ABSTRACT
Purpose
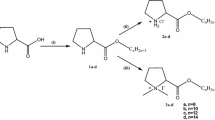
Novel surfactants made of diglutamic acid (DG) polar head linked to lithocholic, arachidonic, linoleic or stearic acids were designed for drug solubilization.
Methods
Surfactants 3-D conformer and packing parameter were determined by molecular modelling and self-assembling properties by pyrene fluorescence measurements. Cytotoxicity was assessed on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) and haemolyitic activity on rat red blood cells. Drug solubilization was quantified and its interaction with hydrophobic moieties was characterized using differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction. Self organisation of stearoyl-DG was observed by cryogenic transmission electron microscopy. Toxicity after repeated injections of stearoyl-DG was investigated in Wistar rats.
Results
DG-based surfactants self-assemble into water and their critical micellar concentrations are comprised between 200 and 920 μg/mL. Cytotoxicity and haemolysis were lower than for polysorbate 80. At best, stearoyl-DG solubilized the drug up to 22% (w/w). Solid-state characterization evidenced drug/lipid interactions leading to the formation of a new complex. Stearoyl-DG formed spherical micelles of 20 nm, as predicted by packing parameter calculation. However, it induced a possible liver toxicity after intravenous administration in rats.
Conclusions
Among the surfactants tested, stearoyl-DG is the more efficient for drug solubilization but its use is limited by its possible liver toxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Engels FK, Mathot RA, Verweij J. Alternative drug formulations of docetaxel: a review. Anticancer Drugs. 2007;18:95–103.
Gelderblom H, Verweij J, Nooter K, Sparreboom A. Cremophor EL: the drawbacks and advantages of vehicle selection for drug formulation. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37:1590–8.
ten Tije AJ, Verweij J, Loos WJ, Sparreboom A. Pharmacological effects of formulation vehicles: implications for cancer chemotherapy. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003;42:665–85.
Nakashio F, Goto M, Matsumoto M, Irie J, Kondo K. Role of surfactants in the behavior of emulsion liquid membranes – development of new surfactants. J Membr Sci. 1988;38:249–60.
Wang Y, Guo R, Xi J. Comparative studies of interactions of hemoglobin with single-chain and with gemini surfactants. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2009;331:470–5.
Zhao X. Design of self-assembling surfactant-like peptides and their applications. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci. 2009;14:340–8.
Chiu YC, Hwang HJ. Rapid dissolution of vitamin E by using sodium N-lauroylsarcosinate ionic surfactant. Colloids Surf, A Physicochem Eng Asp. 1994;90:155–65.
Wen Y, Xu J, He H, Lu B, Li Y, Dong B. Electrochemical polymerization of 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene in aqueous micellar solution containing biocompatible amino acid-based surfactant. J Electroanal Chem. 2009;634:49–58.
Sahu A, Bora U, Kasoju N, Goswami P. Synthesis of novel biodegradable and self-assembling methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-palmitate nanocarrier for curcumin delivery to cancer cells. Acta Biomaterialia. 2008;4:1752–61.
Lavasanifar A, Samuel J, Kwon GS. The effect of fatty acid substitution on the in vitro release of amphotericin B from micelles composed of poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(N-hexyl stearate–aspartamide). J Controlled Release. 2002;79:165–72.
Zhou YY, Du YZ, Wang L, Yuan H, Zhou JP, Hu FQ. Preparation and pharmacodynamics of stearic acid and poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) grafted chitosan oligosaccharide micelles for 10-hydroxycamptothecin. Int J Pharm. 2010;393:144–52.
Lukyanov AN, Torchilin VP. Micelles from lipid derivatives of water-soluble polymers as delivery systems for poorly soluble drugs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004;56:1273–89.
Moroi Y, Okabe M. Micelle formation of sodium ursodeoxycholate and solubilization into the micelle. Colloids Surf, A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2000;169:75–84.
Matsuoka K, Maeda M, Moroi Y. Micelle formation of sodium glyco- and taurocholates and sodium glyco- and taurodeoxycholates and solubilization of cholesterol into their micelles. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2003;32:87–95.
Israelachvili JN, Mitchell DJ. A model for the packing of lipids in bilayer membranes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1975;389:13–9.
Inacio AS, Mesquita KA, Baptista M, Ramalho-Santos J, Vaz WLC, Vieira OV. In vitro surfactant structure-toxicity relationships: implications for surfactant use in sexually transmitted infection prophylaxis and contraception. PLoS One. 2011;6:1–15.
Maupas C, Moulari B, Béduneau A, Lamprecht A, Pellequer Y. Surfactant dependent toxicity of lipid nanocapsules in HaCaT cells. Int J Pharm. 2011;411:136–41.
Fotakis G, Timbrell JA. In vitro cytotoxicity assays: Comparison of LDH, neutral red, MTT and protein assay in hepatoma cell lines following exposure to cadmium chloride. Toxicol Lett. 2006;160:171–7.
Severino P, Pinho SC, Souto EB, Santana MHA. Polymorphism, crystallinity and hydrophilic-lipophilic balance of stearic acid and stearic acid-capric/caprylic triglyceride matrices for production of stable nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2011;86:125–30.
Folmer BM, Nydén M, Holmberg K. Micellization and Adsorption of a Series of Fatty Amide Ethoxylates. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2001;242:404–10.
Brito RO, Silva SG, Fernandes RMF, Marques EF, Enrique-Borges J, do Vale ML. Enhanced interfacial properties of novel amino acid-derived surfactants: Effects of headgroup chemistry and of alkyl chain length and unsaturation. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2011;86:65–70.
Vives MA, Macián M, Seguer J, Infante MR, Vinardell MP. Hemolytic action of anionic surfactants of the Diacyl lysine type, comparative biochemistry and physiology part C: pharmacology. Toxicol Endocrinol. 1997;118:71–4.
Atanackovic M, Posa M, Heinle H, Gojkovic-Bukarica L, Cvejic J. Solubilization of resveratrol in micellar solutions of different bile acids. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2009;72:148–54.
Garidel P, Hildebrand A, Knauf K, Blume A. Membranolytic activity of bile salts: influence of biological membrane properties and composition. Molecules. 2007;12:2292–326.
Söderlind E, Wollbratt M, von Corswant C. The usefulness of sugar surfactants as solubilizing agents in parenteral formulations. Int J Pharm. 2003;252:61–71.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS & DISCLOSUREs
The authors would like to thank X. Quénault for lithocholanoyl-DG synthesis. We would like to thank A. Petit, F. Munari and N. Bongibault-Besnard for 1H RMN experiments for structural determination, P. Vayer for molecular modelling, H. Bertheux and N. Bécourt-Lhote for in vivo toxicity studies from Biologie SERVIER. We also acknowledge M. Lynch for DSC and XRD discussions from Technologie SERVIER. We would like to thank J-P. Lechaire and G. Frébourg (Service de microscopie électronique, IFR de Biologie intégrative-CNRS-Paris VI) and the Région Ile de France for cryo-TEM observations. This work was financially supported by ANRT from the Ministère de l’enseignement supérieur et de la recherche and by Technologie SERVIER. Our laboratory is a member of the Laboratory of Excellence LERMIT supported by a grant from ANR (ANR-10-LABX-33).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 234 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ménard, N., Tsapis, N., Poirier, C. et al. Novel Surfactants with Diglutamic Acid Polar Head Group: Drug Solubilization and Toxicity Studies. Pharm Res 29, 1882–1896 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0714-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0714-8