Abstract
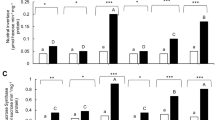
We studied the effects of 15-months of elevated (700 µmol mol−1) CO2 concentration (EC) on the CO2 assimilation rate, saccharide content, and the activity of key enzymes in the regulation of saccharide metabolism (glycolysis and gluconeogenesis) of four C3 perennial temperate grassland species, the dicots Filipendula vulgaris and Salvia nemorosa and the monocots Festuca rupicola and Dactylis glomerata. The acclimation of photosynthesis to EC was downward in F. rupicola and D. glomerata whereas it was upward in F. vulgaris and S. nemorosa. At EC, F. rupicola and F. vulgaris leaves accumulated starch while soluble sugar contents were higher in F. vulgaris and D. glomerata. EC decreased pyrophosphate-D-fructose-6-phosphate l-phosphotransferase (PFP, EC 2.7.1.90) activity assayed with Fru-2,6-P2 in F. vulgaris and D. glomerata and increased it in F. rupicola and S. nemorosa. Growth in EC decreased phosphofructokinase (PFK, EC 2.7.1.11) activity in all four species, the decrease being smallest in S. nemorosa and greatest in F. rupicola. With Fru-2,6-P2 in the assay medium, EC increased the PFP/PFK ratio, except in F. vulgaris. Cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Fru-1,6-P2ase, EC 3.1.3.11) was inhibited by EC, the effect being greatest in F. vulgaris and smallest in F. rupicola. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH EC 1.1.1.49) activity was decreased by growth EC in the four species. Activity ratios of Fru-1,6-P2ase to PFP and PFK suggest that EC may shift sugar metabolism towards glycolysis in the dicots.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
ambient CO2 concentration
- EC:
-
elevated CO2 concentration
- Fru-6-P:
-
fructose-6-phosphate
- Fru-1,6-P2 :
-
fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
- Fru-1,6-P2ase:
-
fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
- Fru-2,6-P2 :
-
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
- G6PDH:
-
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- OPPP:
-
oxidative pentose phosphate pathway
- P N :
-
net photosynthetic rate
- PFP:
-
pyrophosphate-D-fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase
- PFK:
-
phosphofructokinase
- PPFD:
-
photosynthetic photon flux density
- PPi:
-
pyrophosphate
- RuBPCO:
-
ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
References
Arp, W.J., Drake, B.G.: Increased photosynthetic capacity of Scirpus olneyi after 4 years of exposure to elevated CO2.-Plant Cell Environ. 14: 1003–1006, 1991.
Azcón-Bieto, J.: Inhibition of photosynthesis by carbohydrates in wheat leaves.-Plant Physiol. 73: 681–686, 1983.
Bassirirad, H., Tissue, D.T., Reynolds, J.F., Chapin, F.S.: Response of Eriophorum vaginatum to CO2 enrichment at different soil temperatures: Effects on growth, root respiration and PO4 3− uptake kinetics.-New Phytol. 133: 423–430, 1996.
Bowes, G., Vu, J.C.V., Hussain, M.W., Pennanen, A.H., Allen, L.H., Jr.: An overview of how rubisco and carbohydrate-metabolism may be regulated at elevated atmospheric [CO2] and temperature.-Agr. Food Sci. Finland 5: 261–270, 1996.
Bradford, M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein using the principle of protein dye binding.-Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–256, 1976.
Caemmerer, S. von, Farquhar, G.D.: Some relationships between the biochemistry of photosynthesis and the gas exchange of leaves.-Planta 153: 367–387, 1981.
Carnal, N.W., Black, C.C.: Phosphofructokinase activities in photosynthetic organisms. The occurrence of pyrophosphate-dependent 6-phosphofructokinase in plants and algae.-Plant Physiol. 71: 150–155, 1983.
Ceulemans, R., Mousseau, M.: Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on woody plants.-New Phytol. 127: 425–446, 1994.
Chen, Z.H., Walker, R.P., Acheson, R.M., Tecsi, L.I., Wingler, A., Lea, P.J., Leegood, R.C.: Are isocitrate lyase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase involved in gluconeogenesis during senescence of barley leaves and cucumber cotyledons?-Plant Cell Physiol. 41: 960–967, 2000.
Cheng, S.H., Moore, B.D., Seemann, J.R.: Effects of short-and long-term elevated CO2 on the expression of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase genes and carbohydrate accumulation in leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh.-Plant Physiol. 116: 715–723, 1998.
Cséke, C., Balogh, A., Wong, J.H., Buchanan, B.B., Stitt, M., Herzog, B., Heldt, H.W.: Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: a regulator of carbon processing in leaves.-Trends biochem. Sci. 12: 533–535, 1984.
Cséke, C., Weeden, N.F., Buchanan, B.B., Uyeda, K.: A special fructose bisphosphate functions as a cytoplasmic regulatory metabolite in green leaves.-Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 79: 4322–4326, 1982.
Dubois, M., Giles, K.A., Hamilton, J.K., Rebers, P.A., Smith, F.: Colorimetric method for determination of sugar and related substances.-Anal. Chem. 28: 350–356, 1956.
Geiger, M., Haake, V., Ludewig, F., Sonnewald, U., Stitt, M.: The nitrate and ammonium nitrate supply have a major influence on the response of photosynthesis, carbon metabolism, nitrogen metabolism and growth to elevated carbon dioxide in tobacco.-Plant Cell Environ. 22: 1177–1199, 1999.
Gesch, R.W., Vu, J.C.V., Boote, K.J., Allen, L.H., Bowes, G.: Sucrose-phosphate synthase activity in mature rice leaves following changes in growth CO2 is unrelated to sucrose pool size.-New Phytol. 154: 77–84, 2002.
Hajirezaei, M., Sonnewald, U., Viola, R., Carlisle, S., Dennins, D.T., Stitt, M.: Transgenic potato plants with strongly decreased expression of pyrophosphate:fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase show no visible phenotype and only minor changes in metabolic fluxes in their tubers.-Planta 192: 16–30, 1994.
Hauschild, R., Schaewen, A. von: Differential regulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase isoenzyme activities in potato.-Plant Physiol. 133: 47–62, 2003.
Hussain, M.W., Allen, L.H., Jr., Bowes, G.: Up-regulation of sucrose phosphate synthase in rice grown under elevated CO2 and temperature.-Photosynth. Res. 60: 199–208, 1999.
Jarvis, P.G.: Global change and plant water relations.-In: Borghetti, M., Grace, J., Raschi, A. (ed.): Water Transport in Plants Under Climatic Stress. Pp. 1–13. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1993.
Körner, C., Miglietta, F.: Long term effects of naturally elevated CO2 on mediterranean grassland and forest trees.-Oecologia 99: 343–351, 1994.
Krapp, A., Hofmann, B., Schäfer, C., Stitt, M.: Regulation of the expression of rbcS and other photosynthetic genes by carbohydrates: a mechanism for the “sink regulation” of photosynthesis?-Plant J. 3: 817–828, 1993.
Krapp, A., Stitt, M.: Influence of high carbohydrate content on the activity of plastidic and cytosolic isoenzyme pairs in photosynthetic tissues.-Plant Cell Environ. 17: 861–866, 1994.
Lea, P.J., Chen, Z.H., Leegood, R.C., Walker, R.P.: Does phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase have a role in both amino acid and carbohydrate metabolism?-Amino Acids 20: 225–241, 2001.
McCready, R.M., Guggolz, J., Silviera, V., Owens, H.S.: Determination of starch and amylase in vegetables.-Anal. Chem. 22: 1156–1158, 1950.
Nádas, E., Balogh, Á., Kiss, F., Nagy, Z., Szente, K., Tuba, Z.: Some aspects of carbohydrate metabolism in two C3 grassland species under elevated CO2.-Abstr. bot. 21: 323–328, 1997.
Nakano, H., Makino, A., Mae, T.: The effect of elevated partial pressures of CO2 on the relationship between photosynthetic capacity and N content in rice leaves.-Plant Physiol. 115: 191–198, 1997.
Newton, P.C.D.: Direct effects of increasing carbon dioxide on pasture plants and communities.-N. Zeal. J. agr. Res. 34: 1–24, 1991.
Paul, M., Sonnewald, U., Hajirezaei, M., Dennis, D., Stitt, M.: Transgenic potato plants with strongly decreased expression of pyrophosphate: Fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase do not differ significantly from wild type in photosynthate partitioning, plant growth of their ability to cope with limiting phosphate, limiting nitrogen and suboptimal temperatures.-Planta 196: 277–283, 1995.
Peet, M.M., Huber, S.C., Patterson, D.T.: Acclimation to high CO2 in monoecious cucumbers. II. Carbon exchange rates, enzyme activities, and starch and nutrient concentrations.-Plant Physiol. 80: 63–67, 1986.
ap Rees, T.: Hexose phosphate metabolism by non-photosynthetic tissues of higher plants.-In: Preiss, J. (ed.): The Biochemistry of Plants. Pp. 1–33. Academic Press, New York 1988.
Sage, R.F., Sharkey, T.D., Seemann, J.R.: Acclimation of photosynthesis to elevated CO2 in five C3 species.-Plant Physiol. 89: 590–596, 1989.
Seneweera, S.P., Basra, A.S., Barlow, E.W., Conroy, J.P.: Diurnal regulation of leaf blade elongation in rice by CO2. Is it related to sucrose-phosphate synthase activity?-Plant Physiol. 108: 1471–1477, 1995.
Spilatro, R.S., Anderson, J.M.: Carbohydrate metabolism and activity of pyrophosphate: Fructose-6-phosphate phosphotransferase in photosynthetic soybean (Glycine max Merr.) suspension cells.-Plant Physiol. 88: 862–868, 1988.
Stitt, M.: Fine control of sucrose synthesis by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate.-In: Heath, R.L., Preiss, J. (ed.): Regulation of Carbohydrate Partitioning in Photosynthetic Tissue. Pp. 109–126. American Society of Plabnt Physiologists, Rockville 1985.
Stitt, M.: Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate as a regulatory molecule in plants.-Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol. 41: 153–185, 1990.
Stitt, M.: Rising CO2 levels and their potential significance for carbon flow in photosynthetic cells.-Plant Cell Environ. 14: 741–762, 1991.
Stitt, M.: Enhanced CO2, photosynthesis and growth; what should we measure to gain a better understanding of the plant’s response?-In: Schulze, E.D., Mooney, H.A. (ed.): Design and Execution of Experiments on CO2 Enrichment. Pp. 3–28. ECSC-EEC-EAEC, Brussels-Luxembourg 1993.
Stitt, M., Schaewen, A. von, Willmitzer, L.: “Sink” regulation of photosynthetic metabolism in transgenic tobacco plants expressing yeast invertase in their cell wall involves a decrease of the Calvin-cycle enzymes and an increase of glycolytic-enzymes.-Planta 183: 40–50, 1991.
Theodorou, M.E., Kruger, N.J.: Physiological relevance of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the regulation of spinach leaf pyrophosphate: fructose 6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase.-Planta 213: 147–157, 2001.
Theodorou, M.E., Plaxton, W.C.: Induction of pyrophosphate-dependent phosphofructokinase by phosphate starvation in seedlings of Brassica nigra.-Plant Cell Environ. 17: 287–294, 1994.
Tuba, Z., Szente, K., Nagy, Z., Csintalan, Z., Koch, J.: Responses of CO2 assimilation, transpiration and water use efficiency to long-term elevated CO2 in perennial C3 xeric loess steppe species.-J. Plant Physiol. 148: 356–361, 1996.
Uyeda, K.E., Furuya, C.R.: Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate.-Trends biochem. Sci. 7: 329–331, 1982.
van Oosten, J.-J., Afif, D., Dizengremel, P.: Long-term effects of a CO2 enriched atmosphere on enzymes of the primary carbon metabolism of spruce trees.-Plant Physiol. Biochem. 30: 541–547, 1992.
Vu, J.C.V., Gesch, R.W., Pennanen, A.H., Allen, L.H., Boote, K.J., Bowes, G.: Soyabean photosynthesis, Rubisco, and carbohydrate enzymes function at supraoptimal temperatures in elevated CO2.-J. Plant Physiol. 158: 295–307, 2001.
Widodo, W., Vu, J.C.V., Boote, K.J., Baker, J.T., Allen, L.H., Jr.: Elevated growth CO2 delays drought stress and accelerates recovery of rice leaf photosynthesis.-Environ. exp. Bot. 49: 259–272, 2003.
Wong, J.H., Kang, T., Buchanan, B.B.: A novel PFP (pyrophosphate fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase) from carrot roots. Relations to PFK from the same source.-FEBS Lett. 238: 405–410, 1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nádas, E., Balogh, Á., Kiss, F. et al. Role of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, fructose phosphotransferase, and phosphofructokinase in saccharide metabolism of four C3 grassland species under elevated CO2 . Photosynthetica 46, 255–261 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-008-0042-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-008-0042-8