ABSTRACT
Purpose
Fractal analysis was used as a tool in order to study the morphological characteristics of PEGylated liposomes. We report on the morphological characteristics of stealth liposomes composed of DPPC and DPPE-PEG 3000 in two dispersion media using fractal analysis.
Methods
Light scattering techniques were used in order to elucidate the size, the morphology and the surface charge of PEGylated liposomes as a function of PEGylated lipid concentration and temperature. Fluorescence spectroscopy studies revealed a microenvironment of low polarity inside the liposomal membranes.
Results
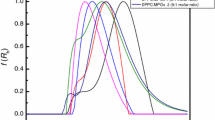
All formulations were found to retain their physicochemical characteristics for at least 3 weeks. The hydrodynamic radii (Rh) of stealth liposomes were stable in the process of heating up to 50°C; while the fractal dimension values (df) which correspond to their morphology, have been changed during heating. Hence, these results are a first indication of the presence of a heterogeneous microdomain structure of the stealth liposomal system. The amphiphilic drug indomethacin (IND) was successfully encapsulated within the liposomes and led to an increased size of stealth liposomes, while the morphology of liposomal vectors changed significantly at the highest molar ratio of PEGylated lipid.
Conclusions
We can state that this approach can promote a new analytical concept based on the morphological characteristics and quantify the shape of drug carriers complementary to that of the conventional analytical techniques.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- df :
-
mass fractal
- DLCA:
-
diffusion-limited cluster aggregation
- DPPC:
-
1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- DPPE-PEG 3000:
-
1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[Methoxy(Polyethylene glycol)-3000]
- ds :
-
surface fractal
- IND:
-
indomethacin
- NSAIDs:
-
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffer saline
- RLCA:
-
reaction-limited cluster aggregation
References
Kingsley JD, Dou H, Morehead J, Rabinow B, Gendelman HE, Destache CJ. Nanotechnology: a focus on nanoparticles as drug delivery system. J Neuroimmume Pharmacol. 2006;1:340–50.
Kayser O, Lemke A, Hernández-Trejo N. The impact of nanobiotechnology on the development of new drug delivery systems. Curr Pharm Biotechol. 2005;6(1):3–5.
Alexis F, Rhee JW, Richie JP, Radovic-Moreno AF, Langer R, Farokhzad OC. New frontiers in nanotechnology for cancer treatment. Urol Oncol. 2008;26(1):74–85.
Rawat M, Singh D, Saraf S, Saraf S. Nanocarriers: promising vesicle for bioactive drugs. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006;29(9):1790–8.
Cattel L, Ceruti M, Dosio F. From conventional to stealth liposomes: a new Frontier in cancer chemotherapy. J Chemother. 2004;16(4):94–7.
Immordino ML, Dosio F, Cattel L. Stealth liposomes: review of the basic science, rationale, and clinical applications, existing and potential. Int J Nanomedicine. 2006;1(3):297–315.
Moghimi SM, Szebeni J. Stealth liposomes and long circulating nanoparticles: critical issues in pharmacokinetics, opsonization and protein-binding properties. Prog Lipid Res. 2003;42(6):463–78.
Samad A, Sultana Y, Aqil M. Liposomal drug delivery systems: an update review. Curr Drug Deliv. 2007;4(4):297–305.
Mufamadi MS, Pillay V, Choonara YE, Du Toit LC, GirishModi G, Naidoo D, et al. A review on composite liposomal technologies for specialized drug delivery. J Drug Delivery. 2011;2011:939851–70.
Sabín J, Prieto G, Ruso JM, Sarmiento F. Fractal aggregates induced by liposome-liposome interaction in the presence of Ca2+. Eur Phys J E. 2007;24:201–10.
Sabín J, Prieto G, Ruso JM, Messina PV, Sarmiento F. Aggregation of liposomes in presence of La3+: a study of the fractal dimension. Phys Rev E. 2007;76(011408):1–7.
Roldán-Vargas S, Barnabas-Rodrígez R, Martín-Molina A, Quesada-Pérez M, Estelrich J, Callejas-Fernández J. Growth of lipid vesicle structures: from surface fractals to mass fractals. Phys Rev E. 2008;78(010902(R)):1–4.
Roldán-Vargas S, Barnabas-Rodrígez R, Quesada-Pérez M, Estelrich J, Callejas-Fernández J. Surface fractals in liposome aggregation. Am Phys Soc Phys Rev. 2009;79:1–14.
Pippa N, Pispas S, Demetzos C. The fractal hologram and elucidation of the structure of liposomal carriers in aqueous and biological media. Int J Pharm. 2012;430(1–2):65–73.
Pippa N, Pispas S, Demetzos C. The delineation of the morphology of charged liposomal vectors via fractal analysis in aqueous and biological media: Physicochemical and self-assembly studies. Int J Pharm. 2012;437:264–74.
Derjaguin BV, Landau LD. Theory of the stability of stronglycharged lyophobic sols and of adhesion of strongly charged particles in solution of electrolytes. Acta Physicochim URRS. 1941;14:633–62.
Verwey EJB, Overbeek JTHG. Theory of the stability of lyophobic colloids. Amsterdan: Elsevier; 1948. p. 108.
Sabín J, Prieto G, Messina PV, Ruso JM, Hidalgo-Álvarez R, Sarmiento F. On the effect of Ca2+ and La3+ on the colloidal stability of liposomes. Langmuir. 2005;21:10968–75.
Sabín J, Prieto G, Ruso JM, Hidalgo-Álvarez R, Sarmiento F. Size and stability of liposomes: a possible role of hydration and osmotic forces. Eur Phys JE. 2006;20:401–8.
Lin MY, Lindsay HM, Weitz DA, Klein R, Ball RC, Meakin P. Universal reaction—limited colloid aggregation. Nature. 1989;339:360–2.
Gregory J. Monitoring particle aggregation processes. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2009;147–148:109–23.
Soh JW, Weinstein IB. Role of COX-indepedent targets of NSAIDs and related coumpounds in cancer prevention and treatment. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 2003;37:261–85.
Xu XC. COX-2 inhibitors in cancer treatment and prevention, a recent development. Anticancer Drugs. 2002;13(2):127–37.
Rao CV, Reddy BS. NSAIDs and chemoprevention. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004;4(1):29–42.
Caruso I, Bianchi PG. Gastroscopic evaluation of anti-inflammatory agents. Br Med J. 1980;280(6207):75–8.
Morris AD, Holt SD, Silvoso GR, Hewitt J, Tatum W, Grandione J, et al. Effect of anti-inflammatory drug administration in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. An endoscopic assessment. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1981;67:131–5.
Zhou Y, Dial EJ, Doyen R, Lichtenberger LM. Effect of indomethacin on bile acid-phospholipid interactions: implication for small intestinal injury induced by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010;298(5):G722–731.
Soehngen EC, Godin-Ostro E, Fielder FG, Ginsberg RS, Slusher MA, Weiner AL. Encapsulation of indomethacin in liposomes provides protection against both gastric and intestinal ulceration when orally administered to rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31(3):414–22.
Chen H, Gao J, Wang F, Liang W. Preparation, characterization and pharmacokinetics of liposomes-encapsulated cyclodextrins inclusion complexes for hydrophobic drugs. Drug Deliv. 2007;14(4):201–8.
Milonaki Y, Kaditi E, Pispas S, Demetzos C. Amphiphilic gradient copolymers of 2-methyl- and 2-phenyl-2-oxazoline: self-organization in aqueous media and drug encapsulation. J Polymer Sci, Part A: Polymer Chem. 2011;50:1226–37.
Jaafar-Maalej C, Charcosset C, Fessi H. A new method for liposome preparation using a membrane contactor. J Liposome Res. 2011;21(3):213–20.
Sugihara H, Yamamoto H, Kawashima Y, Takeuchi H. Effectiveness of submicronized chitosan-coated liposomes in oral absorption of indomethacin. J Liposome Res. 2012;22(1):72–9.
Lim SB, Banerjee A, Onyüksel H. Improvement of drug safety by the use of lipid-based nanocarriers. J Control Release. 2012;163(1):34–45.
Dokoumetzidis A, Karalis V, Iliadis A, Macheras P. The heterogeneous course of drug transit through the body. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004;25(3):140–6.
Dokoumetzidis A, Papadopoulou V, Valsami G, Macheras P. Development of a reaction-limited model of dissolution: application to official dissolution tests experiments. Int J Pharm. 2008;355:114–25.
Dokoumetzidis A, Macheras P. The changing face of the rate concept in biopharmaceutical sciences: from classical to fractal and finally to fractional. Pharm Res. 2011;28:1229–32.
Pereira LM. Fractal pharmacokinetics. Comput Math Methods Med. 2010;11(2):161–84.
Heutault B, Saulnier P, Pech B, Proust JE, Benoit JP. Physico-chemical stability of colloidal lipid particles. Biomaterials. 2003;24:4283–300.
Ganguly R, Asawal VK. Improved micellar hydration and gelation characteristics of PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymer solution in the precence of LiCl. J Phys Chem B. 2008;112:7726–31.
Burchard W. Static and dynamic light scattering from branched polymers and biopolymers. Adv Polym Sci. 1983;48:1–124.
Belsito B, Bartucci R, Sportelli L. Sterically stabilized liposomes of DPPC/DPPE-PEG:2000. A spin label ESR and spectrophotometric study. Biophys Chem. 1998;75(1):33–43.
Silvander M, Hansson P, Edwards K. Liposomal surface potential and bilayer packing as affected by PEG-lipid inclusion. Langmuir. 2000;16:3693–702.
Liu F, Liu D. Long-circulating emulsions (oil in water) as carriers for lipophilic drugs. Pharm Res. 1995;12:1060–4.
Liu F, Liu D. Serum independent liposome uptake by mouse liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1278:5–11.
Shimanouchi T, Sasaki M, Hiroiwa A, Yoshimoto N, Miyagawa K, Umakoshim H, et al. Relationship between the mobility of phosphocholine headgroups of liposomes and the hydrophobicity at the membrane interface: a characterization with spectrophotometric measurements. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011;88:221–30.
Vogtt K, Joworrek C, Garamus VM, Winter R. Microdomains in lipid vesicles: structure and distribution assessed by small-angle scattreing. J Phys Chem B. 2010;114:5643–8.
Giraud MN, Motta C, Romero JJ, Bommelaer G, Lichtenberger LM. Interaction of indomethacin and naproxen with gastric surface-active phospholipids: a possible mechanism for the gastric toxicity of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Biochem Pharmacol. 1999;57(3):247–54.
Lichtenberger LM, Wang ZM, Romero JJ, Ulloa C, Perez JC, Giraud MN, et al. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) associate with zwitterionic phospholipids: insight into the mechanism and reversal of NSAID-induced gastrointestinal injury. Nat Med. 1995;1(2):154–8.
Lichtenberger LM, Zhou Y, Dial EJ, Raphael RM. NSAID injury to the gastrointestinal tract: evidence that NSAIDs interact with phospholipids to weaken the hydrophobic surface barrier and induce the formation of unstable pores in membranes. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2006;58(11):1421–8.
Zhou Y, Raphael RM. Effect of salicylate on the elasticity, bebding stiffness, and strength of SOPC. Biophys J. 2005;89(3):1789–801.
Lúcio M, Bringezu F, Reis S, Lima JL, Brezesinski G. Binding of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to DPPC: structure and thermodynamic aspects. Langmuir. 2008;24(8):4132–9.
Nunes C, Brezesinski G, Pereira-Leite C, Lima JL, Reis S, Lúcio M. NSAIDs interactions with membranes: a biophysical approach. Langmuir. 2011;27(17):10847–58.
Srinath P, Vyas SP, Diwan PV. Preparation and pharmacodynamic evaluation of liposomes of indomethacin. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2000;26(3):313–21.
Srinath P, Vyas SP, Diwan PV. Long-circulating liposomes of indomethacin in arthritic rats—a biodisposition study. Pharm Acta Helv. 2000;74(4):399–404.
Palakurthi S, Vyas SP, Diwan PV. Biodisposition of PEG-coated lipid microspheres of indomethacin in arthritic rats. Int J Pharm. 2005;290:55–62.
Zhou Y, Cho KJ, Plownan SJ, Hancock JF. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs alter the spatiotemporal organization of Ras proteins on the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(20):16586–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pippa, N., Psarommati, F., Pispas, S. et al. The Shape/Morphology Balance: A Study of Stealth Liposomes via Fractal Analysis and Drug Encapsulation. Pharm Res 30, 2385–2395 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-1082-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-1082-8