Abstract
Purpose
Dysregulations of key signaling pathways in metabolic syndrome are multifactorial, eventually leading to cardiovascular events. Hyperglycemia in conjunction with dyslipidemia induces insulin resistance and provokes release of proinflammatory cytokines resulting in chronic inflammation, accelerated lipid peroxidation with further development of atherosclerotic alterations and diabetes. We have proposed a novel combinatorial approach using FDA approved compounds targeting IL-17a and DPP4 to ameliorate a significant portion of the clustered clinical risks in patients with metabolic syndrome. In our current research we have modeled the outcomes of metabolic syndrome treatment using two distinct drug classes.
Methods
Targets were chosen based on the clustered clinical risks in metabolic syndrome: dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, impaired glucose control, and chronic inflammation. Drug development platform, BIOiSIM™, was used to narrow down two different drug classes with distinct modes of action and modalities. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of the most promising drugs were modeling showing predicted outcomes of combinatorial therapeutic interventions.
Results
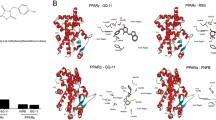
Preliminary studies demonstrated that the most promising drugs belong to DPP-4 inhibitors and IL-17A inhibitors. Evogliptin was chosen to be a candidate for regulating glucose control with long term collateral benefit of weight loss and improved lipid profiles. Secukinumab, an IL-17A sequestering agent used in treating psoriasis, was selected as a repurposed candidate to address the sequential inflammatory disorders that follow the first metabolic insult.
Conclusions
Our analysis suggests this novel combinatorial therapeutic approach inducing DPP4 and Il-17a suppression has a high likelihood of ameliorating a significant portion of the clustered clinical risk in metabolic syndrome.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Neill S, O’Driscoll L. Metabolic syndrome: a closer look at the growing epidemic and its associated pathologies. Obes Rev. 2015;16(1):1–12.
Rochlani Y, Pothineni NV, Kovelamudi S, Mehta JL. Metabolic syndrome: pathophysiology, management, and modulation by natural compounds. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2017;11(8):215–25.
Blanquet M, Legrand A, Pelissier A, Mourgues C. Socio-economics status and metabolic syndrome: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019;13(3):1805–12.
Lear SA, Gasevic D. Ethnicity and Metabolic Syndrome: Implications for Assessment, Management and Prevention. Nutrients. 2019;12(1):15.
Saklayen MG. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018;20(2):12.
Fernandez-Mendoza J, He F, LaGrotte C, Vgontzas AN, Liao D, Bixler EO. Impact of the Metabolic Syndrome on Mortality is Modified by Objective Short Sleep Duration. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6(5):e005479.
Lee MK, Han K, Kim MK, Koh ES, Kim ES, Nam GE, Kwon HS. Changes in metabolic syndrome and its components and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):2313.
NCEP. Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Final Report. Circulation. 2002; 106(25): 3143-421.
Alizadeh S, Ahmadi M, Ghorbani Nejad B, Djazayeri A, Shab-Bidar S. Metabolic syndrome and its components are associated with increased chronic kidney disease risk: Evidence from a meta-analysis on 11 109 003 participants from 66 studies. Int J Clin Pract. 2018;e13201.
Li X, Li X, Lin H, Fu X, Lin W, Li M, Zeng X, Gao Q. Metabolic syndrome and stroke: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;40:34–8.
Mottillo S, Filion KB, Genest J, Joseph L, Pilote L, Poirier P, Rinfret S, Schiffrin EL, Eisenberg MJ. The metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56(14):1113–32.
Ren H, Wang J, Gao Y, Yang F, Huang W. Metabolic syndrome and liver-related events: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019;19(1):40.
Bluher M. Adipose tissue inflammation: a cause or consequence of obesity-related insulin resistance? Clin Sci (Lond). 2016;130(18):1603–14.
Saltiel AR, Olefsky JM. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(1):1–4.
Varghese JF, Patel R, Yadav UCS. Novel Insights in the Metabolic Syndrome-induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation-mediated Atherosclerosis. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2018;14(1):4–14.
Bechara R, McGeachy MJ, Gaffen SL. The metabolism-modulating activity of IL-17 signaling in health and disease. J Exp Med. 2021;218(5):e20202191.
Wang J, Sun C, Gerdes N, Liu C, Liao M, Liu J, Shi MA, He A, Zhou Y, Sukhova GK, Chen H, Cheng XW, Kuzuya M, Murohara T, Zhang J, Cheng X, Jiang M, Shull GE, Rogers S, Yang CL, Ke Q, Jelen S, Bindels R, Ellison DH, Jarolim P, Libby P, Shi GP. Interleukin 18 function in atherosclerosis is mediated by the interleukin 18 receptor and the Na-Cl co-transporter. Nat Med. 2015;21(7):820–6.
Huang PL. A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Dis Model Mech. 2009;2(5–6):231–7.
Dooghaie Moghadam A, Eslami P, Razavi-Khorasani N, Moazzami B, Zahedi-Tajrishi F, Farokhi E, Makhdoomi Sharabiani K, Mansour-Ghanaei A, Mehrvar A, Aghajanpoor Pasha M, Saeedi S, Iravani S. Recurrence of fatty liver disease following liver transplantation for NAFLD-related cirrhosis: Current status and challenges. Caspian J Intern Med. 2020;11(4):346–54.
Marcos-Delgado A, Hernández-Segura N, Fernández-Villa T, Molina AJ, Martín V. The Effect of Lifestyle Intervention on Health-Related Quality of Life in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(3):887.
Phelan S, Wadden TA, Berkowitz RI, Sarwer DB, Womble LG, Cato RK, Rothman R. Impact of weight loss on the metabolic syndrome. Int J Obes. 2007;31(9):1442–8.
Vilar-Gomez E, Martinez-Perez Y, Calzadilla-Bertot L, Torres-Gonzalez A, Gra-Oramas B, Gonzalez-Fabian L, Friedman SL, Diago M, Romero-Gomez M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(2):367-378.e365 (quiz e314-365).
Fujioka K. Metabolic syndrome treatment strategies. Pharmacotherapy. 2006;26(12 Pt 2):222S-S226.
Grundy SM. Advancing drug therapy of the metabolic syndrome. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2009;8(5):341.
Chakravarty K, Antontsev V, Bundey Y, Varshney J. Driving success in personalized medicine through AI-enabled computational modeling. Drug Discovery Today. 2021;26(6):1459–65.
Maharao N, Antontsev V, Hou H, Walsh J, Varshney J. Scalable in silico Simulation of Transdermal Drug Permeability: Application of BIOiSIM Platform. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2020;14:2307–17.
Antontsev V, Jagarapu A, Bundey Y, Hou H, Khotimchenko M, Walsh J, Varshney J. A hybrid modeling approach for assessing mechanistic models of small molecule partitioning in vivo using a machine learning-integrated modeling platform. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):11143.
Wolfram Research I. Mathematica. 2021; Version 13.0.0.
Bruin G, Loesche C, Nyirady J, Sander O. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Secukinumab in Patients With Moderate to Severe Psoriasis. J Clin Pharmacol. 2017;57(7):876–85.
Morrison JF. Kinetics of the reversible inhibition of enzyme-catalysed reactions by tight-binding inhibitors. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Enzymology. 1969;185(2):269–86.
Badman MK, Chen J, Desai S, Vaidya S, Neelakantham S, Zhang J, Gan L, Danis K, Laffitte B, Klickstein LB. Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of the Novel Non-Bile Acid FXR Agonist Tropifexor (LJN452) in Healthy Volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2020;9(3):395–410.
Christopher R, Covington P, Davenport M, Fleck P, Mekki QA, Wann ER, Karim A. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerability of single increasing doses of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor alogliptin in healthy male subjects. Clin Ther. 2008;30(3):513–27.
Graefe-Mody U, Retlich S, Friedrich C. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of linagliptin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012;51(7):411–27.
Gu N, Park MK, Kim TE, Bahng MY, Lim KS, Cho SH, Yoon SH, Cho JY, Jang IJ, Yu KS. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of evogliptin (DA-1229), a novel dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor, in healthy volunteers. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014;8:1709–21.
Aramaki M. Alogliptin, but not voglibose, ameliorates dyslipidemia and LDL particle size in patients with impaired glucose tolerance or Type 2 diabetes. Clin Lipidol. 2013;8(5):533–40.
Chae YN, Kim TH, Kim MK, Shin CY, Jung IH, Sohn YS, Son MH. Beneficial Effects of Evogliptin, a Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitor, on Adiposity with Increased Ppargc1a in White Adipose Tissue in Obese Mice. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0144064.
Inagaki N, Onouchi H, Maezawa H, Kuroda S, Kaku K. Once-weekly trelagliptin versus daily alogliptin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3(3):191–7.
Eliasson B, Moller-Goede D, Eeg-Olofsson K, Wilson C, Cederholm J, Fleck P, Diamant M, Taskinen MR, Smith U. Lowering of postprandial lipids in individuals with type 2 diabetes treated with alogliptin and/or pioglitazone: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia. 2012;55(4):915–25.
Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(6):580–91.
Roman RJ. P-450 metabolites of arachidonic acid in the control of cardiovascular function. Physiol Rev. 2002;82(1):131–85.
Chiamvimonvat N, Ho CM, Tsai HJ, Hammock BD. The soluble epoxide hydrolase as a pharmaceutical target for hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007;50(3):225–37.
Imig JD. Cardiovascular therapeutic aspects of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2006;24(2):169–88.
Imig JD, Zhao X, Capdevila JH, Morisseau C, Hammock BD. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition lowers arterial blood pressure in angiotensin II hypertension. Hypertension. 2002;39(2 Pt 2):690–4.
Imig JD, Zhao X, Zaharis CZ, Olearczyk JJ, Pollock DM, Newman JW, Kim IH, Watanabe T, Hammock BD. An orally active epoxide hydrolase inhibitor lowers blood pressure and provides renal protection in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension. 2005;46(4):975–81.
Ulu A, Davis BB, Tsai HJ, Kim IH, Morisseau C, Inceoglu B, Fiehn O, Hammock BD, Weiss RH. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors reduce the development of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein e-knockout mouse model. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008;52(4):314–23.
Zhang LN, Vincelette J, Cheng Y, Mehra U, Chen D, Anandan SK, Gless R, Webb HK, Wang YX. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuated atherosclerosis, abdominal aortic aneurysm formation, and dyslipidemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29(9):1265–70.
Liu Y, Dang H, Li D, Pang W, Hammock BD, Zhu Y. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates high-fat-diet-induced hepatic steatosis by reduced systemic inflammatory status in mice. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39165.
Wang Q, Pang W, Cui Z, Shi J, Liu Y, Liu B, Zhou Y, Guan Y, Hammock BD, Wang Y, Zhu Y. Upregulation of soluble epoxide hydrolase in proximal tubular cells mediated proteinuria-induced renal damage. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013;304(2):F168–76.
He J, Wang C, Zhu Y, Ai D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase: A potential target for metabolic diseases. J Diabetes. 2016;8(3):305–13.
Cermenati G, Audano M, Giatti S, Carozzi V, Porretta-Serapiglia C, Pettinato E, Ferri C, D’Antonio M, De Fabiani E, Crestani M, Scurati S, Saez E, Azcoitia I, Cavaletti G, Garcia-Segura LM, Melcangi RC, Caruso D, Mitro N. Lack of sterol regulatory element binding factor-1c imposes glial Fatty Acid utilization leading to peripheral neuropathy. Cell Metab. 2015;21(4):571–83.
Chapman MJ, Redfern JS, McGovern ME, Giral P. Niacin and fibrates in atherogenic dyslipidemia: pharmacotherapy to reduce cardiovascular risk. Pharmacol Ther. 2010;126(3):314–45.
Mansour M. The roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in the metabolic syndrome. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014;121:217–66.
Diehl AM, Day C. Cause, Pathogenesis, and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(21):2063–72.
Oosterveer MH, Grefhorst A, van Dijk TH, Havinga R, Staels B, Kuipers F, Groen AK, Reijngoud DJ. Fenofibrate simultaneously induces hepatic fatty acid oxidation, synthesis, and elongation in mice. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(49):34036–44.
Wu P, Peters JM, Harris RA. Adaptive increase in pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 during starvation is mediated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;287(2):391–6.
Simental-Mendia LE, Simental-Mendia M, Sanchez-Garcia A, Banach M, Atkin SL, Gotto AM Jr, Sahebkar A. Effect of fibrates on glycemic parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Pharmacol Res. 2018;132:232–41.
Kilgore KS, Billin AN. PPARbeta/delta ligands as modulators of the inflammatory response. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2008;9(5):463–9.
Kernan WN, Viscoli CM, Furie KL, Young LH, Inzucchi SE, Gorman M, Guarino PD, Lovejoy AM, Peduzzi PN, Conwit R, Brass LM, Schwartz GG, Adams HP Jr, Berger L, Carolei A, Clark W, Coull B, Ford GA, Kleindorfer D, O’Leary JR, Parsons MW, Ringleb P, Sen S, Spence JD, Tanne D, Wang D, Winder TR, Investigators IT. Pioglitazone after Ischemic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(14):1321–31.
Zollner G, Marschall HU, Wagner M, Trauner M. Role of nuclear receptors in the adaptive response to bile acids and cholestasis: pathogenetic and therapeutic considerations. Mol Pharm. 2006;3(3):231–51.
Kir S, Kliewer SA, Mangelsdorf DJ. Roles of FGF19 in liver metabolism. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2011;76:139–44.
Calkin AC, Tontonoz P. Transcriptional integration of metabolism by the nuclear sterol-activated receptors LXR and FXR. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(4):213–24.
Li C, Li J, Weng X, Lan X, Chi X. Farnesoid X receptor agonist CDCA reduces blood pressure and regulates vascular tone in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2015;9(7):507-16.e507.
Massafra V, Pellicciari R, Gioiello A, van Mil SWC. Progress and challenges of selective Farnesoid X Receptor modulation. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;191:162–77.
Li J, Wilson A, Kuruba R, Zhang Q, Gao X, He F, Zhang LM, Pitt BR, Xie W, Li S. FXR-mediated regulation of eNOS expression in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;77(1):169–77.
He F, Li J, Mu Y, Kuruba R, Ma Z, Wilson A, Alber S, Jiang Y, Stevens T, Watkins S, Pitt B, Xie W, Li S. Downregulation of endothelin-1 by farnesoid X receptor in vascular endothelial cells. Circ Res. 2006;98(2):192–9.
Fang S, Suh JM, Reilly SM, Yu E, Osborn O, Lackey D, Yoshihara E, Perino A, Jacinto S, Lukasheva Y, Atkins AR, Khvat A, Schnabl B, Yu RT, Brenner DA, Coulter S, Liddle C, Schoonjans K, Olefsky JM, Saltiel AR, Downes M, Evans RM. Intestinal FXR agonism promotes adipose tissue browning and reduces obesity and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2015;21(2):159–65.
Cipriani S, Mencarelli A, Palladino G, Fiorucci S. FXR activation reverses insulin resistance and lipid abnormalities and protects against liver steatosis in Zucker (fa/fa) obese rats. J Lipid Res. 2010;51(4):771–84.
Watanabe M, Houten SM, Wang L, Moschetta A, Mangelsdorf DJ, Heyman RA, Moore DD, Auwerx J. Bile acids lower triglyceride levels via a pathway involving FXR, SHP, and SREBP-1c. J Clin Invest. 2004;113(10):1408–18.
Angelin B, Einarsson K, Hellström K, Leijd B. Effects of cholestyramine and chenodeoxycholic acid on the metabolism of endogenous triglyceride in hyperlipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1978;19(8):1017–24.
Cariou B, Staels B. FXR: a promising target for the metabolic syndrome? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007;28(5):236–43.
Camilleri M, Nord SL, Burton D, Oduyebo I, Zhang Y, Chen J, Im K, Bhad P, Badman MK, Sanders DS, Walters JRF. Randomised clinical trial: significant biochemical and colonic transit effects of the farnesoid X receptor agonist tropifexor in patients with primary bile acid diarrhoea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;52(5):808–20.
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(2):88–98.
Toulis KA, Nirantharakumar K, Pourzitaki C, Barnett AH, Tahrani AA. Glucokinase Activators for Type 2 Diabetes: Challenges and Future Developments. Drugs. 2020;80(5):467–75.
Yin J, Xing H, Ye J. Efficacy of Berberine in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolism. 2008;57(5):712–7.
Keaney JF Jr, Gaziano JM, Xu A, Frei B, Curran-Celentano J, Shwaery GT, Loscalzo J, Vita JA. Dietary antioxidants preserve endothelium-dependent vessel relaxation in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90(24):11880–4.
Renna NF, Diez EA, Miatello RM. Effects of dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 inhibitor about vascular inflammation in a metabolic syndrome model. PLoS One. 2014;9(9):e106563.
Nakamura Y, Inagaki M, Shimizu T, Fujita K, Inoue M, Gotoh H, Oguchi K, Goto Y. Long-term effects of alogliptin benzoate in hemodialysis patients with diabetes: a 2-year study. Nephron Clin Pract. 2013;123(1–2):46–51.
Araki E, Kawamori R, Inagaki N, Watada H, Hayashi N, Horie Y, Sarashina A, Thiemann S, von Eynatten M, Dugi K, Woerle HJ. Long-term safety of linagliptin monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15(4):364–71.
Ussher JR, Drucker DJ. Cardiovascular biology of the incretin system. Endocr Rev. 2012;33(2):187–215.
Halberg N, Wernstedt-Asterholm I, Scherer PE. The adipocyte as an endocrine cell. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2008;37(3):753–68 (x-xi).
Kaur J. A comprehensive review on metabolic syndrome. Cardiol Res Pract. 2014;2014:943162.
von Stebut E, Boehncke WH, Ghoreschi K, Gori T, Kaya Z, Thaci D, Schaffler A. IL-17A in Psoriasis and Beyond: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Implications. Front Immunol. 2019;10:3096.
McDonald CJ, Calabresi P. Thromboembolic Disorders Associated With Psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 1973;107(6):918.
Mallbris L, Akre O, Granath F, Yin L, Lindelof B, Ekbom A, Stahle-Backdahl M. Increased risk for cardiovascular mortality in psoriasis inpatients but not in outpatients. Eur J Epidemiol. 2004;19(3):225–30.
Gelfand JM, Troxel AB, Lewis JD, Kurd SK, Shin DB, Wang X, Margolis DJ, Strom BL. The risk of mortality in patients with psoriasis: results from a population-based study. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143(12):1493–9.
Herron MD, Hinckley M, Hoffman MS, Papenfuss J, Hansen CB, Callis KP, Krueger GG. Impact of obesity and smoking on psoriasis presentation and management. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141(12):1527–34.
Player MS, Peterson LE. Anxiety disorders, hypertension, and cardiovascular risk: a review. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2011;41(4):365–77.
Naldi L, Chatenoud L, Linder D, Belloni Fortina A, Peserico A, Virgili AR, Bruni PL, Ingordo V, Lo Scocco G, Solaroli C, Schena D, Barba A, Di Landro A, Pezzarossa E, Arcangeli F, Gianni C, Betti R, Carli P, Farris A, Barabino GF, La Vecchia C. Cigarette smoking, body mass index, and stressful life events as risk factors for psoriasis: results from an Italian case-control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125(1):61–7.
Gisondi P, Tessari G, Conti A, Piaserico S, Schianchi S, Peserico A, Giannetti A, Girolomoni G. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriasis: a hospital-based case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157(1):68–73.
Hammerich L, Heymann F, Tacke F. Role of IL-17 and Th17 cells in liver diseases. Clin Dev Immunol. 2011;2011:345803.
Gasse P, Riteau N, Vacher R, Michel ML, Fautrel A, di Padova F, Fick L, Charron S, Lagente V, Eberl G, Le Bert M, Quesniaux VF, Huaux F, Leite-de-Moraes M, Ryffel B. Couillin I. IL-1 and IL-23 mediate early IL-17A production in pulmonary inflammation leading to late fibrosis. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23185.
Lafdil F, Miller AM, Ki SH, Gao B. Th17 cells and their associated cytokines in liver diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010;7(4):250–4.
Teijeiro A, Garrido A, Ferre A, Perna C, Djouder N. Inhibition of the IL-17A axis in adipocytes suppresses diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorders in mice. Nat Metab. 2021;3(4):496–512.
Romacho T, Sell H, Indrakusuma I, Roehrborn D, Castaneda TR, Jelenik T, Markgraf D, Hartwig S, Weiss J, Al-Hasani H, Roden M, Eckel J. DPP4 deletion in adipose tissue improves hepatic insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2020;318(5):E590–9.
DeFronzo RA. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med Clin North Am. 2004;88(4):787–835 (ix).
Andukuri R, Drincic A, Rendell M. Alogliptin: a new addition to the class of DPP-4 inhibitors. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2009;2:117–26.
Moritoh Y, Takeuchi K, Asakawa T, Kataoka O, Odaka H. Combining a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, alogliptin, with pioglitazone improves glycaemic control, lipid profiles and beta-cell function in db/db mice. Br J Pharmacol. 2009;157(3):415–26.
Kim G, Lim S, Kwon HS, Park IB, Ahn KJ, Park CY, Kwon SK, Kim HS, Park SW, Kim SG, Moon MK, Kim ES, Chung CH, Park KS, Kim M, Chung DJ, Lee CB, Kim TH, Lee MK. Efficacy and safety of evogliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, active-controlled, randomized, double-blind study with open-label extension (the EVERGREEN study). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020;22(9):1527–36.
Kim MK, Chae YN, Ahn GJ, Shin CY, Choi SH, Yang EK, Sohn YS, Son MH. Prevention and treatment effect of evogliptin on hepatic steatosis in high-fat-fed animal models. Arch Pharm Res. 2017;40(2):268–81.
Acknowledgments and Disclosures
The authors are all employees of Verisim Life and used a proprietary AI-driven platform to generate the outcomes for the manuscript.
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Maksim Khotimchenko and Nicholas E. Brunk are Co-First Author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khotimchenko, M., Brunk, N.E., Hixon, M.S. et al. In Silico Development of Combinatorial Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Key Signaling Pathways in Metabolic Syndrome. Pharm Res 39, 2937–2950 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03231-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03231-z