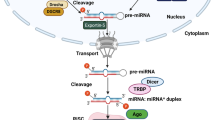
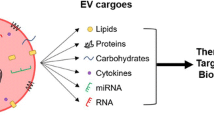
Abstract
Purpose
There is a growing interest in extracellular vesicles (EVs) for ocular applications as therapeutics, biomarkers, and drug delivery vehicles. EVs secreted from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have shown to provide therapeutic benefits in ocular conditions. However, very little is known about the properties of bioreactor cultured-3D human retinal organoids secreted EVs. This study provides a comprehensive morphological, nanomechanical, molecular, and proteomic characterization of retinal organoid EVs and compares it with human umbilical cord (hUC) MSCs.
Methods
The morphology and nanomechanical properties of retinal organoid EVs were assessed using Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and Atomic force microscopy (AFM). Gene expression analysis of exosome biogenesis of early and late retinal organoids were compared using qPCR. The protein profile of the EVs were analyzed with proteomic tools.
Results
NTA indicated the average size of EV as 100–250 nm. A high expression of exosome biogenesis genes was observed in late retinal organoids EVs. Immunoblot analysis showed highly expressed exosomal markers in late retinal organoids EVs compared to early retinal organoids EVs. Protein profiling of retinal organoid EVs displayed a higher differential expression of retinal function-related proteins and EV biogenesis proteins than hUCMSC EVs, implicating that the use of retinal organoid EVs may have a superior therapeutic effect on retinal disorders.
Conclusion
This study provides supplementary knowledge on the properties of retinal organoid EVs and suggests their potential use in the diagnostic and therapeutic treatments for ocular diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed from the current study is available with the corresponding author on reasonable request. The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE partner repository with the dataset identifier.
References
Hartong DT, Berson EL, Dryja TP. Retinitis pigmentosa. The Lancet. 2006;368(9549):1795–809.
Goodwin P. Hereditary retinal disease. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008;19(3):255–62.
Hamel J-F. Les ruines du progrès chez Walter Benjamin: anticipation futuriste, fausse reconnaissance et politique du présent. Protée. 2007;35(2):7–14.
Kutlehria S, Sachdeva MS. Role of in vitro models for development of ophthalmic delivery systems. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2021;38(3).
Buskin A, Zhu L, Chichagova V, Basu B, Mozaffari-Jovin S, Dolan D, Droop A, Collin J, Bronstein R, Mehrotra S. Disrupted alternative splicing for genes implicated in splicing and ciliogenesis causes PRPF31 retinitis pigmentosa. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1–19.
Jin Z-B, Okamoto S, Osakada F, Homma K, Assawachananont J, Hirami Y, Iwata T, Takahashi M. Modeling retinal degeneration using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(2): e17084.
Collin J, Zerti D, Queen R, Santos-Ferreira T, Bauer R, Coxhead J, Hussain R, Steel D, Mellough C, Ader M. CRX expression in pluripotent stem cell-derived photoreceptors marks a transplantable subpopulation of early cones. Stem Cells. 2019;37(5):609–22.
Parfitt DA, Lane A, Ramsden CM, Carr A-JF, Munro PM, Jovanovic K, Schwarz N, Kanuga N, Muthiah MN, Hull S. Identification and correction of mechanisms underlying inherited blindness in human iPSC-derived optic cups. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;18(6):769–81.
Hallam D, Hilgen G, Dorgau B, Zhu L, Yu M, Bojic S, Hewitt P, Schmitt M, Uteng M, Kustermann S. Human-induced pluripotent stem cells generate light responsive retinal organoids with variable and nutrient-dependent efficiency. Stem Cells. 2018;36(10):1535–51.
Eldred KC, Hadyniak SE, Hussey KA, Brenerman B, Zhang P-W, Chamling X, Sluch VM, Welsbie DS, Hattar S, Taylor J. Thyroid hormone signaling specifies cone subtypes in human retinal organoids. Science. 2018;362(6411):eaau6348.
Fligor CM, Langer KB, Sridhar A, Ren Y, Shields PK, Edler MC, Ohlemacher SK, Sluch VM, Zack DJ, Zhang C. Three-dimensional retinal organoids facilitate the investigation of retinal ganglion cell development, organization and neurite outgrowth from human pluripotent stem cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1–14.
Collin J, Queen R, Zerti D, Dorgau B, Hussain R, Coxhead J, Cockell S, Lako M. Deconstructing retinal organoids: single cell RNA-Seq reveals the cellular components of human pluripotent stem cell-derived retina. Stem Cells. 2019;37(5):593–8.
Viczian AS. Advances in retinal stem cell biology. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2013;8(2):147.
Stern JH, Temple S. Stem cells for retinal replacement therapy. Neurotherapeutics. 2011;8(4):736–43.
Cramer AO, MacLaren RE. Translating induced pluripotent stem cells from bench to bedside: application to retinal diseases. Curr Gene Ther. 2013;13(2):139–51.
Gamm DM, Phillips MJ, Singh R. Modeling retinal degenerative diseases with human iPS-derived cells: current status and future implications. Expert review of ophthalmology. 2013;8(3):213–6.
Zhu J, Reynolds J, Garcia T, Cifuentes H, Chew S, Zeng X, Lamba DA. Generation of Transplantable Retinal Photoreceptors from a Current Good Manufacturing Practice-Manufactured Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Line. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(2):210–9.
Singh MS, Park SS, Albini TA, Canto-Soler MV, Klassen H, MacLaren RE, Takahashi M, Nagiel A, Schwartz SD, Bharti K. Retinal stem cell transplantation: Balancing safety and potential. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2020;75: 100779.
Van Niel G, d’Angelo G, Raposo G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213–28.
Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, Antoniou A, Arab T, Archer F, Atkin-Smith GK. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. Journal of extracellular vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750.
Kooijmans SA, Vader P, van Dommelen SM, van Solinge WW, Schiffelers RM. Exosome mimetics: a novel class of drug delivery systems. Int J Nanomed. 2012;7:1525.
Schiller M, Bekeredjian-Ding I, Heyder P, Blank N, Ho AD, Lorenz H-M. Autoantigens are translocated into small apoptotic bodies during early stages of apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(1):183–91.
Doyle LM, Wang MZ. Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells. 2019;8(7):727.
Bai L, Shao H, Wang H, Zhang Z, Su C, Dong L, Yu B, Chen X, Li X, Zhang X. Effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on experimental autoimmune uveitis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):4323. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04559-y.
Gu X, Li Y, Chen K, Wang X, Wang Z, Lian H, Lin Y, Rong X, Chu M, Lin J. Exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate viral myocarditis through activating AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy flux pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(13):7515–30.
Zhang S, Chuah SJ, Lai RC, Hui JHP, Lim SK, Toh WS. MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials. 2018;156:16–27.
Merchant ML, Rood IM, Deegens JKJ, Klein JB. Isolation and characterization of urinary extracellular vesicles: implications for biomarker discovery. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13(12):731–49.
Patel N, Kommineni N, Surapaneni SK, Kalvala A, Yaun X, Gebeyehu A, Arthur P, Duke LC, York SB, Bagde A, Meckes DG, Singh M. Cannabidiol loaded extracellular vesicles sensitize triple-negative breast cancer to doxorubicin in both in-vitro and in vivo models. Int J Pharm. 2021;607: 120943.
Yu B, Shao H, Su C, Jiang Y, Chen X, Bai L, Zhang Y, Li Q, Zhang X, Li X. Exosomes derived from MSCs ameliorate retinal laser injury partially by inhibition of MCP-1. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):1–12.
Mead B, Tomarev S. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes promote survival of retinal ganglion cells through miRNA-dependent mechanisms. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(4):1273–85.
Bai L, Shao H, Wang H, Zhang Z, Su C, Dong L, Yu B, Chen X, Li X, Zhang X. Effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on experimental autoimmune uveitis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1–11.
Zhou J, Flores-Bellver M, Pan J, Benito-Martin A, Shi C, Onwumere O, Mighty J, Qian J, Zhong X, Hogue T. Human retinal organoids release extracellular vesicles that regulate gene expression in target human retinal progenitor cells. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1–17.
He C, Zheng S, Luo Y, Wang B. Exosome theranostics: biology and translational medicine. Theranostics. 2018;8(1):237.
Hajrasouliha AR, Jiang G, Lu Q, Lu H, Kaplan HJ, Zhang H-G, Shao H. Exosomes from retinal astrocytes contain antiangiogenic components that inhibit laser-induced choroidal neovascularization. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(39):28058–67.
Atienzar-Aroca S, Flores-Bellver M, Serrano-Heras G, Martinez-Gil N, Barcia JM, Aparicio S, Perez-Cremades D, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Diaz-Llopis M, Romero FJ. Oxidative stress in retinal pigment epithelium cells increases exosome secretion and promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2016;20(8):1457–66.
Chen M, Ren C, Ren B, Fang Y, Li Q, Zeng Y, Li Y, Chen F, Bian B, Liu Y. Human Retinal Progenitor Cells Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Delay Retinal Degeneration: A Paradigm for Cell-free Therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:748956–748956.
Kang G-Y, Bang JY, Choi AJ, Yoon J, Lee W-C, Choi S, Yoon S, Kim HC, Baek J-H, Park HS. Exosomal proteins in the aqueous humor as novel biomarkers in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. J Proteome Res. 2014;13(2):581–95.
Flores-Bellver M, Mighty J, Aparicio-Domingo S, Li KV, Shi C, Zhou J, Cobb H, McGrath P, Michelis G, Lenhart P. Extracellular vesicles released by human retinal pigment epithelium mediate increased polarised secretion of drusen proteins in response to AMD stressors. Journal of extracellular vesicles. 2021;10(13): e12165.
Kulkarni T, Tam A, Mukhopadhyay D, Bhattacharya S. AFM study: Cell cycle and probe geometry influences nanomechanical characterization of Panc1 cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)- General Subjects. 2019;1863(5):802–12.
Stylianou A, Lekka M, Stylianopoulos T. AFM assessing of nanomechanical fingerprints for cancer early diagnosis and classification: from single cell to tissue level. Nanoscale. 2018;10(45):20930–45.
Bagrov DV, Senkovenko AM, Nikishin II, Skryabin GO, Kopnin PB, Tchevkina EM. Application of AFM, TEM, and NTA for characterization of exosomes produced by placenta-derived mesenchymal cells. J Phys Conf Ser. 1942;1:012013.
Kulkarni T, Mukhopadhyay D, Bhattacharya S. Dynamic alteration of poroelastic attributes as determinant membrane nanorheology for endocytosis of organ specific targeted gold nanoparticles. Journal of nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):1–16.
Bagheri E, Abnous K, Farzad SA, Taghdisi SM, Ramezani M, Alibolandi M. Targeted doxorubicin-loaded mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes as a versatile platform for fighting against colorectal cancer. Life Sci. 2020;261: 118369.
Pei Y, Sierra G, Sivapatham R, Swistowski A, Rao MS, Zeng X. A platform for rapid generation of single and multiplexed reporters in human iPSC lines. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):1–10.
Chirco KR, Chew S, Moore AT, Duncan JL, Lamba DA. Allele-specific gene editing to rescue dominant CRX-associated LCA7 phenotypes in a retinal organoid model. Stem cell reports. 2021;16(11):2690–702.
Rider MA, Hurwitz SN, Meckes DG. ExtraPEG: a polyethylene glycol-based method for enrichment of extracellular vesicles. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):1–14.
Hurwitz SN, Nkosi D, Conlon MM, York SB, Liu X, Tremblay DC, Meckes DG Jr. CD63 regulates epstein-barr virus LMP1 exosomal packaging, enhancement of vesicle production, and noncanonical NF-κB signaling. J Virol. 2017;91(5):e02251-e2316.
Cvjetkovic A, Lötvall J, Lässer C. The influence of rotor type and centrifugation time on the yield and purity of extracellular vesicles. Journal of extracellular vesicles. 2014;3(1):23111.
Reiner AT, Witwer KW, Van Balkom BW, De Beer J, Brodie C, Corteling RL, Gabrielsson S, Gimona M, Ibrahim AG, De Kleijn D. Concise review: Developing best-practice models for the therapeutic use of extracellular vesicles. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(8):1730–9.
Shlyakhtenko LS, Gall AA, Lyubchenko YL. Mica functionalization for imaging of DNA and protein-DNA complexes with atomic force microscopy. Cell Imaging Techniques: Springer; 2012. p. 295–312.
Nkosi D, Sun L, Duke LC, Meckes DG Jr. Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 manipulates the content and functions of extracellular vesicles to enhance metastatic potential of recipient cells. PLoS Pathog. 2020;16(12): e1009023.
Capowski EE, Samimi K, Mayerl SJ, Phillips MJ, Pinilla I, Howden SE, Saha J, Jansen AD, Edwards KL, Jager LD. Reproducibility and staging of 3D human retinal organoids across multiple pluripotent stem cell lines. Development. 2019;146(1):dev171686.
Sridhar A, Hoshino A, Finkbeiner CR, Chitsazan A, Dai L, Haugan AK, Eschenbacher KM, Jackson DL, Trapnell C, Bermingham-McDonogh O. Single-cell transcriptomic comparison of human fetal retina, hPSC-derived retinal organoids, and long-term retinal cultures. Cell Rep. 2020;30(5):1644-1659. e4.
Woo S, Rothemund PW. Self-assembly of two-dimensional DNA origami lattices using cation-controlled surface diffusion. Nat Commun. 2014;5(1):1–11.
Colombo M, Raposo G, Théry C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:255–89.
Deng C-L, Hu C-B, Ling S-T, Zhao N, Bao L-H, Zhou F, Xiong Y-C, Chen T, Sui B-D, Yu X-R. Photoreceptor protection by mesenchymal stem cell transplantation identifies exosomal MiR-21 as a therapeutic for retinal degeneration. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(3):1041–61.
Yu B, Li X-R, Zhang X-M. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as a new therapeutic strategy for ocular diseases. World journal of stem cells. 2020;12(3):178.
Adak S, Magdalene D, Deshmukh S, Das D, Jaganathan BG. A review on mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of retinal diseases. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports. 2021;17(4):1154–73.
Zhou Y, Tian T, Zhu Y, Jaffar Ali D, Hu F, Qi Y, Sun B, Xiao Z. Exosomes transfer among different species cells and mediating miRNAs delivery. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(12):4267–74.
Hagstrom SA, Duyao M, North MA, Li T. Retinal degeneration in tulp1−/− mice: vesicular accumulation in the interphotoreceptor matrix. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999;40(12):2795–802.
Spencer WJ, Ding J-D, Lewis TR, Yu C, Phan S, Pearring JN, Kim K-Y, Thor A, Mathew R, Kalnitsky J, Hao Y, Travis AM, Biswas SK, Lo W-K, Besharse JC, Ellisman MH, Saban DR, Burns ME, Arshavsky VY. PRCD is essential for high-fidelity photoreceptor disc formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2019;116(26):13087–96.
Klingeborn M, Dismuke WM, Bowes Rickman C, Stamer WD. Roles of exosomes in the normal and diseased eye. Progress Retinal Eye Res. 2017;59:158–77.
Xu W, Wu Y, Hu Z, Sun L, Dou G, Zhang Z, Wang H, Guo C, Wang Y. Exosomes from Microglia Attenuate Photoreceptor Injury and Neovascularization in an Animal Model of Retinopathy of Prematurity. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids. 2019;16:778–90.
Liu S, Wang Y. Application of AFM in microbiology: a review. Scanning. 2010;32(2):61–73.
Jia Z, Lv Y, Zhang W, Zhang X, Li F, Lu X, Zhao S. Mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes-based immunological signature in a rat model of corneal allograft rejection therapy. Frontiers in Bioscience (Landmark Edition). 2022;27(3):86–86.
Rocha S, Carvalho J, Oliveira P, Voglstaetter M, Schvartz D, Thomsen AR, Walter N, Khanduri R, Sanchez JC, Keller A. 3D cellular architecture affects microRNA and protein cargo of extracellular vesicles. Advanced science. 2019;6(4):1800948.
Haraszti RA, Miller R, Stoppato M, Sere YY, Coles A, Didiot M-C, Wollacott R, Sapp E, Dubuke ML, Li X. Exosomes produced from 3D cultures of MSCs by tangential flow filtration show higher yield and improved activity. Mol Ther. 2018;26(12):2838–47.
Eguchi T, Sogawa C, Okusha Y, Uchibe K, Iinuma R, Ono K, Nakano K, Murakami J, Itoh M, Arai K. Organoids with cancer stem cell-like properties secrete exosomes and HSP90 in a 3D nanoenvironment. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(2): e0191109.
Marzano M, Bejoy J, Cheerathodi MR, Sun L, York SB, Zhao J, Kanekiyo T, Bu G, Meckes DG, Li Y. Differential effects of extracellular vesicles of lineage-specific human pluripotent stem cells on the cellular behaviors of isogenic cortical spheroids. Cells. 2019;8(9):993.
Jeske R, Bejoy J, Marzano M, Li Y. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: characteristics and applications. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;26(2):129–44.
Borys BS, Dang T, So T, Rohani L, Revay T, Walsh T, Thompson M, Argiropoulos B, Rancourt DE, Jung S. Overcoming bioprocess bottlenecks in the large-scale expansion of high-quality hiPSC aggregates in vertical-wheel stirred suspension bioreactors. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):1–19.
Acknowledgements
This research is partly funded by the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities, Grant/Award Number: U54 MD007582, and NSF-CREST Center for Complex Materials Design for Multidimensional Additive Processing (CoManD), Grant/Award Number:1735968. Work was supported, in part, by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01- EY032197 and U24 EY029891 to D.A. L, R01-NS125016 to Y.L.) P30 Vision Core grant to UCSF Dept of Ophthalmology (EY002162), the Research to Prevent Blindness (unrestricted grant to UCSF Dept of Ophthalmology) and Eagles fifth District Cancer Telethon−Cancer Research Fund and Jay and Deanie Stein Career Development Award for Cancer Research at Mayo Clinic Jacksonville, 2019 Benefactor Funded Champions for Hope Pancreatic Cancer to S.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 114 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arthur, P., Kandoi, S., Sun, L. et al. Biophysical, Molecular and Proteomic Profiling of Human Retinal Organoid-Derived Exosomes. Pharm Res 40, 801–816 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03350-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03350-7