Abstract
Purpose
To gain knowledge of lung clearance mechanisms of inhaled tissue plasminogen activator (tPA).
Methods
Using an in vivo mouse model and ex vivo murine whole organ cell suspensions, we examined the capability of the lungs to utilize LRP1 receptor-mediated endocytosis (RME) for the uptake of exogenous tPA with and without an LRP1 inhibitor, receptor associated protein (RAP), and quantitatively compared it to the liver. We also used a novel imaging technique to assess the amount LRP1 in sections of mouse liver and lung.
Results
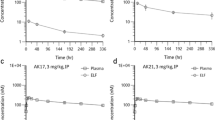
Following intratracheal administration, tPA concentrations in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) declined over time following two-compartment pharmacokinetics suggestive of a RME clearance mechanism. Ex vivo studies showed that lung and liver cells are similarly capable of tPA uptake via LRP1 RME which was reduced by ~50% by RAP. The comparable lung and liver uptake of tPA is likely due to equivalent amounts of LRP1 of which there was an abundance in the alveolar epithelium.
Conclusions
Our findings indicate that LRP1 RME is a candidate clearance mechanism for inhaled tPA which has implications for the development of safe and effective dosing regimens of inhaled tPA for the treatment of plastic bronchitis and other fibrin-inflammatory airway diseases in which inhaled tPA may have utility.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PB:
-
Plastic bronchitis
- tPA:
-
Tissue plasminogen activator
- RME:
-
Receptor mediated endocytosis
- RAP:
-
Receptor associated protein
- LRP1:
-
Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1
- MI:
-
Myocardial infarction
- AIS:
-
Acute ischemic stroke
- IT:
-
Intratracheal
- BALF:
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
References
Heath L, Ling S, Racz J, Mane G, Schmidt L, Myers JL, et al. Prospective, longitudinal study of plastic bronchitis cast pathology and responsiveness to tissue plasminogen activator. Pediatr Cardiol. 2011;32(8):1182–9.
Racz J, Mane G, Ford M, Schmidt L, Myers J, Standiford TJ, et al. Immunophenotyping and protein profiling of Fontan-associated plastic bronchitis airway casts. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013;10(2):98–107.
Schumacher KR, Stringer KA, Donohue JE, Yu S, Shaver A, Caruthers RL, et al. Fontan-associated protein-losing enteropathy and plastic bronchitis. J Pediatr. 2015.
Kunder R, Kunder C, Sun HY, Berry G, Messner A, Frankovich J, et al. Pediatric plastic bronchitis: case report and retrospective comparative analysis of epidemiology and pathology. Case Rep Pulmonol. 2013;2013:649365.
Brooks K, Caruthers RL, Schumacher KR, Stringer KA. Pharmacotherapy challenges of Fontan-associated plastic bronchitis: a rare pediatric disease. Pharmacotherapy. 2013;33(9):922–34.
Costello JM, Steinhorn D, McColley S, Gerber ME, Kumar SP. Treatment of plastic bronchitis in a Fontan patient with tissue plasminogen activator: a case report and review of the literature. Pediatrics. 2002;109(4), e67.
Do TB, Chu JM, Berdjis F, Anas NG. Fontan patient with plastic bronchitis treated successfully using aerosolized tissue plasminogen activator: a case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Cardiol. 2009;30(3):352–5.
Gibb E, Blount R, Lewis N, Nielson D, Church G, Jones K, et al. Management of plastic bronchitis with topical tissue-type plasminogen activator. Pediatrics. 2012;130(2):e446–50.
Lubcke NL, Nussbaum VM, Schroth M. Use of aerosolized tissue plasminogen activator in the treatment of plastic bronchitis. Ann Pharmacother. 2013;47(3), e13.
Collen D, Lijnen HR, Todd PA, Goa KL. Tissue-type plasminogen activator. A review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use as a thrombolytic agent. Drugs. 1989;38(3):346–88.
Loscalzo J, Braunwald E. Tissue plasminogen activator. N Engl J Med. 1988;319(14):925–31.
Kruithof EK, Dunoyer-Geindre S. Human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Thromb Haemost. 2014;112(2):243–54.
Seifried E, Tanswell P, Ellbruck D, Haerer W, Schmidt A. Pharmacokinetics and haemostatic status during consecutive infusions of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Thromb Haemost. 1989;61(3):497–501.
Seifried E, Tanswell P, Rijken DC, Barrett-Bergshoeff MM, Su CA, Kluft C. Pharmacokinetics of antigen and activity of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator after infusion in healthy volunteers. Arzneimittelforschung. 1988;38(3):418–22.
Tanswell P, Heinzel G, Greischel A, Krause J. Nonlinear pharmacokinetics of tissue-type plasminogen activator in three animal species and isolated perfused rat liver. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990;255(1):318–24.
Krippendorff BF, Kuester K, Kloft C, Huisinga W. Nonlinear pharmacokinetics of therapeutic proteins resulting from receptor mediated endocytosis. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2009;36(3):239–60.
Warshawsky I, Bu G, Schwartz AL. LRP and the receptor-mediated endocytosis of plasminogen activators. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994;737:70–87.
Camani C, Kruithof EK. Clearance receptors for tissue-type plasminogen activator. Int J Hematol. 1994;60(2):97–109.
Bu G, Williams S, Strickland DK, Schwartz AL. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor is an hepatic receptor for tissue-type plasminogen activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89(16):7427–31.
Lillis AP, Van Duyn LB, Murphy-Ullrich JE, Strickland DK. LDL receptor-related protein 1: unique tissue-specific functions revealed by selective gene knockout studies. Physiol Rev. 2008;88(3):887–918.
Moestrup SK, Gliemann J, Pallesen G. Distribution of the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in human tissues. Cell Tissue Res. 1992;269(3):375–82.
Strickland DK, Gonias SL, Argraves WS. Diverse roles for the LDL receptor family. Trends Endocrinol Metab TEM. 2002;13(2):66–74.
Uhlen M, Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM, Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science New York, NY. 2015;347(6220):1260419.
Wygrecka M, Wilhelm J, Jablonska E, Zakrzewicz D, Preissner KT, Seeger W, et al. Shedding of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184(4):438–48.
Soler Artigas M, Loth DW, Wain LV, Gharib SA, Obeidat M, Tang W, et al. Genome-wide association and large-scale follow up identifies 16 new loci influencing lung function. Nat Genet. 2011;43(11):1082–90.
Meng H, Chen G, Zhang X, Wang Z, Thomas DG, Giordano TJ, et al. Stromal LRP1 in lung adenocarcinoma predicts clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2011;17(8):2426–33.
Lackowski NP, Pitzer JE, Tobias M, Van Rheen Z, Nayar R, Mosharaff M, et al. Safety of prolonged, repeated administration of a pulmonary formulation of tissue plasminogen activator in mice. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010;23(2):107–14.
Stringer KA, Tobias M, Dunn JS, Campos J, Van Rheen Z, Mosharraf M, et al. Accelerated dosing frequency of a pulmonary formulation of tissue plasminogen activator is well-tolerated in mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008;35(12):1454–60.
Stringer KA, Racz J, Heath L, Southard S, Lackowski NP, Tsai WC, Caruthers RL. Low expression of low density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein (LRP)-1 in the airway contributes to the slow elimination of lung delivered Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA). Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183.
Bauman KA, Wettlaufer SH, Okunishi K, Vannella KM, Stoolman JS, Huang SK, et al. The antifibrotic effects of plasminogen activation occur via prostaglandin E2 synthesis in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(6):1950–60.
Okunishi K, Sisson TH, Huang SK, Hogaboam CM, Simon RH, Peters-Golden M. Plasmin overcomes resistance to prostaglandin E2 in fibrotic lung fibroblasts by reorganizing protein kinase A signaling. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(37):32231–43.
Millien VO, Lu W, Mak G, Yuan X, Knight JM, Porter P, et al. Airway fibrinogenolysis and the initiation of allergic inflammation. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014;11 Suppl 5:S277–83.
Corti M, Brody AR, Harrison JH. Isolation and primary culture of murine alveolar type II cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1996;14(4):309–15.
Ballinger MN, Newstead MW, Zeng X, Bhan U, Horowitz JC, Moore BB, et al. TLR signaling prevents hyperoxia-induced lung injury by protecting the alveolar epithelium from oxidant-mediated death. J Immunol (Baltim Md: 1950). 2012;189(1):356–64.
Chen J, Chen Z, Narasaraju T, Jin N, Liu L. Isolation of highly pure alveolar epithelial type I and type II cells from rat lungs. Lab Investig. 2004;84(6):727–35.
Dunn JS, Nayar R, Campos J, Hybertson BM, Zhou Y, Manning MC, et al. Feasibility of tissue plasminogen activator formulated for pulmonary delivery. Pharm Res. 2005;22(10):1700–7.
Foster WM, Walters DM, Longphre M, Macri K, Miller LM. Methodology for the measurement of mucociliary function in the mouse by scintigraphy. J Appl Physiol. 2001;90(3):1111–7.
Sakamoto A, Matsumaru T, Yamamura N, Suzuki S, Uchida Y, Tachikawa M, et al. Drug transporter protein quantification of immortalized human lung cell lines derived from tracheobronchial epithelial cells (Calu-3 and BEAS2-B), bronchiolar-alveolar cells (NCI-H292 and NCI-H441), and alveolar type II-like cells (A549) by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Sci. 2015.
Patton JS, Brain JD, Davies LA, Fiegel J, Gumbleton M, Kim KJ, et al. The particle has landed-characterizing the fate of inhaled pharmaceuticals. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010;23:S71–87.
Takano M, Kawami M, Aoki A, Yumoto R. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of macromolecules and strategy to enhance their transport in alveolar epithelial cells. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014;1–13.
Biessen EA, van Teijlingen M, Vietsch H, Barrett-Bergshoeff MM, Bijsterbosch MK, Rijken DC, et al. Antagonists of the mannose receptor and the LDL receptor-related protein dramatically delay the clearance of tissue plasminogen activator. Circulation. 1997;95(1):46–52.
Luo M, Hajjar KA. Annexin A2 system in human biology: cell surface and beyond. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2013;39(4):338–46.
Hu K, Yang J, Tanaka S, Gonias SL, Mars WM, Liu Y. Tissue-type plasminogen activator acts as a cytokine that triggers intracellular signal transduction and induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(4):2120–7.
Lin L, Wu C, Hu K. Tissue plasminogen activator activates NF-kappaB through a pathway involving annexin A2/CD11b and integrin-linked kinase. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN. 2012;23(8):1329–38.
Mantuano E, Lam MS, Gonias SL. LRP1 assembles unique co-receptor systems to initiate cell signaling in response to tissue-type plasminogen activator and myelin-associated glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(47):34009–18.
Liu Z, Ma Y, Moyer MP, Zhang P, Shi C, Qin H. Involvement of the mannose receptor and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway of the microdomain of the integral membrane protein after enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection. Infect Immun. 2012;80(4):1343–50.
Hastings RH, Folkesson HG, Matthay MA. Mechanisms of alveolar protein clearance in the intact lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004;286(4):L679–89.
Dobbs LG, Johnson MD. Alveolar epithelial transport in the adult lung. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2007;159(3):283–300.
Santos Cavaiola T, Edelman S. Inhaled insulin: a breath of fresh air? A review of inhaled insulin. Clin Ther. 2014;36(8):1275–89.
Weers JG, Bell J, Chan HK, Cipolla D, Dunbar C, Hickey AJ, et al. Pulmonary formulations: what remains to be done? J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010;23:S5–S23.
Hickey AJ. Back to the future: inhaled drug products. J Pharm Sci. 2013;102(4):1165–72.
Zhang C, An J, Strickland DK, Yepes M. The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 mediates tissue-type plasminogen activator-induced microglial activation in the ischemic brain. Am J Pathol. 2009;174(2):586–94.
Nilsson A, Vesterlund L, Oldenborg PA. Macrophage expression of LRP1, a receptor for apoptotic cells and unopsonized erythrocytes, can be regulated by glucocorticoids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;417(4):1304–9.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS AND DISCLOSURES
This study was supported, in part, by a grant (HD065594 to KAS) from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), a grant (HL071439 to KAS) from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI), and a grant (GM078200 to GRR) from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NICHD, NHLBI, NIGMS or the National Institutes of Health.
We would like to acknowledge and thank Dr. Katherine Eichinger (Benz) and Nicholas Lackowski for their help with the in vivo mouse work and Dr. Ingrid Bergin of the University of Michigan Laboratory Animal Medicine Pathology core for her invaluable help and guidance with the LRP1 staining.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, S., Racz, J., Tai, M.F. et al. A Role for Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 in the Cellular Uptake of Tissue Plasminogen Activator in the Lungs. Pharm Res 33, 72–82 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-015-1763-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-015-1763-6