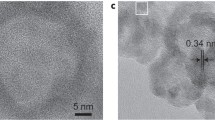
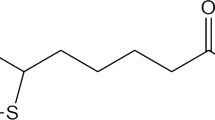
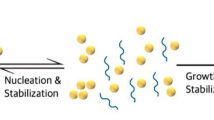
ABSTRACT
Purpose
We describe a nucleation-based method which allows for the generation of monodisperse lipid nanoparticles over a range of diameters. Using a set of novel zwitterionic lipids and inverse phosphocholine lipids with pKas ranging from 2 to 5, we showed how the hydrodynamic diameter of lipid nanoparticles can be systematically manipulated over a 60 nm to 500 nm size range.
Method
Lipid nanoparticles were prepared by adding an anti-solvent, such as water, to the organic phase containing the lipid components. This led to super-saturation and the spontaneous formation of particles.
Results
The growth and final particle size was controlled by the ratio of the components in the ternary system: lipid, organic solvent and aqueous phase. Particles with diameter below 125 nm were formed under conditions where the super-saturation coefficient was between 2.3 and 20. PEG-lipid served as an efficient growth inhibitor except at very high and low lipid concentrations. Encapsulation efficiency of siRNA into lipid nanoparticles was shown to be pH-dependent and requires the protonation of the anionic carboxylate groups of the zwitterionic lipids, emphasizing the importance of electrostatic forces.
Conclusion
This process enables high encapsulation efficiency of nucleic acids and allows the size of lipid nanoparticles to be controlled.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Nguyen J, Szoka FC. Nucleic acid delivery: the missing pieces of the puzzle? Accounts of Chemical Research. 2012.
Akinc A, Goldberg M, Qin J, Dorkin JR, Gamba-Vitalo C, Maier M, et al. Development of lipidoid-siRNA formulations for systemic delivery to the liver. Mol Ther. 2009;17(5):872–9.
Semple SC, Akinc A, Chen J, Sandhu AP, Mui BL, Cho CK, et al. Rational design of cationic lipids for siRNA delivery. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(2):172–6.
Gaumet M, Vargas A, Gurny R, Delie F. Nanoparticles for drug delivery: the need for precision in reporting particle size parameters. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;69(1):1–9.
Nagayasu A, Uchiyama K, Kiwada H. The size of liposomes: a factor which affects their targeting efficiency to tumors and therapeutic activity of liposomal antitumor drugs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1999;40(1–2):75–87.
Li W, Szoka Jr FC. Lipid-based nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery. Pharm Res. 2007;24(3):438–49.
Wisse E, Jacobs F, Topal B, Frederik P, De Geest B. The size of endothelial fenestrae in human liver sinusoids: implications for hepatocyte-directed gene transfer. Gene Ther. 2008;15(17):1193–9.
Hirota S, de Ilarduya CT, Barron LG, Szoka Jr FC. Simple mixing device to reproducibly prepare cationic lipid-DNA complexes (lipoplexes). Biotechniques. 1999;27(2):286–90.
Semple SC, Klimuk SK, Harasym TO, Dos Santos N, Ansell SM, Wong KF, et al. Efficient encapsulation of antisense oligonucleotides in lipid vesicles using ionizable aminolipids: formation of novel small multilamellar vesicle structures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1510(1–2):152–66.
Jeffs LB, Palmer LR, Ambegia EG, Giesbrecht C, Ewanick S, MacLachlan I. A scalable, extrusion-free method for efficient liposomal encapsulation of plasmid DNA. Pharm Res. 2005;22(3):362–72.
D’Addio SM, Prud’homme RK. Controlling drug nanoparticle formation by rapid precipitation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(6):417–26.
Horn D, Rieger J. Organic nanoparticles in the aqueous phase-theory, experiment, and use. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2001;40(23):4330–61.
Mahajan A, Kirwan D. Nucleation and growth-kinetics of biochemicals measured at high supersaturations. J Chryst Growth. 1994;144:281–90.
Walsh CL, Nguyen J, Szoka FC. Synthesis and characterization of novel zwitterionic lipids with pH-responsive biophysical properties. Chem Commun, in press.
Perttu EK, Kohli AG, Szoka FC. Inverse-phosphocholine lipids: a remix of a common phospholipid. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134(10):4485–8.
Kumar VV. Complementary molecular shapes and additivity of the packing parameter of lipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88(2):444–8.
Shew RL, Deamer DW. A novel method for encapsulation of macromolecules in liposomes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1985;816(1):1–8.
Szoka Jr F, Papahadjopoulos D. Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978;75(9):4194–8.
Zhang N, Tan C, Cai P, Jiang Y, Zhang P, Zhao Y. Synthesis and properties of morpholino chimeric oligonucleotides. Tetrahedon Lett. 2008;49(22):3570–3.
Schmid P, Hunter E. Extraction and purification of lipids. I. Solubility of lipids in biologically important solvents. Physiol Chem Phys. 1971;3:98–102.
Aubry J, Ganachaud F, Cohen Addad JP, Cabane B. Nanoprecipitation of polymethylmethacrylate by solvent shifting: 1. Boundaries. Langmuir. 2009;25(4):1970–9.
Bar LK, Garti N, Sarig S, Bar R. Solubilities of cholesterol, sitosterol, and cholesteryl acetate in polar organic solvents. J Chem Eng Data. 1984;29(4):440–3.
Chen T, D’Addio SM, Kennedy MT, Swietlow A, Kevrekidis IG, Panagiotopoulos AZ, et al. Protected peptide nanoparticles: experiments and brownian dynamics simulations of the energetics of assembly. Nano Lett. 2009;9(6):2218–22.
Liu Y, Kathan K, Saad W, Prud’homme RK. Ostwald ripening of beta-carotene nanoparticles. Phys Rev Lett. 2007;98(3):036102.
Cao G. Nanostructures & nanomaterials: synthesis, properties & applications. 2004.
Lasic DD, Ceh B, Stuart MC, Guo L, Frederik PM, Barenholz Y. Transmembrane gradient driven phase transitions within vesicles: lessons for drug delivery. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1239(2):145–56.
Guo X, Szoka Jr FC. Steric stabilization of fusogenic liposomes by a low-pH sensitive PEG–diortho ester–lipid conjugate. Bioconjug Chem. 2001;12(2):291–300.
Holland JW, Hui C, Cullis PR, Madden TD. Poly(ethylene glycol)–lipid conjugates regulate the calcium-induced fusion of liposomes composed of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine. Biochemistry. 1996;35(8):2618–24.
Guida V. Thermodynamics and kinetics of vesicles formation processes. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2010;161(1–2):77–88.
Lasic DD, Joannic R, Keller BC, Frederik PM, Auvray L. Spontaneous vesiculation. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2001;89–90:337–49.
DeMello AJ. Control and detection of chemical reactions in microfluidic systems. Nature. 2006;442(7101):394–402.
Huang X, Caddell R, Yu B, Xu S, Theobald B, Lee LJ, et al. Ultrasound-enhanced microfluidic synthesis of liposomes. Anticancer Res. 2010;30(2):463–6.
Jahn A, Stavis SM, Hong JS, Vreeland WN, DeVoe DL, Gaitan M. Microfluidic mixing and the formation of nanoscale lipid vesicles. ACS Nano. 2010;4(4):2077–87.
Jahn A, Vreeland WN, DeVoe DL, Locascio LE, Gaitan M. Microfluidic directed formation of liposomes of controlled size. Langmuir. 2007;23(11):6289–93.
Jahn A, Vreeland WN, Gaitan M, Locascio LE. Controlled vesicle self-assembly in microfluidic channels with hydrodynamic focusing. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126(9):2674–5.
Mengeaud V, Josserand J, Girault HH. Mixing processes in a zigzag microchannel: finite element simulations and optical study. Anal Chem. 2002;74(16):4279–86.
Stroock AD, Dertinger SK, Ajdari A, Mezic I, Stone HA, Whitesides GM. Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science. 2002;295(5555):647–51.
Valencia PM, Basto PA, Zhang L, Rhee M, Langer R, Farokhzad OC, et al. Single-step assembly of homogenous lipid-polymeric and lipid-quantum dot nanoparticles enabled by microfluidic rapid mixing. ACS Nano. 2010;4(3):1671–9.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS & DISCLOSURES
We are grateful for the financial support from the NIH (2R01EB003008-08) and Pfizer QB3. Juliane Nguyen is supported by the postdoctoral research fellowship from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG). Colin Walsh and Emily Perttu are supported by the NSF pre-doctoral fellowship. Michael Motion is supported by a fellowship of the NIH NIGMS. We acknowledge Charles Noble and Mark Hayes for their technical help with the HPLC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, J., Walsh, C.L., Motion, J.P.M. et al. Controlled Nucleation of Lipid Nanoparticles. Pharm Res 29, 2236–2248 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0752-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0752-2