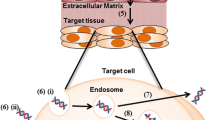
Abstract
Gene therapy is one of the most widely studied treatments and has the potential to treat a variety of intractable diseases. The skin's limited permeability, as the body's initial protective barrier, drastically inhibits the delivery effect of gene medicine. Given the potential adverse effects and physicochemical features of the medications, improving generic drug penetration into the skin barrier and achieving an effective level of target tissues remains a challenge. Microneedles have made tremendous improvements in aided gene transfer and medication delivery as a unique method. Microneedles offer the advantage of being minimally invasive and painless, as well as the ability to distribute gene medicines straight through the stratum corneum. Microneedles have been used to penetrate skin tissue with various nucleic acids and medicines in recent years, allowing for a wide range of applications in the treatment of skin ailments. This review focuses on skin-related disorders and immunity, and it primarily discusses the progress of microneedle transdermal gene therapy in recent years. It also complements the current major vectors and related microneedle gene therapy applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mostafavi Yazdi SJ, Baqersad J. Mechanical modeling and characterization of human skin: A review. J Biomech. 2022;130: 110864.
Ain QU, Campos EVR, Huynh A, Witzigmann D, Hedtrich S. Gene Delivery to the Skin - How Far Have We Come? Trends Biotechnol. 2021;39(5):474–87.
Berdyshev E, Bronova I, Leung DYM, Goleva E. Methodological Considerations for Lipid and Polar Component Analyses in Human Skin Stratum Corneum. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021;79(3):659–68.
Gawronska-Kozak B. Foxn1 Control of Skin Function. Appl Sci. 2020;10(16):5685.
Tavakoli S, Klar AS. Advanced Hydrogels as Wound Dressings Biomolecules. 2020;10(8):1169.
Rasmont V, Valois A, Gueniche A, Sore G, Kerob D, Nielsen M, et al. Vichy volcanic mineralizing water has unique properties to strengthen the skin barrier and skin defenses against exposome aggressions. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36(Suppl 2):5–15.
Mariath LM, Santin JT, Schuler-Faccini L, Kiszewski AE. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: update on the clinical and genetic aspects. An Bras Dermatol. 2020;95(5):551–69.
Has C, Bauer JW, Bodemer C, Bolling MC, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Diem A, et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183(4):614–27.
Li Y, Kong Q, Yue J, Gou X, Xu M, Wu X. Genome-edited skin epidermal stem cells protect mice from cocaine-seeking behaviour and cocaine overdose. Nat Biomed Eng. 2019;3(2):105–13.
Sand FL, Thomsen SF. Skin diseases of the vulva: Infectious diseases. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;37(7):840–8.
Ma CC, Wang ZL, Xu T, He ZY, Wei YQ. The approved gene therapy drugs worldwide: from 1998 to 2019. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;40: 107502.
Choate KA, Kinsella TM, Williams ML, Nolan GP, Khavari PA. Transglutaminase 1 delivery to lamellar ichthyosis keratinocytes. Hum Gene Ther. 1996;7(18):2247–53.
Kovacik A, Kopecna M, Vavrova K. Permeation enhancers in transdermal drug delivery: benefits and limitations. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020;17(2):145–55.
Jiang T, Xu G, Chen G, Zheng Y, He B, Gu Z. Progress in transdermal drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. Nano Res. 2020;13(7):1810–24.
Yadavar-Nikravesh M-S, Ahmadi S, Milani A, Akbarzadeh I, Khoobi M, Vahabpour R, et al. Construction and characterization of a novel Tenofovir-loaded PEGylated niosome conjugated with TAT peptide for evaluation of its cytotoxicity and anti-HIV effects. Adv Powder Technol. 2021;32(9):3161–73.
Jiang T, Ma S, Shen Y, Li Y, Pan R, Xing H. Topical anesthetic and pain relief using penetration enhancer and transcriptional transactivator peptide multi-decorated nanostructured lipid carriers. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):478–86.
A N, Kovooru L, Behera AK, Kumar KPP, Srivastava P. A critical review of synthesis procedures, applications and future potential of nanoemulsions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2021;287:102318.
Simon J, Jouanmiqueou B, Rols M-P, Flahaut E, Golzio M. Transdermal Delivery of Macromolecules Using Two-in-One Nanocomposite Device for Skin Electroporation. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(11):1805.
Zhang X, Chen G, Liu Y, Sun L, Sun L, Zhao Y. Black phosphorus-loaded separable microneedles as responsive oxygen delivery carriers for wound healing. ACS Nano. 2020;14(5):5901–8.
Zhi D, Yang T, Zhang T, Yang M, Zhang S, Donnelly RF. Microneedles for gene and drug delivery in skin cancer therapy. J Control Release. 2021;335:158–77.
Duarah S, Sharma M, Wen J. Recent advances in microneedle-based drug delivery: Special emphasis on its use in paediatric population. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019;136:48–69.
Jung JH, Jin SG. Microneedle for transdermal drug delivery: current trends and fabrication. J Pharm Investig. 2021:1–15.
Zhang Y, Feng P, Yu J, Yang J, Zhao J, Wang J, et al. ROS-responsive microneedle patch for acne vulgaris treatment. Advanced Therapeutics. 2018;1(3):1800035.
Qin M, Du G, Sun X. Recent advances in the noninvasive delivery of mRNA. Acc Chem Res. 2021;54(23):4262–71.
Tavernier G, Wolfrum K, Demeester J, De Smedt SC, Adjaye J, Rejman J. Activation of pluripotency-associated genes in mouse embryonic fibroblasts by non-viral transfection with in vitro-derived mRNAs encoding Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and cMyc. Biomaterials. 2012;33(2):412–7.
Mastrobattista E, Hennink WE, Schiffelers RM. Delivery of nucleic acids. Pharm Res. 2007;24(8):1561–3.
Golombek S, Pilz M, Steinle H, Kochba E, Levin Y, Lunter D, et al. Intradermal delivery of synthetic mRNA using hollow microneedles for efficient and rapid production of exogenous proteins in skin. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids. 2018;11:382–92.
Koh KJ, Liu Y, Lim SH, Loh XJ, Kang L, Lim CY, et al. Formulation, characterization and evaluation of mRNA-loaded dissolvable polymeric microneedles (RNApatch). Scientific Reports. 2018;8(1).
Dul M, Stefanidou M, Porta P, Serve J, O’Mahony C, Malissen B, et al. Hydrodynamic gene delivery in human skin using a hollow microneedle device. J Control Release. 2017;265:120–31.
Wang M, Han Y, Yu X, Liang L, Chang H, Yeo DC, et al. Upconversion nanoparticle powered microneedle patches for transdermal delivery of siRNA. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(2): e1900635.
Wang Z, Luan J, Seth A, Liu L, You M, Gupta P, et al. Microneedle patch for the ultrasensitive quantification of protein biomarkers in interstitial fluid. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021;5(1):64–76.
Li J, Lu H, Wang Y, Yang S, Zhang Y, Wei W, et al. Interstitial fluid biomarkers’ minimally invasive monitoring using microneedle sensor arrays. Anal Chem. 2022;94(2):968–74.
Picanco-Castro V, Pereira CG, Covas DT, Porto GS, Athanassiadou A, Figueiredo ML. Emerging patent landscape for non-viral vectors used for gene therapy. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38(2):151–7.
Shi HP, Xue T, Yang Y, Jiang CY, Huang SX, Yang Q, et al. Microneedle-mediated gene delivery for the treatment of ischemic myocardial disease. Science Advances. 2020;6(25):eaaz3621.
Yiu G, Chung SH, Mollhoff IN, Nguyen UT, Thomasy SM, Yoo J, et al. Suprachoroidal and subretinal injections of AAV using transscleral microneedles for retinal gene delivery in nonhuman primates. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020;16:179–91.
Chung SH, Mollhoff IN, Mishra A, Sin TN, Ngo T, Ciulla T, et al. Host immune responses after suprachoroidal delivery of AAV8 in nonhuman primate eyes. Hum Gene Ther. 2021;32(13–14):682–93.
Hadianamrei R, Zhao X. Current state of the art in peptide-based gene delivery. J Control Release. 2022;343:600–19.
Cao X, Wang J, Deng W, Chen J, Wang Y, Zhou J, et al. Photoluminescent cationic carbon dots as efficient non-viral delivery of plasmid SOX9 and chondrogenesis of fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):7057.
Filipczak N, Pan J, Yalamarty SSK, Torchilin VP. Recent advancements in liposome technology. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;156:4–22.
Qiu Y, Guo L, Zhang S, Xu B, Gao Y, Hu Y, et al. DNA-based vaccination against hepatitis B virus using dissolving microneedle arrays adjuvanted by cationic liposomes and CpG ODN. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(7):2391–8.
Mohammadinejad R, Dehshahri A, Sagar Madamsetty V, Zahmatkeshan M, Tavakol S, Makvandi P, et al. In vivo gene delivery mediated by non-viral vectors for cancer therapy. J Control Release. 2020;325:249–75.
Tomono T. A new way to control the internal structure of microneedles: a case of chitosan lactate. Materials Today Chemistry. 2019;13:79–87.
Iqbal S, Zhao Z. Poly (beta amino esters) Copolymers: novel potential vectors for delivery of genes and related therapeutics. Int J Pharm. 2021:121289.
Qu M, Kim HJ, Zhou X, Wang C, Jiang X, Zhu J, et al. Biodegradable microneedle patch for transdermal gene delivery. Nanoscale. 2020;12(32):16724–9.
Pan J, Ruan W, Qin M, Long Y, Wan T, Yu K, et al. Intradermal delivery of STAT3 siRNA to treat melanoma via dissolving microneedles. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1117.
Li X, Xu Q, Wang J, Zhang P, Wang Y, Ji J. A gene-coated microneedle patch based on industrialized ultrasonic spraying technology with a polycation vector to improve antitumor efficacy. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(27):5528–36.
Doudna JA. The promise and challenge of therapeutic genome editing. Nature. 2020;578(7794):229–36.
Mavilio F, Ferrari S, Di Nunzio F, Maruggi G, Bonini C, Capurro S, et al. Correction of laminin-5-deficient junctional epidermolysis bullosa by transplantation of genetically modified epidermal stem cells. A Phase-I Clinical Trial Molecular Therapy. 2006;13:S280.
Zhu Y, Li Y, Bai B, Fang J, Zhang K, Yin X, et al. Construction of an attenuated goatpox virus AV41 strain by deleting the TK gene and ORF8-18. Antiviral Res. 2018;157:111–9.
Wan T, Pan Q, Ping Y. Microneedle-assisted genome editing: A transdermal strategy of targeting NLRP3 by CRISPR-Cas9 for synergistic therapy of inflammatory skin disorders. Science Advances. 2021;7(11): eabe2888.
Ruan W, Zhai Y, Yu K, Wu C, Xu Y. Coated microneedles mediated intradermal delivery of octaarginine/BRAF siRNA nanocomplexes for anti-melanoma treatment. Int J Pharm. 2018;553(1–2):298–309.
Ohn J, Jang M, Kang BM, Yang H, Hong JT, Kim KH, et al. Dissolving candlelit microneedle for chronic inflammatory skin diseases. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(14):2004873.
Zhang N, Zhou X, Liu L, Zhao L, Xie H, Yang Z. Dissolving polymer microneedles for transdermal delivery of insulin. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12: 719905.
Shi H, Zhou J, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Lin D, Lei L, et al. A rapid corneal healing microneedle for efficient ocular drug delivery. Small. 2021:2104657.
Garcia-Souto F, Lorente-Lavirgen AI, Bernabeu-Wittel J, Rojas C, Lorente R. Long-lasting contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis or psoriasis. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61(4):342–5.
Sevilla LM, Bigas J, Chiner-Oms A, Comas I, Sentandreu V, Perez P. Glucocorticoid-dependent transcription in skin requires epidermal expression of the glucocorticoid receptor and is modulated by the mineralocorticoid receptor. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):18954.
Ciazynska M, Bednarski IA, Wodz K, Narbutt J, Lesiak A. NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes as a new approach to skin carcinogenesis. Oncol Lett. 2020;19(3):1649–56.
Wang D, Duncan B, Li X, Shi J. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in infection-related, immune-mediated and autoimmune skin diseases. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;98(3):146–51.
Wu X, Huang H, Yu B, Zhang J. A blue light-inducible CRISPR-Cas9 system for inhibiting progression of melanoma cells. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7: 606593.
Yang CD, Chen YH, Huang HY, Huang HD, Tseng CP. CRP represses the CRISPR/Cas system in Escherichia coli: evidence that endogenous CRISPR spacers impede phage P1 replication. Mol Microbiol. 2014;92(5):1072–91.
Lan X, Zhu W, Huang X, Yu Y, Xiao H, Jin L, et al. Microneedles loaded with anti-PD-1-cisplatin nanoparticles for synergistic cancer immuno-chemotherapy. Nanoscale. 2020;12(36):18885–98.
Sajadimajd S, Bahramsoltani R, Iranpanah A, Kumar Patra J, Das G, Gouda S, et al. Advances on natural polyphenols as anticancer agents for skin cancer. Pharmacol Res. 2020;151: 104584.
Shaw FM, Weinstock MA. Comparing topical treatments for basal cell carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138(3):484–6.
Schadendorf D, van Akkooi ACJ, Berking C, Griewank KG, Gutzmer R, Hauschild A, et al. Melanoma. The Lancet. 2018;392(10151):971–84.
Kiyohara T, Nagano N, Miyamoto M, Shijimaya T, Nakamaru S, Makimura K, et al. BRAF-mutated, acral verrucous melanoma successfully treated by dabrafenib plus trametinib combination therapy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44(8):945–6.
Xue L, Yan Y, Kos P, Chen X, Siegwart DJ. PEI fluorination reduces toxicity and promotes liver-targeted siRNA delivery. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021;11(1):255–60.
Li X, Xu Q, Zhang P, Zhao X, Wang Y. Cutaneous microenvironment responsive microneedle patch for rapid gene release to treat subdermal tumor. J Control Release. 2019;314:72–80.
Amani H, Shahbazi MA, D’Amico C, Fontana F, Abbaszadeh S, Santos HA. Microneedles for painless transdermal immunotherapeutic applications. J Control Release. 2021;330:185–217.
Zhang S, Zhao S, Jin X, Wang B, Zhao G. Microneedles Improve the Immunogenicity of DNA Vaccines. Hum Gene Ther. 2018;29(9):1004–10.
McCaffrey J, Donnelly RF, McCarthy HO. Microneedles: an innovative platform for gene delivery. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2015;5(4):424–37.
Kim NW, Lee MS, Kim KR, Lee JE, Lee K, Park JS, et al. Polyplex-releasing microneedles for enhanced cutaneous delivery of DNA vaccine. J Control Release. 2014;179:11–7.
Cole G, McCaffrey J, Ali AA, McBride JW, McCrudden CM, Vincente-Perez EM, et al. Dissolving microneedles for DNA vaccination: Improving functionality via polymer characterization and RALA complexation. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017;13(1):50–62.
Duong HTT, Kim NW, Thambi T, Giang Phan VH, Lee MS, Yin Y, et al. Microneedle arrays coated with charge reversal pH-sensitive copolymers improve antigen presenting cells-homing DNA vaccine delivery and immune responses. J Control Release. 2018;269:225–34.
Leone M, Romeijn S, Slutter B, O’Mahony C, Kersten G, Bouwstra JA. Hyaluronan molecular weight: Effects on dissolution time of dissolving microneedles in the skin and on immunogenicity of antigen. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020;146: 105269.
Du G, Hathout RM, Nasr M, Nejadnik MR, Tu J, Koning RI, et al. Intradermal vaccination with hollow microneedles: A comparative study of various protein antigen and adjuvant encapsulated nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2017;266:109–18.
Ali AA, McCrudden CM, McCaffrey J, McBride JW, Cole G, Dunne NJ, et al. DNA vaccination for cervical cancer; a novel technology platform of RALA mediated gene delivery via polymeric microneedles. Nanomedicine. 2017;13(3):921–32.
Yan Q, Cheng Z, Liu H, Shan W, Cheng Z, Dai X, et al. Enhancement of Ag85B DNA vaccine immunogenicity against tuberculosis by dissolving microneedles in mice. Vaccine. 2018;36(30):4471–6.
Hu Y, Xu B, Xu J, Shou D, Liu E, Gao J, et al. Microneedle-assisted dendritic cell-targeted nanoparticles for transcutaneous DNA immunization. Polym Chem. 2015;6(3):373–9.
Inoue M, Lorenz M, Muto H, Wesch R, Hashimoto Y. Effect of a single dose of insulin glargine/lixisenatide fixed ratio combination (iGlarLixi) on postprandial glucodynamic response in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A phase I randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(8):2001–5.
Zhu S, Zhang B, Wang Y, He Y, Qian G, Deng L, et al. A bilayer microneedle for therapeutic peptide delivery towards the treatment of diabetes in db/db mice. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology. 2021;62: 102336.
Chen X, Yu H, Wang L, Shen D, Li C, Zhou W. Cross-linking-density-changeable microneedle patch prepared from a glucose-responsive hydrogel for insulin delivery. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(10):4870–82.
Hong C, Zhang G, Zhang W, Liu J, Zhang J, Chen Y, et al. Hair grows hair: Dual-effective hair regrowth through a hair enhanced dissolvable microneedle patch cooperated with the pure yellow light irradiation. Appl Mater Today. 2021;25: 101188.
Yang G, Chen Q, Wen D, Chen Z, Wang J, Chen G, et al. A therapeutic microneedle patch made from hair-derived keratin for promoting hair regrowth. ACS Nano. 2019;13(4):4354–60.
Cui M, Zheng M, Wiraja C, Chew SWT, Mishra A, Mayandi V, et al. Ocular delivery of predatory bacteria with cryomicroneedles against eye infection. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(21): e2102327.
Wu Y, Vora LK, Wang Y, Adrianto MF, Tekko IA, Waite D, et al. Long-acting nanoparticle-loaded bilayer microneedles for protein delivery to the posterior segment of the eye. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021;165:306–18.
Zhao J, Xu G, Yao X, Zhou H, Lyu B, Pei S, et al. Microneedle-based insulin transdermal delivery system: current status and translation challenges. Drug Delivery and Translational Research. 2021.
Arya J, Henry S, Kalluri H, McAllister DV, Pewin WP, Prausnitz MR. Tolerability, usability and acceptability of dissolving microneedle patch administration in human subjects. Biomaterials. 2017;128:1–7.
Vrdoljak A, Allen EA, Ferrara F, Temperton NJ, Crean AM, Moore AC. Induction of broad immunity by thermostabilised vaccines incorporated in dissolvable microneedles using novel fabrication methods. J Control Release. 2016;225:192–204.
Kalluri H, Choi S-O, Guo XD, Lee JW, Norman J, Prausnitz MR. Evaluation of microneedles in human subjects. percutaneous penetration enhancers physical methods in penetration enhancement 2017. p. 325–40.
Donnelly RF, Majithiya R, Singh TR, Morrow DI, Garland MJ, Demir YK, et al. Design, optimization and characterisation of polymeric microneedle arrays prepared by a novel laser-based micromoulding technique. Pharm Res. 2011;28(1):41–57.
O’Mahony C. Structural characterization and in-vivo reliability evaluation of silicon microneedles. Biomed Microdevices. 2014;16(3):333–43.
Troy SB, Kouiavskaia D, Siik J, Kochba E, Beydoun H, Mirochnitchenko O, et al. Comparison of the immunogenicity of various booster doses of inactivated polio vaccine delivered intradermally versus intramuscularly to HIV-infected adults. J Infect Dis. 2015;211(12):1969–76.
Shu W, Heimark H, Bertollo N, Tobin DJ, O’Cearbhaill ED, Annaidh AN. Insights into the mechanics of solid conical microneedle array insertion into skin using the finite element method. Acta Biomater. 2021;135:403–13.
Sheng T, Luo B, Zhang W, Ge X, Yu J, Zhang Y, et al. Microneedle-mediated vaccination: innovation and translation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;179: 113919.
Lee JW, Choi S-O, Felner EI, Prausnitz MR. Dissolving microneedle patch for transdermal delivery of human growth hormone. Small. 2011;7(4):531–9.
Vicente-Perez EM, Quinn HL, McAlister E, O’Neill S, Hanna LA, Barry JG, et al. The use of a pressure-indicating sensor film to provide feedback upon hydrogel-forming microneedle array self-application in vivo. Pharm Res. 2016;33(12):3072–80.
Bariya SH, Gohel MC, Mehta TA, Sharma OP. Microneedles: an emerging transdermal drug delivery system. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012;64(1):11–29.
D.V. McAllister PMW, S.P. Davis, J. Park, P.J. Canatella, M.G. Allen,, Prausnitz MR. Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: fabrication methods and transport studies. Proc Nat Acad Sci. 2003;100:13755–60.
Richter-Johnson J, Kumar P, Choonara YE, du Toit LC, Pillay V. Therapeutic applications and pharmacoeconomics of microneedle technology. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2018;18(4):359–69.
Zhao ZM, Anselmo AC, Mitragotri S. Viral vector-based gene therapies in the clinic. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine.10258.
Cai Y, Huang S, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Zhu X, Chen X, et al. Bioinspired Rotation Microneedles for Accurate Transdermal Positioning and Ultraminimal-Invasive Biomarker Detection with Mechanical Robustness. Research (Wash D C). 2022;2022:9869734.
Pere CPP, Economidou SN, Lall G, Ziraud C, Boateng JS, Alexander BD, et al. 3D printed microneedles for insulin skin delivery. Int J Pharm. 2018;544(2):425–32.
Acknowledgements
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82003670), Science & Technology Support Program of Changzhou (CJ20200075), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu (BK20190566), the Starting Scientific Research of Changzhou University (ZMF19020383), Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (SJCX22_1449).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ting Zhu, Pengfei Cui, Jianhao Wang contributed to the conception of the work. Ting Zhu, Wenya Zhang wrote the manuscript. Pengju Jiang, Shuwen Zhou contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation. Lin Qiu revised it critically for important intellectual content. Cheng Wang, Honglei Shi helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, T., Zhang, W., Jiang, P. et al. Progress in Intradermal and Transdermal Gene Therapy with Microneedles. Pharm Res 39, 2475–2486 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03376-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03376-x