Abstract
Purpose
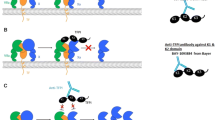
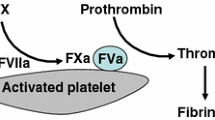
Activated superFactor V (superFVa) is a novel engineered FV with excellent prohemostatic efficacy. SuperFVa has three APC cleavage site mutations and an interdomain disulfide bond. Stability, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenic and thrombogenic potential are reported here.
Methods
Stability and circulating half-life were determined after incubation in buffer and human plasma, and after injection into FVIII-deficient mice. Immunogenicity potential was assessed by B- and T-cell specific epitope prediction and structural analysis using surface area and atomic depth computation. Thrombogenic potential was determined by quantification of lung fibrin deposition in wild-type mice after intravenous injection of superFVa (200 U/kg), recombinant human (rh) Tissue Factor (0.4–16 pmol/kg), rhFVIIa (3 mg/kg) or saline.
Results
FVa retained full activity over 30 h in buffer, the functional half-life in human plasma was 4.9 h, and circulating half-life in FVIII-deficient mice was ~30 min. Predicted immunogenicity was not increased compared to human FV. While rh Tissue Factor, the positive control, resulted in pronounced lung fibrin depositions (mean 121 μg/mL), superFVa did not (6.7 μg/mL), and results were comparable to fibrin depositions with rhFVIIa (7.6 μg/mL) or saline (5.6 μg/mL).
Conclusion
FVa has an appropriate safety and stability profile for further preclinical development as a prohemostatic against severe bleeding.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APC:
-
activated protein C
- DOAC:
-
direct oral anticoagulant
- ETP:
-
endogenous thrombin potential
- FVa:
-
activated factor V
- FVDP:
-
factor V deficient plasma
- FVIII:
-
factor VIII
- PC:
-
phosphatidyl choline
- PS:
-
phosphatidyl serine
- rh:
-
recombinant human
- rhTF:
-
recombinant human tissue factor
- SuperFVa:
-
activated super factor V
References
Gale AJ, Xu X, Pellequer JL, Getzoff ED, Griffin JH. Interdomain engineered disulfide bond permitting elucidation of mechanisms of inactivation of coagulation factor Va by activated protein C. Protein Sci. 2002;11(9):2091–101.
von Drygalski A, Cramer TJ, Bhat V, Griffin JH, Gale AJ, Mosnier LO. Improved hemostasis in hemophilia mice by means of an engineered factor Va mutant. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12(3):363–72.
Mann KG, Jenny RJ, Krishnaswamy S. Cofactor proteins in the assembly and expression of blood clotting enzyme complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:915–56.
Schlachterman A, Schuettrumpf J, Liu JH, Freguia CF, Toso R, Poncz M, et al. Factor V Leiden improves in vivo hemostasis in murine hemophilia models. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(12):2730–7.
Franchini M, Lippi G. Factor V Leiden and hemophilia. Thromb Res. 2010;125(2):119–23.
Kalafatis M, Egan JO, Van’t Veer C, Cawthern KM, Mann KG. The regulation of clotting factors. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1997;7(3):241–80.
Bos MH, Meijerman DW, Van der Zwaan C, Mertens K. Does activated protein C-resistant factor V contribute to thrombin generation in hemophilic plasma? J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(3):522–30.
Toso R, Camire RM. Removal of B-domain sequences from factor V rather than specific proteolysis underlies the mechanism by which cofactor function is realized. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(20):21643–50.
Bhat V, von Drygalski A, Gale AJ, Griffin JH, Mosnier LO. Improved coagulation and hemostasis in hemophilia with inhibitors by combinations of superFactor Va and factor VIIa. Thromb Haemost. 2016;115(3):551–61.
Bhat V, Gale AJ, Griffin JH, Mosnier LO, von Drygalski A. Reversal of novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC)-induced bleeding in mice by engineered superFactor Va. Blood. 2014;124(21):695.
von Drygalski A, Bhat V, Gale AJ, Burnier L, Cramer TJ, Griffin JH, et al. An engineered factor Va prevents bleeding induced by anticoagulant wt activated protein C. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e104304.
Hoots WK. Arthropathy in inhibitor patients: differences in the joint status. Semin Hematol. 2008;45(2 Suppl 1):S42–9.
Astermark J, Donfield SM, Dimichele DM, Gringeri A, Gilbert SA, Waters J, et al. A randomized comparison of bypassing agents in hemophilia complicated by an inhibitor: the FEIBA NovoSeven comparative (FENOC) study. Blood. 2007;109(2):546–51.
Astermark J, Santagostino E, Keith HW. Clinical issues in inhibitors. Haemophilia. 2010;16 Suppl 5:54–60.
Howard BM, Daley AT, Cohen MJ. Prohemostatic interventions in trauma: resuscitation-associated Coagulopathy, acute traumatic Coagulopathy, hemostatic resuscitation, and other hemostatic interventions. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2012;38(3):250–8.
Levy JH, Spyropoulos AC, Samama CM, Douketis J. Direct oral anticoagulants: new drugs and new concepts. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7(12):1333–51.
Cramer TJ, Griffin JH, Gale AJ. Factor V is an anticoagulant cofactor for activated protein C during inactivation of factor Va. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb. 2010;37(1):17–23.
Radtke KP, Griffin JH, Riceberg J, Gale AJ. Disulfide bond-stabilized factor VIII has prolonged factor VIIIa activity and improved potency in whole blood clotting assays. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5(1):102–8.
Mesters RM, Houghten RA, Griffin JH. Identification of a sequence of human activated protein C (residues 390–404) essential for its anticoagulant activity. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(36):24514–9.
Hemker HC, Giesen P, Al Dieri R, Regnault V, De Smedt E, Wagenvoord R, et al. Calibrated automated thrombin generation measurement in clotting plasma. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb. 2003;33(1):4–15.
Hendrickx ML, Zatloukalova M, Hassanzadeh-Ghassabeh G, Muyldermans S, Gils A, Declerck PJ. Identification of a novel, nanobody-induced, mechanism of TAFI inactivation and its in vivo application. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12(2):229–36.
Pellequer JL, Westhof E, Van Regenmortel MH. Correlation between the location of antigenic sites and the prediction of turns in proteins. Immunol Lett. 1993;36(1):83–99.
Odorico M, Pellequer JL. BEPITOPE: predicting the location of continuous epitopes and patterns in proteins. J Mol Recognit. 2003;16(1):20–2.
Larsen JE, Lund O, Nielsen M. Improved method for predicting linear B-cell epitopes. Immunome Res. 2006;2:2.
Rezaie AR. Regulation of the protein C anticoagulant and antiinflammatory pathways. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(19):2059–69.
Larsen MV, Lundegaard C, Lamberth K, Buus S, Lund O, Nielsen M. Large-scale validation of methods for cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope prediction. BMC Bioinforma. 2007;8:424.
Chen SW, Pellequer JL. Adepth: new representation and its implications for atomic depths of macromolecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:W412–6.
Gale AJ, Yegneswaran S, Xu X, Pellequer JL, Griffin JH. Characterization of a factor Xa binding site on factor Va near the Arg-506 activated protein C cleavage site. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(30):21848–55.
Rand MD, Hanson SR, Mann KG. Factor V turnover in a primate model. Blood. 1995;86(7):2616–23.
Tranholm M, Kristensen K, Kristensen AT, Pyke C, Rojkjaer R, Persson E. Improved hemostasis with superactive analogs of factor VIIa in a mouse model of hemophilia A. Blood. 2003;102(10):3615–20.
Mei B, Pan C, Jiang H, Tjandra H, Strauss J, Chen Y, et al. Rational design of a fully active, long-acting PEGylated factor VIII for hemophilia A treatment. Blood. 2010;116(2):270–9.
Elm T, Karpf DM, Ovlisen K, Pelzer H, Ezban M, Kjalke M, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a new recombinant FVIII (N8) in haemophilia A mice. Haemophilia. 2012;18(1):139–45.
Bunce MW, Toso R, Camire RM. Zymogen-like factor Xa variants restore thrombin generation and effectively bypass the intrinsic pathway in vitro. Blood. 2011;117(1):290–8.
Metzner HJ, Pipe SW, Weimer T, Schulte S. Extending the pharmacokinetic half-life of coagulation factors by fusion to recombinant albumin. Thromb Haemost. 2013;110(5):931–9.
Yatuv R, Robinson M, Dayan I, Baru M. Enhancement of the efficacy of therapeutic proteins by formulation with PEGylated liposomes; a case of FVIII, FVIIa and G-CSF. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2010;7(2):187–201.
Chitlur M, Warrier I, Rajpurkar M, Lusher JM. Inhibitors in factor IX deficiency a report of the ISTH-SSC international FIX inhibitor registry (1997–2006). Haemophilia. 2009;15(5):1027–31.
Kreuz W, Ettingshausen CE. Inhibitors in patients with haemophilia A. Thromb Res. 2014;134 Suppl 1:S22–6.
Mahlangu JN, Weldingh KN, Lentz SR, Kaicker S, Karim FA, Matsushita T, et al. Changes in the amino acid sequence of the rFVIIa analog, vatreptacog alfa, are associated with clinical immunogenicity. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13(11):1989–98.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS AND DISCLOSURES
This work was funded by grant support from an Early Career Development Award from Bayer Hemophilia (AvD), by National Institutes of Health grants HL104165 (LOM) and HL03195 and HL052246 (JHG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
AvD has received honoraria for participating in scientific advisory board panels, consulting, and speaking engagements for Baxalta, Pfizer, Biogen, CSL-Behring, Novo Nordisk, and Grifols. LOM has received research funding and honoraria for participating in scientific advisory board panels for Bayer. UCSD and TSRI hold intellectual property rights related to superFVa on which AvD, AJG, JHG, and LOM are listed as inventors. AvD, AJG, and LOM are founders of Hematherix LLC., a biotech company that is developing superFVa therapy for bleeding complications. AvD and LOM are members of the Board of Directors of Hematherix LLC.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gale, A.J., Bhat, V., Pellequer, JL. et al. Safety, Stability and Pharmacokinetic Properties of superFactor Va, a Novel Engineered Coagulation Factor V for Treatment of Severe Bleeding. Pharm Res 33, 1517–1526 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-016-1895-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-016-1895-3