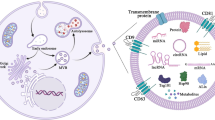
Abstract
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs, “exosomes”) in milk have attracted considerable attention for use in delivering therapeutics to diseased tissues because of the following qualities. The production of milk sEVs is scalable, e.g., more than 1021 sEVs may be obtained annually from a single cow. Milk EVs protect their cargo against degradation in the gastrointestinal tract and during industrial processing. Milk sEVs and their cargo are absorbed following oral administration and they cross barriers such as intestinal mucosa, placenta and the blood–brain barrier in humans, pigs, and mice. Milk sEVs do no alter variables of liver and kidney function, or hematology, and do not elicit immune responses in humans, rats, and mice. Protocols are available for loading milk sEVs with therapeutic cargo, and a cell line is available for assessing effects of milk sEV modifications on drug delivery. Future research will need to assess and optimize sEV shelf-life and storage and effects of milk sEV modifications on the delivery of therapeutic cargo to diseased tissues.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESCRT:
-
Endosomal complex required for transport
- EV:
-
Extracellular vesicle
- MVB:
-
Multivesicular body
- sEV:
-
Small EV
References
Gyorgy B, Szabo TG, Pasztoi M, Pal Z, Misjak P, Aradi B, et al. Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(16):2667–88.
O’Brien K, Breyne K, Ughetto S, Laurent LC, Breakefield XO. RNA delivery by extracellular vesicles in mammalian cells and its applications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(10):585–606.
Rai A, Greening DW, Xu R, Chen M, Suwakulsiri W, Simpson RJ. Secreted midbody remnants are a class of extracellular vesicles molecularly distinct from exosomes and microparticles. Commun Biol. 2021;4(1):400.
Zhang H, Freitas D, Kim HS, Fabijanic K, Li Z, Chen H, et al. Identification of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(3):332–43.
Gurung S, Perocheau D, Touramanidou L, Baruteau J. The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun Signal. 2021;19(1):47.
Ngu A, Wang S, Wang H, Khanam A, Zempleni J. Milk exosomes in nutrition and drug delivery. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022;322(5):C865–74.
Hurley JH. ESCRT complexes and the biogenesis of multivesicular bodies. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20(1):4–11.
Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, Rajendran L, Wenzel D, Wieland F, et al. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science. 2008;319(5867):1244–7.
Villarroya-Beltri C, Gutierrez-Vazquez C, Sanchez-Cabo F, Perez-Hernandez D, Vazquez J, Martin-Cofreces N, et al. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2980.
Shurtleff MJ, Temoche-Diaz MM, Karfilis KV, Ri S, Schekman R. Y-box protein 1 is required to sort microRNAs into exosomes in cells and in a cell-free reaction. eLife. 2016;5:e19276.
Liu XM, Ma L, Schekman R. Selective sorting of microRNAs into exosomes by phase-separated YBX1 condensates. Elife. 2021;10: e71982.
Garcia-Martin R, Wang G, Brandao BB, Zanotto TM, Shah S, Kumar Patel S, et al. MicroRNA sequence codes for small extracellular vesicle release and cellular retention. Nature. 2021;(in press).
Takahashi A, Okada R, Nagao K, Kawamata Y, Hanyu A, Yoshimoto S, et al. Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15287.
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373–83.
Purushothaman A, Bandari SK, Liu J, Mobley JA, Brown EE, Sanderson RD. Fibronectin on the surface of myeloma cell-derived exosomes mediates exosome-cell interactions. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(4):1652–63.
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654–9.
Thery C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750.
Leiferman A, Shu J, Upadhyaya B, Cui J, Zempleni J. Storage of extracellular vesicles in human milk, and microRNA profiles in human milk exosomes and infant formulas. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2019;69(2):235–8.
Sukreet S, Pereira Braga C, An TT, Adamec J, Cui J, B. T, et al. Isolation of extracellular vesicles from byproducts of cheese making by tangential flow filtration yields heterogeneous fractions of nanoparticles. J Dairy Sci. 2021;104:9478–93.
Mecocci S, Pietrucci D, Milanesi M, Pascucci L, Filippi S, Rosato V, et al. Transcriptomic characterization of cow, donkey and goat milk extracellular vesicles reveals their anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory potential. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(23).
Santos-Coquillat A, Gonzalez MI, Clemente-Moragon A, Gonzalez-Arjona M, Albaladejo-Garcia V, Peinado H, et al. Goat milk exosomes as natural nanoparticles for detecting inflammatory processes by optical imaging. Small. 2022;18(6): e2105421.
Statista, Inc. Milk produced per cow in the United States from 1999 to 2020 (in pounds) [Internet]. 2021 [cited 5/24/2021]. Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/194935/quantity-of-milk-produced-per-cow-in-the-us-since-1999/.
Marsh SR, Pridham KJ, Jourdan J, Gourdie RG. Novel protocols for scalable production of high quality purified small extracellular vesicles from bovine milk. Nanotheranostics. 2021;5(4):488–98.
Izumi H, Kosaka N, Shimizu T, Sekine K, Ochiya T, Takase M. Bovine milk contains microRNA and messenger RNA that are stable under degradative conditions. J Dairy Sci. 2012;95(9):4831–41.
Ibuki F, Mori T, Matsushita S, Hata T. Ribonuclease in bovine milk. Agr Biol Chem. 1965;29(7):635–40.
Barker R, Abrahamsson B, Kruusmagi M. Application and validation of an advanced gastrointestinal in vitro model for the evaluation of drug product performance in pharmaceutical development. J Pharm Sci. 2014;103(11):3704–12.
Howard KM, Jati Kusuma R, Baier SR, Friemel T, Markham L, Vanamala J, et al. Loss of miRNAs during processing and storage of cow’s (Bos taurus) milk. J Agric Food Chem. 2015;63(2):588–92.
Baier SR, Nguyen C, Xie F, Wood JR, Zempleni J. MicroRNAs are absorbed in biologically meaningful amounts from nutritionally relevant doses of cow’s milk and affect gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, HEK-293 kidney cell cultures, and mouse livers. J Nutr. 2014;144:1495–500.
Wolf T, Baier SR, Zempleni J. The intestinal transport of bovine milk exosomes is mediated by endocytosis in human colon carcinoma caco-2 cells and rat small intestinal IEC-6 cells. J Nutr. 2015;145:2201–6.
Manca S, Upadhyaya B, Mutai E, Desaulniers AT, Cederberg RA, White BR, et al. Milk exosomes are bioavailable and distinct microRNA cargos have unique tissue distribution patterns. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):11321.
Sadri M, Shu J, Kachman SD, Cui J, Zempleni J. Milk exosomes and microRNAs cross the placenta and promote embryo survival in mice. Reproduction. 2020;160:501–9.
Zhou F, Ebea P, Mutai E, Wang H, S. S, Navazesh SE, et al. Small extracellular vesicles in milk cross the blood-brain barrier in murine cerebral cortex endothelial cells and promote dendritic complexity in the hippocampus and brain function in C57BL/6J mice. Front Nutr. 2022;9:838543.
Munagala R, Aqil F, Jeyabalan J, Gupta RC. Bovine milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2016;371(1):48–61.
Leiferman A, Shu J, Grove R, Cui J, Adamec J, Zempleni J. A diet defined by its content of bovine milk exosomes and their RNA cargos has moderate effects on gene expression, amino acid profiles and grip strength in skeletal muscle in C57BL/6 mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2018;59:123–8.
Sukreet S, Pereira Braga C, An TT, J. A, Cui J, Zempleni J. Ultrasonication of milk decreases the content of exosomes and microRNAs in an exosome-defined rodent diet. J Nutr. 2022;152:961–70.
Mutai E, Ramer-Tait AE, Zempleni J. MicroRNAs in bovine milk exosomes are bioavailable in humans but do not elicit a robust pro-inflammatory cytokine response. BMC exRNA. 2020;2:2.
Sterzenbach U, Putz U, Low LH, Silke J, Tan SS, Howitt J. Engineered exosomes as vehicles for biologically active proteins. Mol Ther. 2017;25:1269–78.
Agrawal AK, Aqil F, Jeyabalan J, Spencer WA, Beck J, Gachuki BW, et al. Milk-derived exosomes for oral delivery of paclitaxel. Nanomedicine. 2017;13(5):1627–36.
Gee P, Lung MSY, Okuzaki Y, Sasakawa N, Iguchi T, Makita Y, et al. Extracellular nanovesicles for packaging of CRISPR-Cas9 protein and sgRNA to induce therapeutic exon skipping. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1334.
Kang RH, Jang JE, Huh E, Kang SJ, Ahn DR, Kang JS, et al. A brain tumor-homing tetra-peptide delivers a nano-therapeutic for more effective treatment of a mouse model of glioblastoma. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020;5(8):1213–25.
Liu Y, Li D, Liu Z, Zhou Y, Chu D, Li X, et al. Targeted exosome-mediated delivery of opioid receptor Mu siRNA for the treatment of morphine relapse. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17543.
Zhou Y, Yuan Y, Liu M, Hu X, Ouan Y, Chen X. Tumor-specific delivery of KRAS siRNA with iRGD-exoxomes efficiently inhibits tumor grwoth. BMC exRNA. 2019;1:28.
Kamerkar S, LeBleu VS, Sugimoto H, Yang S, Ruivo CF, Melo SA, et al. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2017;546(7659):498–503.
Mendt M, Kamerkar S, Sugimoto H, McAndrews KM, Wu CC, Gagea M, et al. Generation and testing of clinical-grade exosomes for pancreatic cancer. JCI Insight. 2018;3(8): e99263.
Hashizume H, Baluk P, Morikawa S, McLean JW, Thurston G, Roberge S, et al. Openings between defective endothelial cells explain tumor vessel leakiness. Am J Pathol. 2000;156(4):1363–80.
Grossen P, Portmann M, Koller E, Duschmale M, Minz T, Sewing S, et al. Evaluation of bovine milk extracellular vesicles for the delivery of locked nucleic acid antisense oligonucleotides. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021.
Huynh HT, Robitaille G, Turner JD. Establishment of bovine mammary epithelial cells (MAC-T): an in vitro model for bovine lactation. Exp Cell Res. 1991;197(2):191–9.
Alsaweed M, Lai CT, Hartmann PE, Geddes DT, Kakulas F. Human milk miRNAs primarily originate from the mammary gland resulting in unique miRNA profiles of fractionated milk. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20680.
Le Guillou S, Leduc A, Laubier J, Barbey S, Rossignol MN, Lefebvre R, et al. Characterization of Holstein and Normande whole milk miRNomes highlights breed specificities. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):20345.
Ogunnaike M, Wang H, Zempleni J. Bovine mammary alveolar MAC-T cells afford a tool for studies of bovine milk exosomes in drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2021;15(610): 121263.
Wang H, Wu D, Sukreet S, Delaney A, Belfort MB, J. Z. Quantitation of exosomes and their microRNA cargos in frozen human milk. JPGN Reports. 2022;3(1):e172.
Wijenayake S, Eisha S, Tawhidi Z, Pitino MA, Steele MA, Fleming AS, et al. Comparison of methods for pre-processing, exosome isolation, and RNA extraction in unpasteurized bovine and human milk. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(9): e0257633.
Pullan J, Dailey K, Bhallamudi S, Feng L, Alhalhooly L, Froberg J, et al. Modified bovine milk exosomes for doxorubicin delivery to triple-negative breast cancer cells. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022;5(5):2163–75.
Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, Betts C, Lakhal S, Wood MJ. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(4):341–5.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (P20GM104320 and OD028749), the National Institute of Food and Agriculture (2016–67001-25301, 2020–67017-30834, and 2022–67021-36407), the U.S. Department of Agriculture (Hatch, and W-4002) and the SynGAP Research Fund (all to J. Zempleni).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J. Zempleni wrote the draft version and final manuscript and prepared the figures. J. Munir, Alice Ngu, H. Wang, and Denise M. O. Ramirez have revised the draft version critically for important intellectual content. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript, and have agreed to be accountable for all aspects of this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
J. Zempleni is a consultant for PureTech Health, Inc. (Boston, MA). The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Munir, J., Ngu, A., Wang, H. et al. Review: Milk Small Extracellular Vesicles for Use in the Delivery of Therapeutics. Pharm Res 40, 909–915 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03404-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03404-w