3