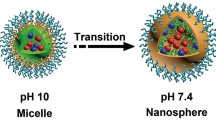
ABSTRACT
Purpose
To develop a multimodal imaging guided and triggered drug delivery system based on a novel emulsion formulation composed of iron oxide nanoparticles, nanoscopic bubbles, and oil containing drugs.
Methods
Iron oxide paramagnetic nanoparticles were synthesized and modified with surface conjugation of polyethylenimide (PEI) or Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA). Both particles were used to disperse and stabilize oil in water emulsions containing coumarin-6 as the model drug. Sulfur hexafluoride was introduced into the oil phase to form nanoscopic bubbles inside the emulsions. The resulted gas containing emulsions were evaluated for their magnetic resonance (MR) and ultrasound (US) imaging properties. The drug release profile triggered by ultrasound was also examined.
Results
We have successfully prepared the highly integrated multi-component emulsion system using the surface modified iron oxide nanoparticles to stabilize the interfaces. The resulted structure had distinctive MR and US imaging properties. Upon application of ultrasound waves, the gas containing emulsion would burst and encapsulated drug could be released.
Conclusion
The integrated emulsion formulation was multifunctional with paramagnetic, sono-responsive and drug-carrying characteristics, which may have potential applications for disease diagnosis and imaging guided drug release.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Voliani V, Signore G, Nifosi R, Ricci F, Luin S, Beltram F. Smart delivery and controlled drug release with gold nanoparticles: new frontiers in nanomedicine. Recent Patents Nanomed. 2012;2:34–44.
Kelkar SS, Reineke TM. Theranostics: combining imaging and therapy. Bioconjug Chem. 2011;22:1879–903.
Janib SM, Moses AS, MacKay JA. Imaging and drug delivery using theranostic nanoparticles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62:1052–63.
Li S, Goins B, Zhang L, Bao A. Novel multifunctional theranostic liposome drug delivery system: construction, characterization, and multimodality MR, near-infrared fluorescent, and nuclear imaging. Bioconjug Chem. 2012;23:1322–32.
Terreno E, Uggeri F, Aime S. Image guided therapy: the advent of theranostic agents. J Control Release. 2012;161:328–37.
Lorenzato C, Cernicanu A, Meyre ME, Germain M, Pottier A, Levy L, et al. MRI contrast variation of thermosensitive magnetoliposomes triggered by focused ultrasound: a tool for image-guided local drug delivery. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2013;8:185–92.
Lee GY, Qian WP, Wang L, Wang YA, Staley CA, Satpathy M, et al. Theranostic nanoparticles with controlled release of gemcitabine for targeted therapy and MRI of pancreatic cancer. ACS Nano. 2013;7:2078–89.
Staruch R, Chopra R, Hynynen K. Localised drug release using MRI-controlled focused ultrasound hyperthermia. Int J Hyperthermia. 2011;27:156–71.
Zhang K, Wu W, Guo K, Chen J, Zhang P. Magnetic polymer enhanced hybrid capsules prepared from a novel Pickering emulsion polymerization and their application in controlled drug release. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2009;349:110–6.
Taratula O, Garbuzenko O, Savla R, Wang YA, He H, Minko T. Multifunctional nanomedicine platform for cancer specific delivery of siRNA by superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles-dendrimer complexes. Curr Drug Deliv. 2011;8:59–69.
Khemtong C, Kessinger CW, Gao J. Polymeric nanomedicine for cancer MR imaging and drug delivery. Chem Commun (Camb). 2009;24:3497–510.
Tai LA, Tsai PJ, Wang YC, Wang YJ, Lo LW, Yang CS. Thermosensitive liposomes entrapping iron oxide nanoparticles for controllable drug release. Nanotechnology. 2009;20:135101.
Park JH, von Maltzahn G, Ong LL, Centrone A, Hatton TA, Ruoslahti E, et al. Cooperative nanoparticles for tumor detection and photothermally triggered drug delivery. Adv Mater. 2010;22:880–5.
Geers B, Dewitte H, De Smedt SC, Lentacker I. Crucial factors and emerging concepts in ultrasound-triggered drug delivery. J Control Release. 2012;164:248–55.
Marin A, Muniruzzaman M, Rapoport N. Acoustic activation of drug delivery from polymeric micelles: effect of pulsed ultrasound. J Control Release. 2001;71:239–49.
Sridhar-Keralapura M, Thirumalai S, Mobed-Miremadi M. Structural changes and imaging signatures of acoustically sensitive microcapsules under ultrasound. Ultrasonics. 2013;53:1044–57.
Deckersand R, Moonen CT. Ultrasound triggered, image guided, local drug delivery. J Control Release. 2010;148:25–33.
Gao MZ, Fain HD, Rapoport N. Ultrasound-enhanced tumor targeting of polymeric micellar drug carriers. Mol Pharm. 2004;1:317–30.
Schroeder A, Honen R, Turjeman K, Gabizon A, Kost J, Barenholz Y. Ultrasound triggered release of cisplatin from liposomes in murine tumors. J Control Release. 2009;137:63–8.
Wang Y, Li X, Zhou Y, Huang P, Xu Y. Preparation of nanobubbles for ultrasound imaging and intracelluar drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2010;384:148–53.
de Smet M, Heijman E, Langereis S, Hijnen NM, Grüll H. Magnetic resonance imaging of high intensity focused ultrasound mediated drug delivery from temperature-sensitive liposomes: an in vivo proof-of-concept study. J Control Release. 2011;150:102–10.
de Smet M, Hijnen NM, Langereis S, Elevelt A, Heijman E, Dubois L, et al. Magnetic resonance guided high-intensity focused ultrasound mediated hyperthermia improves the intratumoral distribution of temperature-sensitive liposomal doxorubicin. Investig Radiol. 2013;48:395–405.
Liu SP, Wei XH, Chu MQ, Peng JL, Xu YH. Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide/polymer composite nanoparticles with pendent functional groups. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2006;51:101–6.
Prestidgeand C, Simovic S. Nanoparticle encapsulation of emulsion droplets. Int J Pharm. 2006;324:92–100.
Saleh N, Sarbu T, Sirk K, Lowry G, Matyjaszewski K, Tilton R. Oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by highly charged polyelectrolyte-grafted silica nanoparticles. Langmuir. 2005;21:9873–8.
Wang C, Zhang C, Li Y, Chen Y, Tong Z. Facile fabrication of nanocomposite microspheres with polymer cores and magnetic shells by Pickering suspension polymerization. React Funct Polym. 2009;69:750–4.
Whitby C, Fornasiero D, Ralston J. Structure of oil-in-water emulsions stabilised by silica and hydrophobised titania particles. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2010;342:205–9.
Simovic S, Hui H, Song Y, Davey A, Rades T, Prestidge C. An oral delivery system for indomethicin engineered from cationic lipid emulsions and silica nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2010;143:367–73.
Simovicand S, Prestidge C. Nanoparticle layers controlling drug release from emulsions. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007;67:39–47.
Yang F, Li Y, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Wu J, Gu N. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle-embedded encapsulated microbubbles as dual contrast agents of magnetic resonance and ultrasound imaging. Biomaterials. 2009;30:3882–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Li, D., Zhu, Ja. et al. A Magnetic Nanoparticle Stabilized Gas Containing Emulsion for Multimodal Imaging and Triggered Drug Release. Pharm Res 31, 1477–1484 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-014-1365-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-014-1365-8